A Unique RNA-Binding Protein to Combat Tau Aggregation
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease that is most commonly characterized by the progressive impairment of cognitive and behavioural functions. A key molecular feature of the disease is the buildup of insoluble filamentous aggregates referred to as neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). These tangles are composed of hyperphosphorylated forms of the microtubule-associated protein tau. In healthy brains, tau is highly soluble and promotes the assembly of tubulin into stable microtubules (MTs). In diseased conditions, tau detaches from MTs, allowing them to become unstable and disintegrate. The dysregulation of these crucial microtubule dynamics consequently results in neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration. A growing body of evidence, supported by recent findings, suggests that RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) further augment neurodegeneration by promoting pathological protein aggregation.
A recent study published in Neuron by Wang et al., describes an RBP — Ras GTPase-activating protein-binding protein 2 (G3BP2) — that defies this pattern and, instead, exerts a neuroprotective effect by binding directly to tau via the microtubule-binding region, and inhibiting tau aggregation. The beneficial effects of G3BP2 in tau aggregation identified in this study could offer a new perspective in the development of novel anti-tau therapeutics to promote tau clearance in Alzheimer’s disease.
Increased prevalence of G3BP2-tau complexes in Alzheimer’s disease
The study began by investigating endogenous tau protein-interacting partners. G3BP2 and five other RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) were identified using immunoprecipitation combined with mass spectrometry in human-induced pluripotent stem cel (hiPSC)-derived neurons. Proximity ligation assays (PLA) — used to monitor expression levels and subcellular locations of tau and the six candidates — revealed basal level interactions with all protein candidates in healthy patients. G3BP2 was selected for further study as, unlike the other protein complexes, G3BP2-tau complexes increased in postmortem temporal cortical tissues harvested from patients with Alzheimer’s disease compared to control and basal level samples.
Loss of G3BP2 leads to tau aggregation
A key factor underlying the progression of Alzheimer’s disease is the spread of tau aggregates between neurons, which induce misfolding and aggregation of physiological tau. To assess tau aggregation and spread, researchers from Roche, in collaboration with academic researchers, employed StressMarq’s Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils (Baculovirus/Sf9) (catalog# SPR-471) as a seeding agent for tau seeding assays. Upon depletion of G3BP2 using small interfering RNA (siRNA) in human neurons, an 87% increase in aggregated tau was measured using a homogenous time-resolved fluorescence energy transfer (HTRF) immunoassay. Interestingly, the loss of G3BP2 did not impact the number of intracellular seeds, as confirmed using StressMarq’s fluorescent Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils: ATTO 488 (catalog# SPR-329-A488). The ability of G3BP2 to inhibit tau fibril formation was further confirmed with tau fibrillization assays.
G3BP2 interacts directly with tau
To determine whether G3BP2 binds directly to tau to modulate tau aggregation, an optical technique that measures molecular interactions in real-time — surface plasmon resonance (SPR) — was used. For this, StressMarq’s Tau-441 (2N4R) Wild-Type Monomers (catalogue # SPR-479) were immobilized on the surface, and different concentrations of G3BP2 were injected as the analyte. Direct protein interactions were then measured using SPR measurements, which represented changes in the refractive index near the sensor surface. Tau and G3BP2 exhibited clear dose-dependent association and dissociation, indicating a direct interaction between the proteins. Furthermore, structural characterization using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy determined that the microtubule-binding region in tau — a region prone to aggregation — was responsible for the interaction with G3BP2.
Utilizing StressMarq products to investigate tau protein interaction
Recently, RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) have emerged as tau interactors that are important in driving tau pathology. Unlike other RNA-binding proteins that induce tau pathology, G3BP2 was identified in the study to induce a protective effect against tau aggregation in the context of Alzheimer’s disease. StressMarq’s Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils (Baculovirus/Sf9) (catalog# SPR-471) and fluorescent Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils: ATTO 488 (catalog# SPR-329-A488) were crucial as the seeding competent tau species to assess the effect of G3BP2 in decelerating tau fibrillization and aggregation.
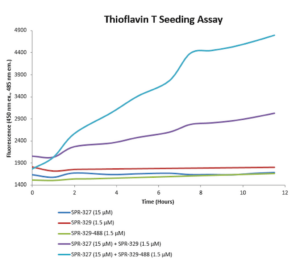
Figure 1. StressMarq’s ATTO 488-conjugated Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-329-A488) combined with tau monomers demonstrate increased seeding compared to unconjugated tau pre-formed fibrils. Binding to tau fibrils is monitored using Thioflavin T fluorescent dye, which bind to beta-sheet rich structures
Summary
Hyperphosphorylation of tau leads to detachment of tau from MTs with subsequent incorporation into insoluble filamentous aggregates in NFTs — the defining feature of Alzheimer’s disease. This study by Wang et al., identifies how G3BP2, unlike other RNA-binding proteins, protects against tau fibrillization and aggregation. The direct binding of G3BP2 to tau implicates the microtubule-binding region of tau, which is also targeted by anti-tau antibodies currently undergoing clinical trials. The results of the study have highlighted the potential benefit of utilizing compounds or peptides mimicking G3BP2 to prevent pathological tau aggregation.
Related StressMarq products
Our recently launched Tau-441 (2N4R) Wild-Type Monomers (catalog# SPR-496) and Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-498) are expressed using Baculovirus/Sf9, fibrilize without the use of heparin, and are readily hyperphosphorylated. Visit our website for more details on our tau, alpha synuclein, and amyloid beta proteins, along with the latest scientific publications using our specialized product portfolio.
References
- Increased G3BP2-Tau interaction in tauopathies is a natural defense against tau aggregation. Wang, C., et al. Neuron 2023.


Leave a Reply