Akt Signaling, Cell Growth and Survival
Akt is a serine/threonine kinase that is activated downstream of phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K). It functions as a critical regulator of cell survival and proliferation, exerting its effects by phosphorylating a broad range of substrates. Dysregulation of PI3K/Akt signaling has been implicated in conditions including cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and various neurological disorders. As such, Akt and other members of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway represent important targets for drug discovery.
Discovery and significance of Akt
Akt was first discovered in 1987 as an oncogene transduced by the acute transforming retrovirus Akt-81. Just four years later, three independent groups cloned and characterized the cellular homolog of v-Akt, naming it c-Akt, Related to A- and C-kinase (RAC), and protein kinase B (PKB), respectively2. Akt is now known to exist as three isoforms – Akt1, Akt2, and Akt3 – each of which comprises an N-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, a central kinase domain containing a conserved threonine residue (Thr308/Thr309/Thr305 in human Akt1/Akt2/Akt3), and a hydrophobic C-terminal regulatory domain featuring a conserved serine (Ser473/Ser474/Ser472 in human Akt1/Akt2/Akt3). Importantly, both the threonine residue and the serine residue must be phosphorylated for Akt to become fully activated3. Akt has a central role in regulating cellular metabolism, growth, apoptosis, and survival, making it a valuable therapeutic target.
Akt activation and function
The PI3K/Akt signaling cascade is activated in response to nutrients, growth factors, and other extracellular stimuli. These bind to transmembrane proteins such as cytokine receptors, G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), integrins, B and T cell receptors, and receptor tyrosine kinases, inducing PI3K to produce a lipid known as phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5) trisphosphate (PIP3)4. PIP3 acts as a plasma membrane docking site for Akt, which binds via the PH domain and is subsequently phosphorylated by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1) at Thr308. Following this, phosphorylation at Ser473 by proteins such as integrin-linked kinase (ILK), mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2), and members of the PI3K-related kinase (PIKK) family, including DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK), fully activates Akt. Activation enables Akt to perform functions that include regulating cellular metabolism (e.g., by activating AS160), controlling cell growth (e.g., via TSC1/TSC2 and mTORC1 signaling), promoting cell survival (e.g., by inhibiting the pro-apoptotic protein Bad), and stimulating proliferation (e.g., by phosphorylating p21), among others4. Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is an important negative regulator of Akt, dephosphorylating PIP3 to exert a tumor suppressor function.
Akt dysregulation and disease
Dysregulated Akt signaling has been implicated in many different disease states. These include cancer, where abnormal over-expression or activation of Akt is frequently observed and PTEN is often disrupted, and cardiovascular disease, where different Akt isoforms have been shown to have distinct effects on atherosclerosis, vascular remodeling, and aneurysm formation5-7. Abnormal Akt signaling has also been linked to the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus, with insulin resistance exacerbating the PI3K/AKT pathway, and to neurological disorders including Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease8,9.
Supporting the study of Akt
StressMarq has developed an extensive range of products for studying Akt and the various signaling pathways in which it is involved. These include antibodies to Akt1 (SPC-1100) and its Tyr315 (SPC-911) and Thr308 (SPC-910) phosphorylated isoforms, all of which have been validated for Western blot and are available conjugated to various dyes. Additionally, we offer several antibodies to Akt1 that have been validated for use in IHC, including SPC-768, SPC-789, Akt1 Antibody (pThr308) (SPC-1341) and Akt1 Antibody (pSer473) (SPC-1340).
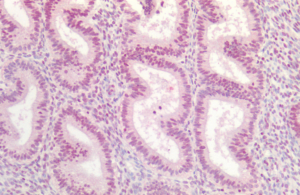
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Rabbit Anti-AKT1 Polyclonal Antibody (SPC-768). Tissue: Uterus. Species: Human. Fixation: Formalin fixed paraffin-embedded.
We also offer antibodies to Akt2 (SPC-1101 and SPC-148) and Akt3 ( SPC-769 and SPC-1102), in addition to several well-known Akt activators and inhibitors including Deguelin, GSK690693 Hydrochloride and SC 79.
References
- Molecular cloning of the akt oncogene and its human homologues AKT1 and AKT2: amplification of AKT1 in a primary human gastric adenocarcinoma, Staal SP, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987 Jul;84(14):5034-7
- AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating the Network, Manning BD and Toker A, Cell. 2017 Apr 20;169(3):381-405
- The activation of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival, Song G et al, J Cell Mol Med. Jan-Mar 2005;9(1):59-71
- The Akt pathway in oncology therapy and beyond (Review), Nitulescu GM et al, Int J Oncol. 2018 Dec;53(6):2319-2331
- AKT as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer, Song M et al, Cancer Res. 2019 Mar 15;79(6):1019-1031
- Therapeutic targeting of cancers with loss of PTEN function, Dillon LM and Miller TW, Curr Drug Targets. 2014 Jan;15(1):65-79
- Akt isoforms in vascular disease, Yu H et al, Vascul Pharmacol. 2015 Aug;71:57-64
- The PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes, Huang X et al, Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Aug 6;14(11):1483-1496
- PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway: A Target of Natural Products in the Prevention and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease, Long H-Z et al, Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 15;12:648636

Leave a Reply