Primary Antibody Conjugates
Conjugated primary antibodies are an excellent alternative to using a secondary antibody for detection of your target protein. A conjugated primary antibody is created by pre-attaching (conjugating) a tag of your choice (fluorophore, enzyme, or protein), to a primary antibody, allowing for visualization of your target protein without the need to purchase a costly secondary antibody.
Conjugated primary antibodies can easily replace your previous primary/secondary antibody pairs in the following applications*:
Western blot (WB), Immunohistochemistry (IHC), Immunofluorescence (IF), Immunocytochemistry (ICC), Flow Cytometry (FCM), Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS), Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)
Most of StressMarq’s primary antibodies are available conjugated.
To order a conjugated antibody online, simply find your desired primary antibody, then choose the conjugate from the “Conjugate” drop-down list in the ordering section on the product’s page and select “Add to Cart”.
Protein and Enzymes:
Fluorophores:
| Label | Excitation Max. | Emission Max. | Extinction Coefficient | Substitute for: | Emission |
| ATTO 390 |
390
|
479
|
2.4×104
|
–
|
|
|
494
|
520
|
7.3×104
|
Alexa Fluor® 488
|
||
|
501
|
523
|
9.0×104 |
Alexa Fluor® 488
FITC |
||
|
565
|
575
|
2.0×106
|
TRITC | ||
|
601
|
627
|
1.2×105 |
Alexa Fluor® 594
Texas Red® |
||
|
650
|
660
|
7.0×105 | Cy®5 Alexa Fluor® 647 Alexa Fluor® 660 |
||
|
482
|
677
|
1.96 x 106 |
–
|
Protein and Enzymes
HRP (Horseradish peroxidase)
Properties:
- Enzymatic activity is used to amplify weak signals and increase visibility of a target
- Readily combines with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to form HRP-H2O2 complex which can oxidize various hydrogen donors
- Catalyzes the conversion of:
- Chromogenic substrates (e.g. TMB, DAB, ABTS) into coloured products
- Chemiluminescent substrates (e.g. luminol and isoluminol) into light emitting products via enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL)
- Fluorogenic substrates (e.g. tyramine, homovanillic acid, and 4-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid) into fluorescent products
- High turnover rate enables rapid generation of a strong signal
- 44 kDa glycoprotein
- Extinction coefficient: 100 (403 nm)
- Applications: Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA
Biotin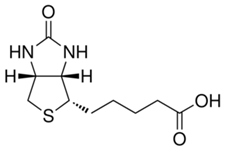
Properties:
Fluorophores
Fluorophores, also known as fluorochromes or fluorescent dyes, are chemicals that are excited by light at a specific wavelength and then emit light (fluoresce) at another wavelength.
Key features of fluorophores:
Maximum Excitation Wavelength (λex): The peak in the excitation spectra measured in nanometers (nm).
Maximum emission Wavelength (λem): The peak in the emission spectra measured in nanometers (nm).
Stokes Shift: The difference in the maximum wavelength peaks between the emission and excitation spectra, measured in nanometers.
Extinction Coefficient (εmax): The capacity for the fluorophore to absorb light at a specific wavelength. Usually measured at the maximum excitation wavelength with the units M−1cm−1.
Fluorescence Quantum yield (Φf): The number of photons emitted per absorbed photon. This number will range between 0 and 1. A high quantum yield is important.
Fluorescence Decay Time (τfl): The time interval after which the number of excited fluorophore molecules decreases to 1/e (approx. 37%), usually measured in nanoseconds.
Brightness: The fluorescence output per fluorophore measured in with the units M−1cm−1. Calculated as the product of the extinction coefficient (at the relevant excitation wavelength) and the fluorescence quantum yield divided by 1000.
All ATTO fluorescent dyes are characterized by:
- Strong absorption (high extinction coefficient)
- High fluorescence quantum yield
- High photostability
| ATTO 390 | ||
| Overview: | 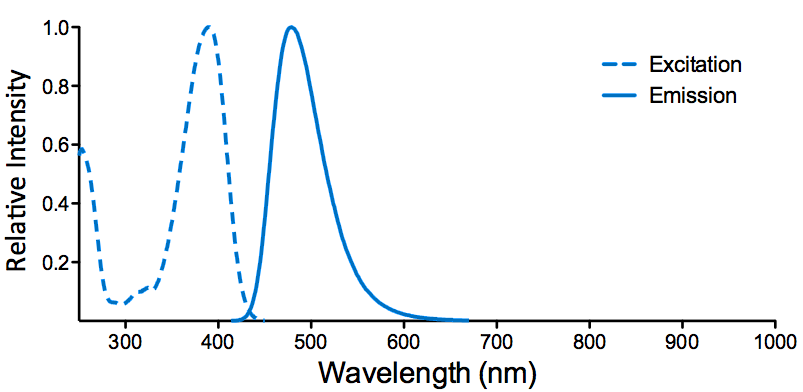 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 390 nm |
| FITC (Fluorescein) | ||
| Overview: | 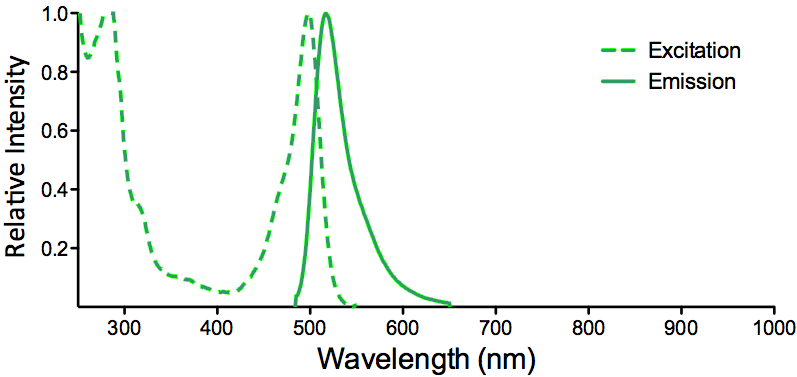 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 494 nm |
| ATTO 488 | ||
| Overview:
|
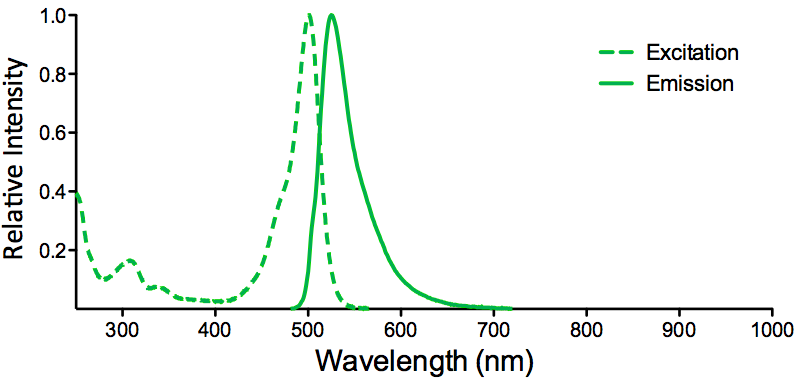 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 501 nm |
| R-PE (R-Phycoerythrin) | ||
| Overview: | 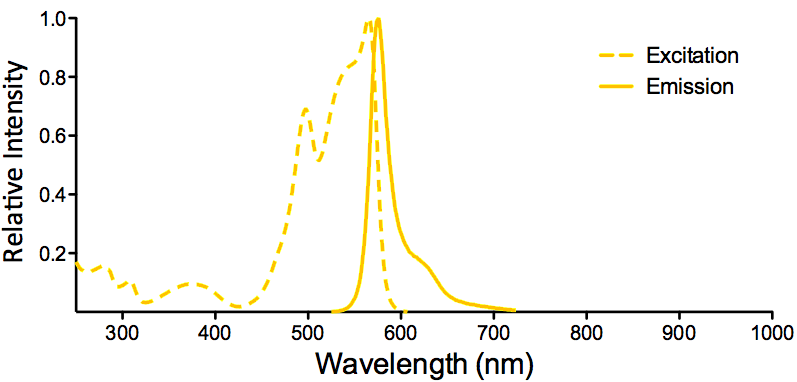 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 565 nm |
| ATTO 594 | ||
| Overview: | 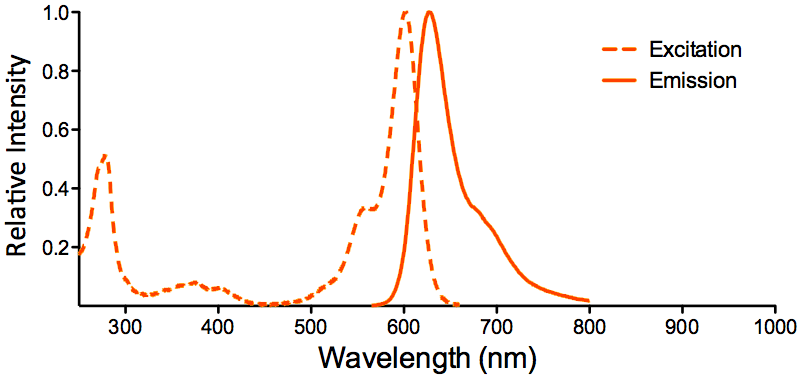 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 601 nm |
| APC (Allophycocyanin) | ||
| Overview: | 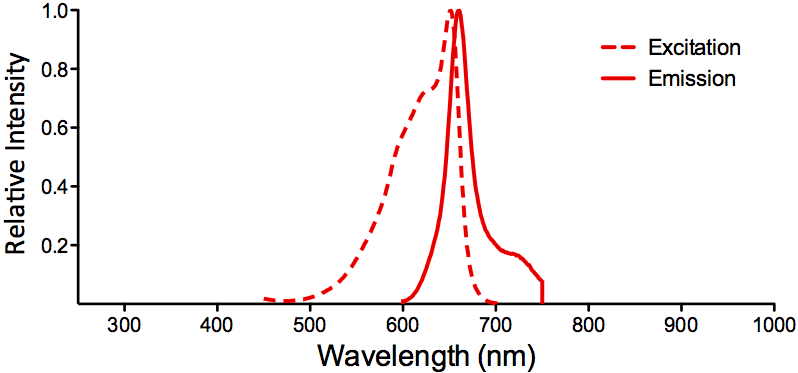 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 650 nm |
| PerCP | ||
| Overview: | 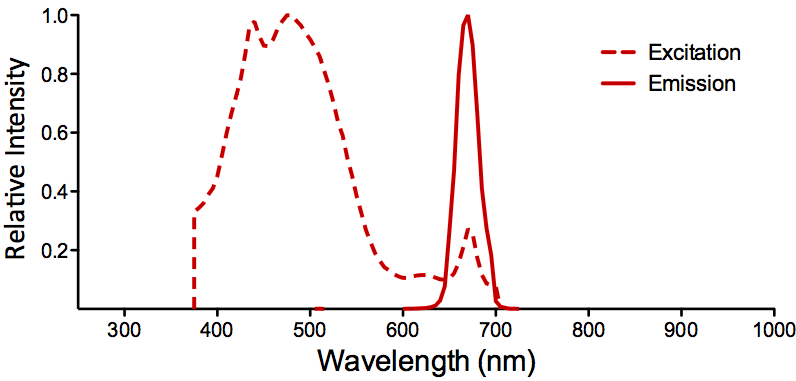 |
Optical Properties:
λex = 482 nm |
*The applications listed above are a general list indicating which applications conjugated antibodies can be used in. It does not guarantee that any antibody-conjugate combination has been tested for use in the application.
**Excludes lyophilized antibodies. Please see product detail pages for conjugate availability.
Please note: It is possible that the conjugate tag may bind in the paratope of the antibody, thereby limiting binding of the antibody to the antigen. Although this is unlikely, it could affect the ability of the antibody to bind to the antigen in various species and applications. As we cannot control the binding of the conjugate to the antibody, there is no way to confirm or guarantee the location of the antibody tag.
