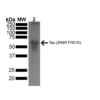
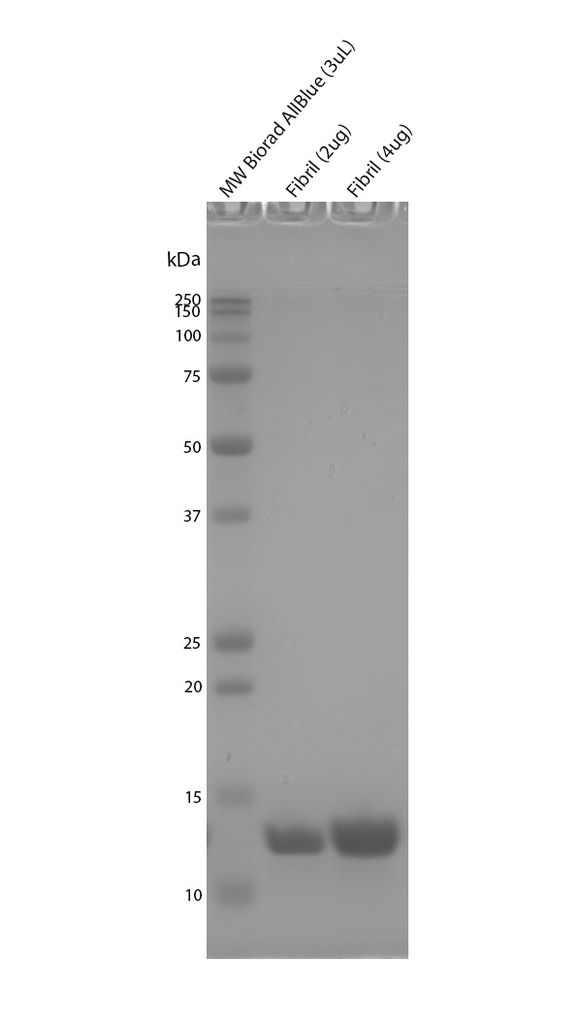
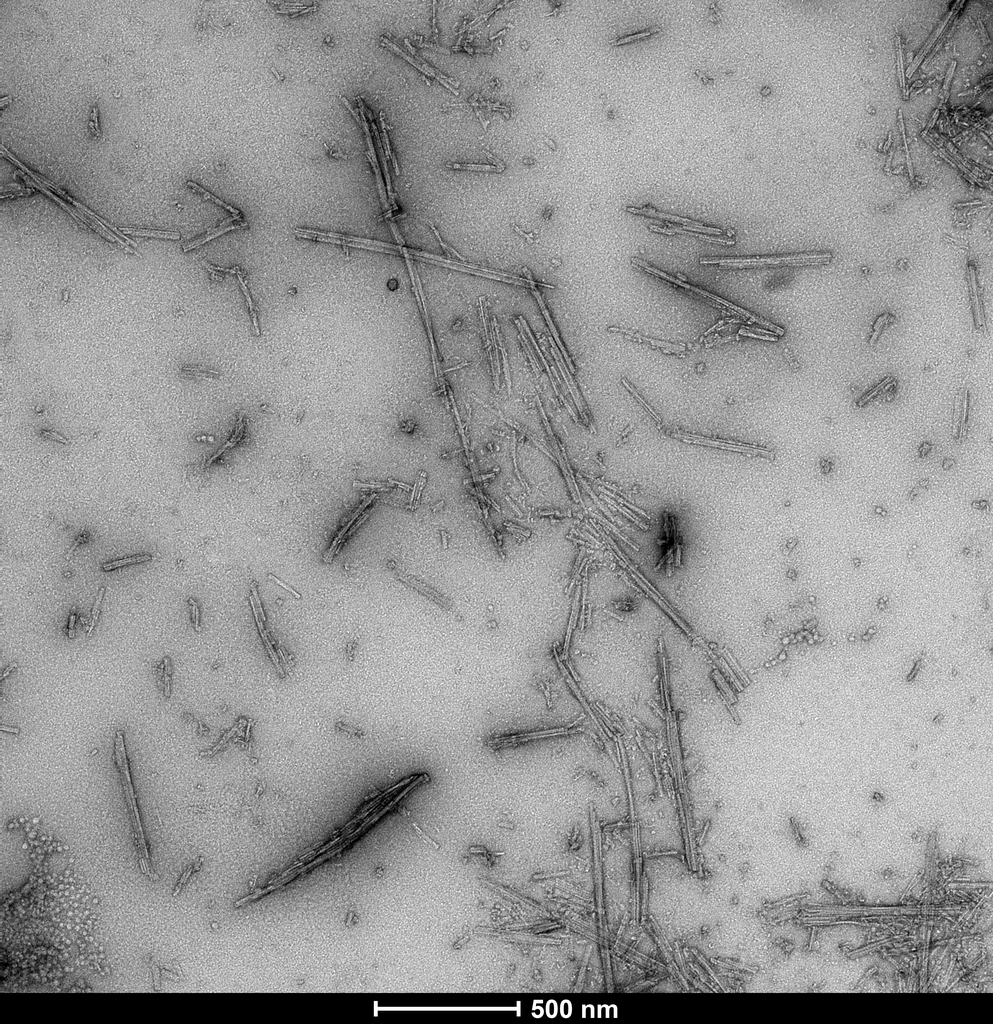
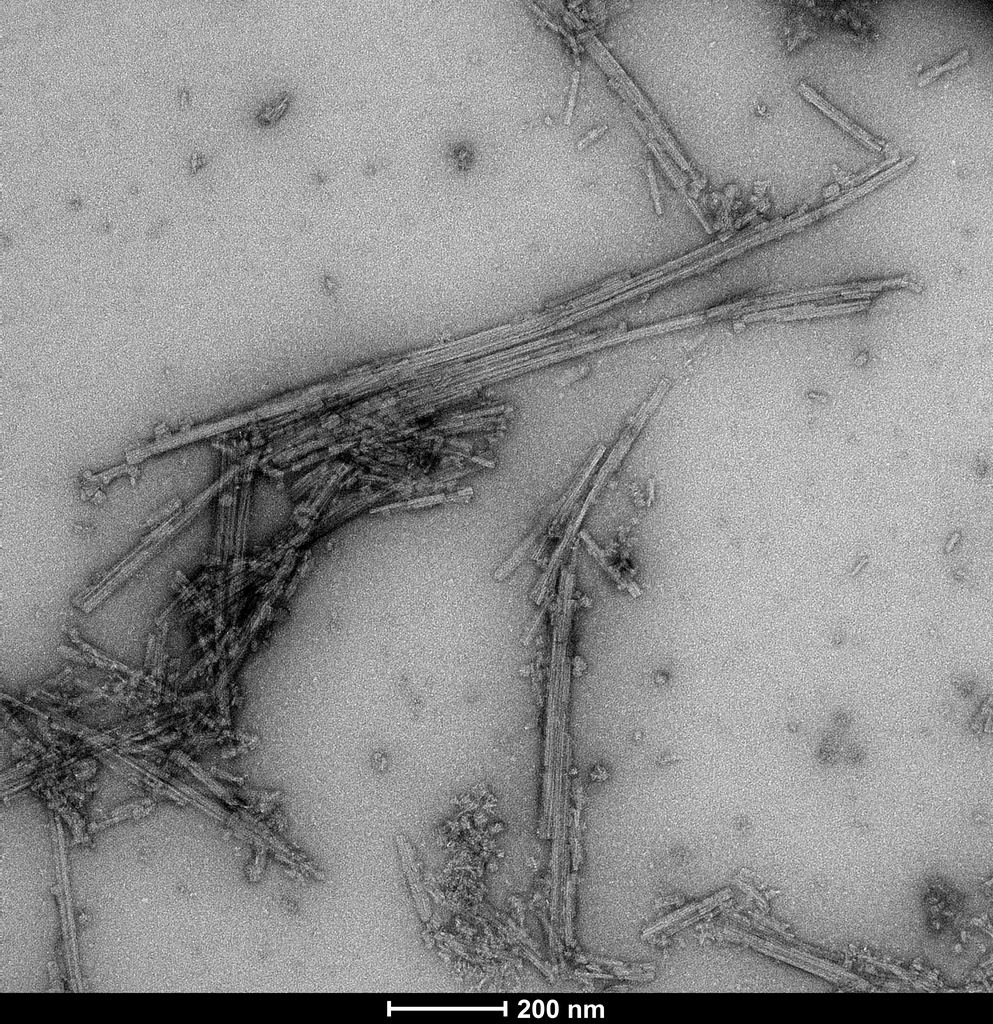
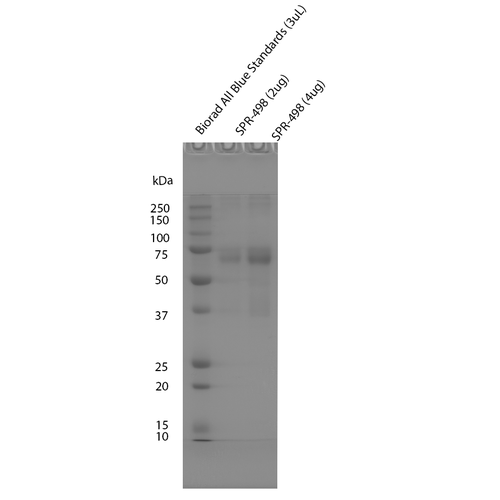
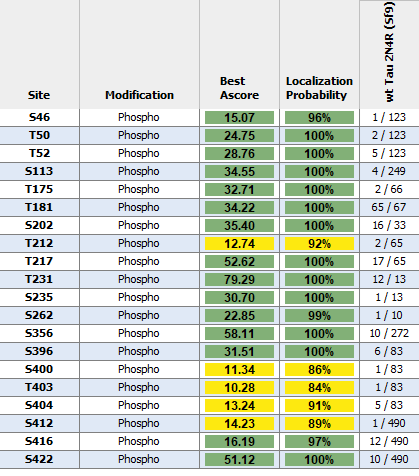
Tau
StressMarq Biosciences is a leading provider of high-quality fibrillar, oligomeric, and monomeric protein preparations—including alpha synuclein, tau, amyloid beta, TDP-43, SOD1, TTR and more—designed to support cutting-edge neurodegenerative disease research. With a focus on pathology-inducing protein aggregates, our products support the development of robust disease models and accelerate drug discovery for conditions such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and ALS. StressMarq is committed to scientific excellence— empowering researchers worldwide with tools that accelerate discovery and translational research.
Tau Pre-formed Fibrils (PFFs), Oligomers, Filaments & Monomers
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein that stabilizes neuronal cytoskeletal structure and regulates axonal transport. In neurodegenerative diseases, tau undergoes abnormal phosphorylation and misfolding, leading to the formation of toxic oligomers and neurofibrillary tangles. These aggregates disrupt cellular function and propagate pathology, contributing to a class of disorders known as tauopathies, which include Alzheimer’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), corticobasal degeneration (CBD), and frontotemporal dementia (FTD).
StressMarq Biosciences offers a wide range of monomeric, oligomeric, and fibrillar tau constructs, including full-length, truncated, and mutant variants. These reagents are validated for activity, purity, and disease relevance, enabling researchers to model tau pathology in vitro and in vivo. Our tau aggregates support studies on phosphorylation, aggregation kinetics, neurotoxicity, and drug discovery—empowering scientists to advance translational research in neurodegeneration. Explore our catalog to find the right tools for your research, and watch our video to see how StressMarq’s tau reagents can accelerate disease modeling and drug discovery.
Tau Pre-formed Fibrils (PFFs)
StressMarq manufactures active tau protein constructs to help researchers study tau aggregation, a hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s. StressMarq is the leading commercial source of tau pre-formed fibrils (PFFs) for neuroscience research, and offers the broadest range of tau constructs to researchers worldwide.
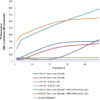
The process of tau aggregation can be seeded by active tau PFFs, which recruit monomers to form larger tau fibrils. This is demonstrated in thioflavin T assays, where an increase in fluorescence – indicative of tau fibrillization – is seen when active tau PFFs are combined with active tau monomers.
StressMarq offers a wide selection of tau monomers, pre-formed fibrils (PFFs) and oligomers with various isoforms, lengths, and mutations.
Product List | PFFs
Tau & Alpha Synuclein Co-Polymer Fibrils (Mixed Fibrils/PFFs)
StressMarq’s co-polymer fibrils are developed by co-incubating monomers together to form fibrils that contain both tau and alpha synuclein proteins within a single fibril. These co-polymer fibrils have been demonstrated to seed fibril formation of both tau monomers and of a mixture of alpha synuclein and tau monomers.
Product List | Co-Polymer Fibrils
| Human Tau-352 (fetal 0N3R) & Human Alpha Synuclein Co-Polymer Fibrils, catalog# SPR-494 |
| Human Tau-441 (2N4R) & Human Alpha Synuclein Co-Polymer Fibrils, catalog# SPR-495 |
Tau Oligomers
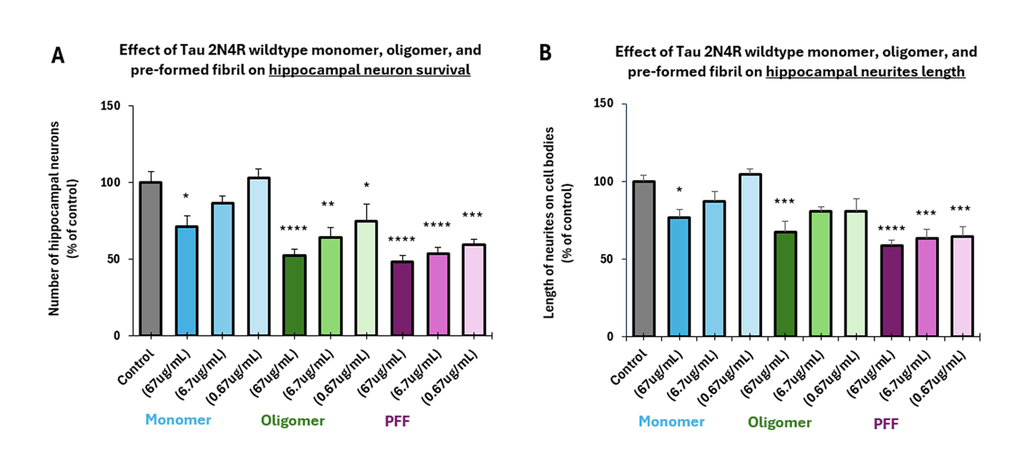
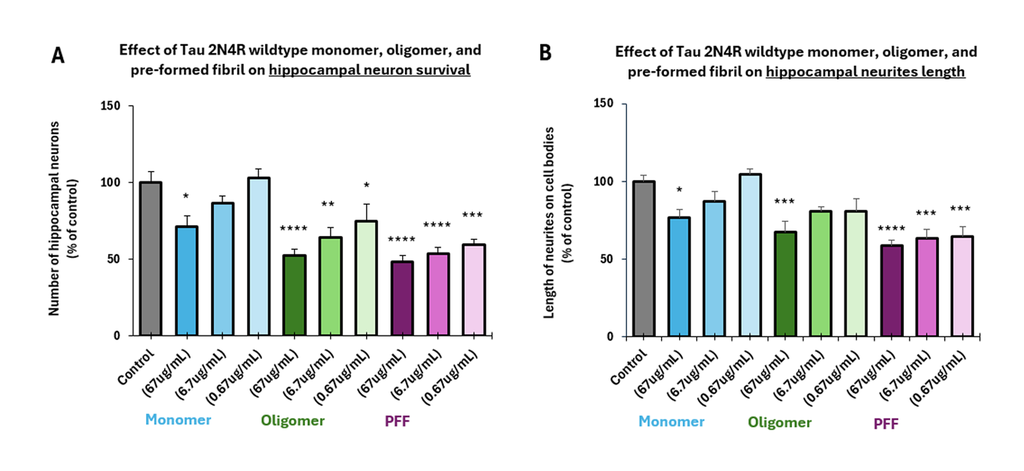
Tauopathies such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are characterized by neurofibrillary tangles containing hyper-phosphorylated tau fibrils, with consensus that tau oligomers are the most toxic species initiating neurodegeneration. StressMarq’s tau oligomers exert a dose-dependent toxicity to hippocampal neurons.
Product List | Oligomers
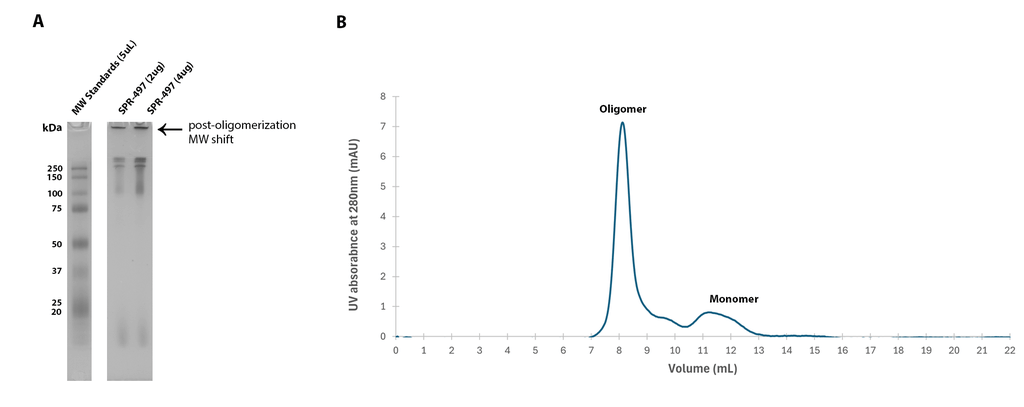
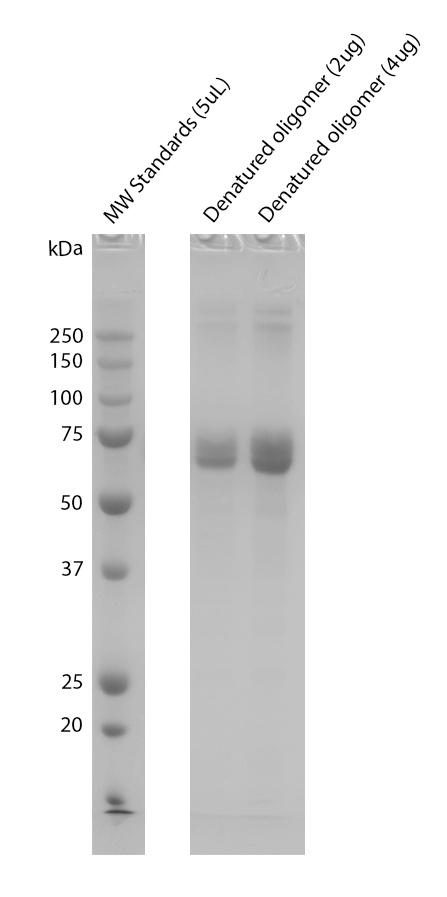
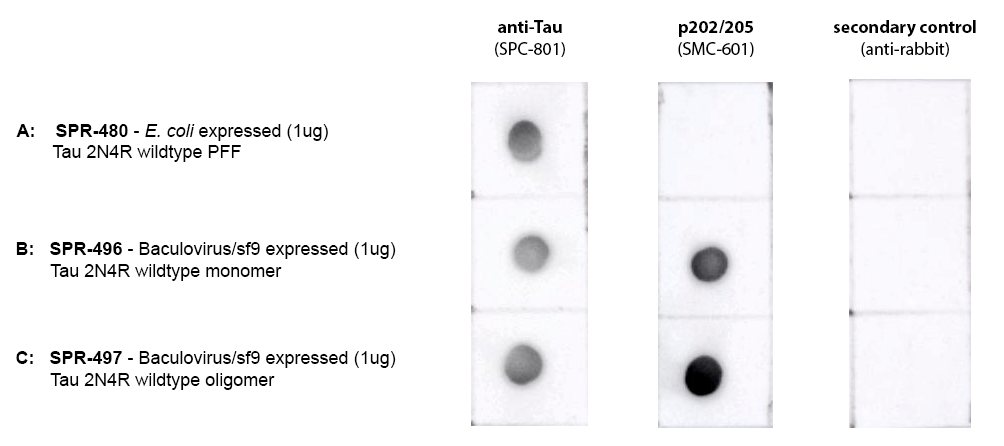
| Human Tau-441 (2N4R) Wild-Type Oligomers (Baculovirus/Sf9), catalog# SPR-497 |
Tau Monomers
StressMarq’s tau monomers are capable of aggregation. They do not show neurodegenerative activity.
Product List | Monomers
Selected Scientific & Product Information
Tau Isoforms
Tau-441 (2N4R) is the longest isoform found in the adult human brain, with a molecular weight of approximately 46 kDa. Additional tau isoforms present in the adult human brain include Tau-381 (1N3R), Tau-383 (0N4R) and Tau-412 (1N4R). Tau-352 is expressed in the fetal brain.1 NMR data indicates that both 3R and 4R tau are incorporated into AD-tau seeded fibrils.2 All tau isoforms play a crucial role in microtubule stabilization and dynamics in neurons, however, their dysregulation has been associated with neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia.
Tau Fragments
Tau fragments, including K18 and dGAE, also have significance in Alzheimer’s disease research.
K18 tau is a truncated form of human tau containing only the 4 microtubule binding repeats (4R), with a molecular weight of approximately 15 kDa. StressMarq’s Tau (K18) P301L Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-330) have been shown to induce aggregation and pathology in transgenic mice.
The dGAE fragment (amino acids 297-391), with a molecular weight of approximately 10 kDa, has been found in the core of Paired Helical Filaments (PHFs) from AD brains and assembles into PHF-like fibrils in vitro without additives or templates.3 Recent studies have led to the development of optimized dGAE fibrils, purified and fibrilized under specific conditions, which closely mimic PHFs isolated from Alzheimer’s disease brains.4
Tau Mutations
Tau proteins are available in both wild-type and mutated forms. P301S and P301L mutations occur in exon 10 and are associated with frontotemporal dementia. The P301S mutation reduces tau’s ability to assemble microtubules, while the P301L mutation promotes beta-sheet formation and the formation of PHFs. Transgenic mouse models carrying both P301S and P301L mutations are used extensively in tau research. The K280 deletion mutation is also associated with frontotemporal dementia and promotes fibrillization into PHFs in the absence of heparin and other inducers.5 Additionally, the C322A mutation also increases tau’s ability to form PHFs.3
While the majority of StressMarq tau proteins are expressed in E. coli, preparations expressed in Baculovirus/Sf9 and Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells are also available. Using these expression systems results in recombinant proteins with post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation or glycosylation and may better mimic tau that is found in human AD brains.
Unlike most amyloidogenic proteins such as alpha synuclein, tau monomers exhibit a low propensity to spontaneously aggregate into fibrils. However, various scaffolds including heparin, RNA and fatty acids (i.e. arachidonic acid) can stimulate tau aggregation by providing surfaces or templates for the nucleation and fibril growth. Most tau preparations require heparin for fibrillization, however, excess heparin is removed post-fibrillization. Studies have shown that certain types of RNA molecules, including tRNA, rRNA, and mRNA can interact with tau and promote its aggregation into fibrils.6 StressMarq’s soluble tau filaments are fibrillized using t-RNA as a scaffold. According to literature, certain mutations and post-translational modifications have been shown to enhance tau’s aggregation propensity, leading to fibrillization without the need for scaffolds.7 StressMarq offers a range of tau preparations including dGAE tau, K18 K280 deletion mutant tau, and post-translationally modified tau expressed in baculovirus/Sf9 and mammalian cells, which are generated without any induction scaffolds.
References
-
- Goedert, et al. (1989) Neuron 3(4):519-26.
- Dregni, A.J. et al. (2022) Nat Commun 13, 2967.
- Al-Hilaly, Y.K. et al. (2017) J. Mol. Biol. 429(23):3650-3665.
- Lovestam, S. et al. (2022) eLife. 11: e76494.
- Von Bergen, M. et al. (2001) J Biol Chem. 276(51):48165-48174.
- Zwierzchowski-Zarate A.N. (2022) J. Biol. Chem. 298(8):102132.
- Oakley, S. et al. (2020) Front. Neurol. 11.
Selected Tau Product Images
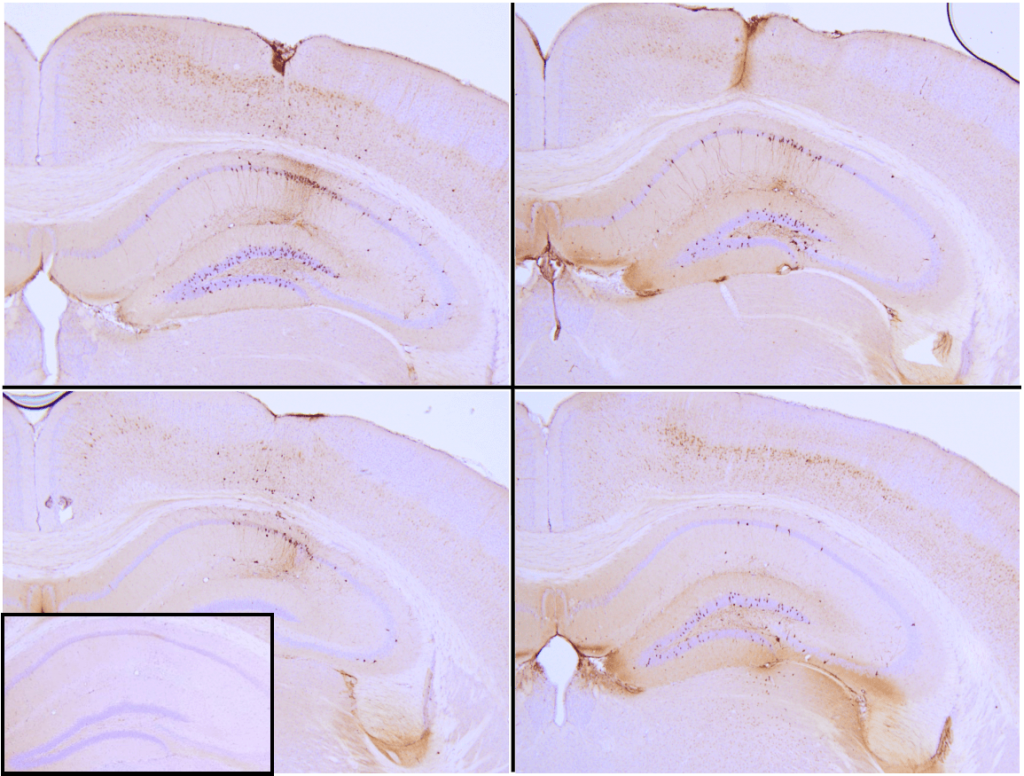
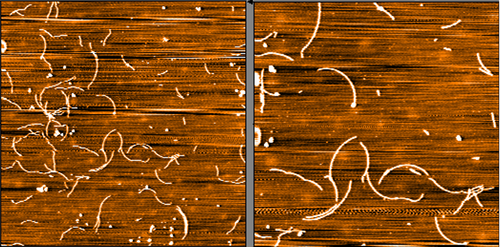
Immunohistochemistry analysis of P301L mouse hippocampus injected with Recombinant Tau (K18) P301L Mutant Protein Pre-formed Fibrils, catalog# SPR-330 shows seeding of tau pathology at injection site nine weeks post-injection. AT8 (pSer202/pThr205) tau antibody shows tangle-like inclusions. Inset: negative control. Experiments performed at reMYND.
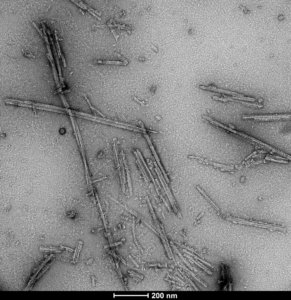
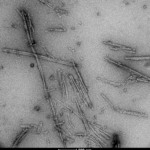
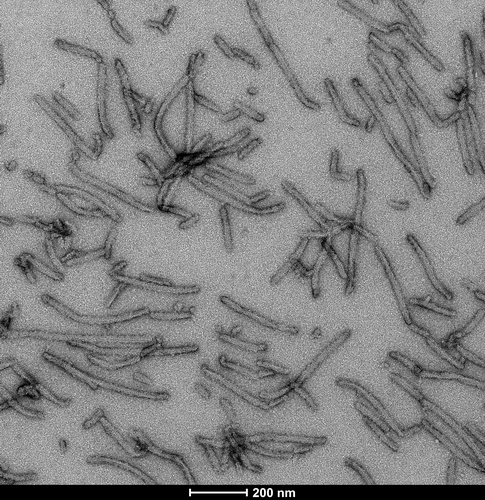
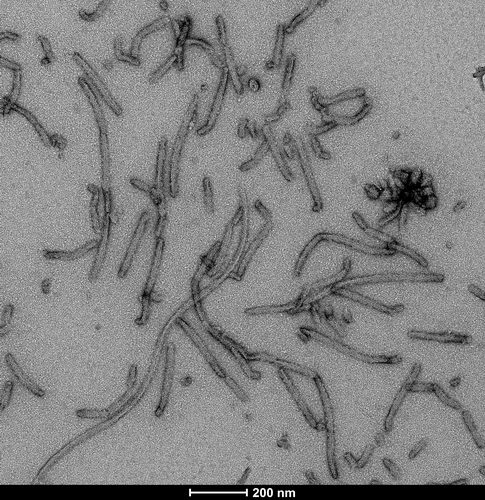
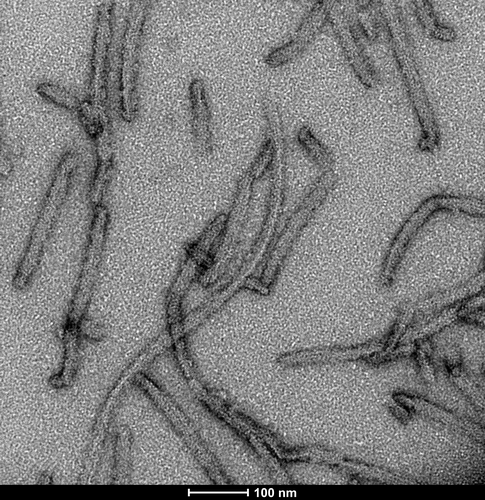
TEM of Recombinant Tau dGAE (297-391) AD-mimic Pre-formed Fibrils, catalog# SPR-502.
Product Citations
StressMarq’s proteins for neurodegenerative disease research have been cited in many peer-reviewed scientific journals. Below is a list of the most recent product citations for our tau proteins. A complete list of citations for tau proteins can be seen here.
Most Recent Tau Citations
- Highly sensitive chemiluminescence imaging of misfolded proteins in neurodegenerative nodels. Zhu, B. et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. Jan 2026.
- Catalog# SPR-330: Human Recombinant Tau (K18) P301L Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils
- Integrative genomic and functional analyses reveal NINL as a modulator of tau aggregation. Swift, S. K. et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. Dec 2025.
- Tau-targeting active immunotherapy slows progression and reduces pathology in mouse models of tauopathy. Brown, C. M. et al. Brain Pathol. Dec 2025.
- Catalog# SPR-463: Human Recombinant Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant Filaments
- Catalog# SPR-479: Human Recombinant Tau-441 (2N4R) Wild-Type Monomers
- Catalog# SPR-480: Human Recombinant Tau-441 (2N4R) Wild-Type Pre-formed Fibrils
Supplemental Learning Materials
Technical Support Resources
- Handling Instructions | Tau
- Protocols | Tau
- Sonication Protocol | PFFs
- Frequently Asked Questions | Neuro Proteins
Selected Media from the StressMarq YouTube Channel
- Video | Tau Pre-formed Fibrils for Neurodegenerative Disease Modelling
- Webinar | Tools for Alzheimer’s & Parkinson’s Research | Presented by Dr. Jacob McPhail, R&D Scientist, StressMarq
- Open Theatre | Fibrillar & Oligomeric Constructs of Neurodegenerative Disease Asssociated Peptides | Presented by Dr. Ariel Louwrier, President & CEO, StressMarq
Selected Articles from the StressMarq Blog
- Tau Fibrillar Constructs | Learn about tau fibrils, filaments, isoforms, and mutations of interest.
- Exploring Tau Oligomers in Neurodegenerative Diseases | Oligomeric tau is considered the most toxic species in neurodegenerative disease pathology.
- Microglial Receptors Mediate Tau Clearance | Complement receptor 4 (CR4) enhances microglia-mediated tau clearance.
- A Novel Long Non-Coding RNA Regulates Tau Degradation | Long non-coding RNA FAM151B-DT links tau and α-synuclein degradation.
Have a question about Tau?