Alpha Synuclein Phosphorylation at Serine 129
Alpha synuclein is the primary protein of interest in Parkinson’s disease, a condition characterized by involuntary shaking, slow movement, and muscular rigidity. These symptoms result from the progressive degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of the brain and are associated with the appearance of fibrillar aggregates of alpha-synuclein known as Lewy bodies. In a healthy brain, approximately 4% of the total alpha synuclein content is phosphorylated at Serine 129. However, within Lewy bodies, the level of Serine 129 phosphorylation is close to 90%, suggesting that this post-translational modification may play an important role in regulating alpha synuclein aggregation1. By understanding the mechanisms that underlie Serine 129 phosphorylation, researchers aim to identify approaches to tackle Parkinson’s disease and other alpha synucleinopathies.
What is the role of pSer129 alpha synuclein in synucleinopathies?
In recent years, numerous studies have reported that alpha synuclein within Lewy bodies undergoes a range of post-translational modifications. Yet while phosphorylation, ubiquitination, cross-linking, truncations and nitration have all been proposed to modulate the function of alpha synuclein, it is phosphorylation at Serine 129 that has received the most attention2. The main reason for this is the dramatic accumulation of pSer129 alpha synuclein in the brains of patients suffering from alpha synucleinopathies3, as well as in in vivo models of Parkinson’s disease4.
Although the role of pSer129 and its effects on the structure, function and aggregation of alpha synuclein are poorly understood, several hypotheses are under investigation. Studies focused on the interaction of alpha synuclein with vesicles of different lipid composition have addressed the possibility that pSer129 is required for membrane interaction5, while the influence of pSer129 on the binding of alpha synuclein to various metal ions that drive fibrillization is also being explored1. Further research efforts concern the relevance of pSer129 to alpha synuclein turnover and subcellular localization, and the interaction of alpha synuclein with other proteins.
How is pSer129 alpha synuclein linked to Lewy body pathology?
Alpha synuclein pre-formed fibrils have been widely used to study Parkinson’s disease and other alpha synucleinopathies. In the recombinant form, these structures lack pSer129, yet when they are used to treat primary neurons, they have been shown to promote the formation of Lewy bodies containing alpha synuclein that is hyperphosphorylated at Serine 1296. Accumulation of the hyperphosphorylated protein has been linked to decreased levels of synaptic proteins, progressive impairments in neuronal activity, and eventual neuron death. Other methods to study Lewy body pathology include cell graft models and the over-expression of alpha synuclein by viral vectors7.
Supporting the study of alpha synuclein pSer129 in Parkinson’s disease
We offer a broad selection of reagents to support research efforts aimed at uncovering the role of alpha synuclein pSer129 in Parkinson’s disease. These include our highly popular rabbit monoclonal anti-alpha synuclein (pSer129) antibody (catalog# SMC-600), which benefits from extremely low background; and our rabbit polyclonal anti-alpha synuclein (pSer129) antibody (catalog# SPC-742) which has been independently reviewed on pAbmAbs.
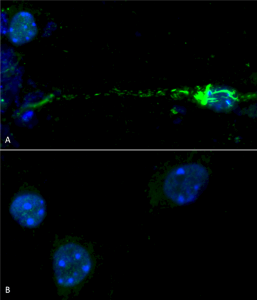
Phospho serine 129 antibody (catalog# SPC-742) was used to detect phosphorylated alpha synuclein in primary mouse hippocampal neurons treated with 100 nM sonicated mouse alpha synuclein PFFs (SPR-324) (A). Phosphorylated alpha synuclein was visible in perinucleus and neurites compared to untreated control (B). Read the protocol at pAbmAbs. Image courtesy of Trine Rasmussen, Simon Molgaard Jensen at Aarhus University.
REFERENCES
- Implication of Alpha-Synuclein Phosphorylation at S129 in Synucleinopathies: What Have We Learned in the Last Decade? Oueslati A, J Parkinsons Dis. 2016;6(1):39-51
- Role of post-translational modifications in modulating the structure, function and toxicity of alpha-synuclein: implications for Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis and therapies, Oueslati A et al, Prog Brain Res. 2010;183:115-45
- alpha-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions, Fujiwara H et al, Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Feb;4(2):160-4
- The role of Ser129 phosphorylation of α -synuclein in neurodegeneration of Parkinson’s disease: a review of in vivo models, Sato H et al, Rev Neurosci. 2013;24(2):115-23
- Alpha-synuclein function and dysfunction on cellular membranes. Exp Neurobiol, 23, 292-313, Snead D and Eliezer D, Exp Neurobiol. 2014 Dec;23(4):292-313
- Exogenous α-Synuclein Fibrils Induce Lewy Body Pathology Leading to Synaptic Dysfunction and Neuron Death, Volpicelli-Daley LA et al, Neuron. 2011 Oct 6;72(1):57-71
- Modeling α-Synuclein Propagation with Preformed Fibril Injections, Ching HK et al, J Mov Disord. 2019 Sep;12(3):139-151

Leave a Reply