Amyloid Beta Fibrillar Constructs
One of the main hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease is the accumulation of amyloid plaques in the brain. These plaques consist of extracellular deposits of the amyloid beta (Aβ) protein, which, under pathological conditions, undergoes misfolding and forms larger aggregates. Amyloid beta monomers can assemble into various structures such as oligomers, protofibrils and fibrils. Soluble oligomers can further aggregate to soluble protofibrils and finally to insoluble fibrils and amyloid plaques. Among these, oligomers are considered the most neurotoxic species and contribute to the cognitive decline seen in Alzheimer’s disease. Due to their neurotoxic properties, amyloid beta oligomers have recently drawn significant attention as a primary target for drug development in AD.

StressMarq offers Human Synthetic Amyloid Beta 1-42 Monomers (catalog# SPR-485), Oligomers (catalog# SPR-488) and Pre-formed Fibrils (PFFs) (catalog# SPR-487) as well as Human Amyloid Beta Pyroglutamate 3-42 PFFs (catalog# SPR-492) to support Alzheimer’s disease research.
Amyloid Beta Peptide
The amyloid beta (Aβ) peptide, ranging from 36 to 43 amino acids, is derived by proteolysis of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) through cleavage of beta- and gamma-secretases. The cleavage of APP can result in various forms of Aβ peptides, with Aβ40 (40 residues long) and Aβ42 (42 residues long) being the predominant variants in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Specifically, Aβ42 is the dominant form found in amyloid plaques and exhibits higher toxicity and aggregation propensity compared to Aβ40.
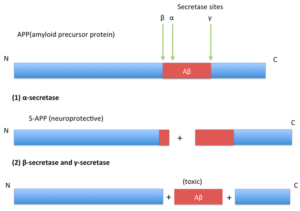
APP cleavage produces toxic amyloid beta in Alzheimer’s disease. (Source: Wen Xu, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0., via Wikimedia Commons)
In addition to these prevalent variants, the AD human brain also shows the presence of N-terminal truncated species with pyroglutamate Aβ 3-42 (AβN3(pE)) peptide emerging as a primary component. Post-translational modification occurs at the third position of the N-terminus of Aβ, leading to the formation of N-terminal pyroglutamate (pE) through dehydration catalyzed by glutaminyl cyclase (QC) activity. AβN3(pE) exhibits a progressive accumulation in the brain, even during the early stages of AD and precedes the onset of clinical symptoms. It also exhibits higher aggregation propensity and neurotoxicity compared to Aβ42, making it a promising target in AD therapeutic development.
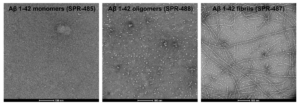
Human Synthetic Amyloid Beta 1-42 Peptide (HFIP-treated, monomeric): StressMarq’s peptide is produced synthetically and treated with 1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-propanol (HFIP) prior to drying which breaks down pre-formed fibrils and monomerizes the peptide. Upon resuspension in Ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH), StresMarq’s Aβ42 presents as a monomeric peptide without fibrils when observed under TEM, AFM, and on a Western Blot with an anti-amyloid beta antibody.
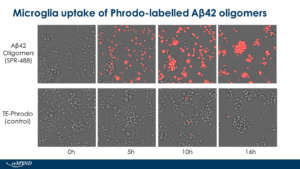
Human iPSC-derived microglia uptake of StressMarq Amyloid Beta 1-42 Oligomers (catalog# SPR-488) conjugated to Phrodo dye. Live cell imaging performed by reMYND (Leuven, Belgium) using Ex560 Em585.
Human Synthetic Amyloid Beta 1-42 Oligomers: StressMarq’s Aβ42 Oligomers are generated from amyloid beta peptide 1-42. These oligomers present as globular oligomers when observed under TEM and AFM and have a unique dimer/trimer and oligomer signal on a Western Blot with an anti-amyloid beta antibody. In toxicity experiments on rat primary cortical neurons, the oligomers show dose-dependent toxicity.
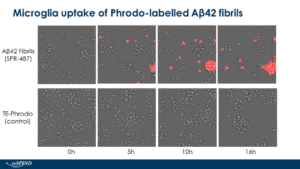
Human iPSC-derived microglia uptake of StressMarq Amyloid Beta 1-42 Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-487) conjugated to Phrodo dye. Live cell imaging performed by reMYND (Leuven, Belgium) using Ex560 Em585.
Human Synthetic Amyloid Beta 1-42 Pre-formed Fibrils: StressMarq’s Aβ42 Pre-formed Fibrils are generated from amyloid beta peptide. These fibrils present as long strands when observed under TEM and AFM and have a unique high molecular weight signal on a Western Blot with an anti-amyloid beta antibody. The fibrils also show dose-dependent toxicity to primary rat cortical neurons.
StressMarq’s Amyloid Beta Toxicity Experiments
Primary rat cortical neurons were treated with amyloid beta 1-42 monomers, oligomers and fibrils for 14 days in different concentrations. The amyloid beta monomers (catalog# SPR-485) have no impact on cortical neurons survival. On the other hand, the amyloid beta fibrils (catalog# SPR-487) and oligomers (catalog# SPR-488) exhibit a dose-dependent toxicity to the neurons.
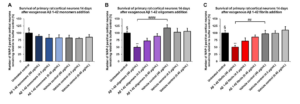
Survival of rat primary cortical neurons 14 days after treatment with different concentrations of Human Synthetic Amyloid Beta 1-42 (A) Monomers (catalog# SPR-485), (B) Oligomers (catalog# SPR-488) or (C) Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-487), quantified by MAP2 positive neurons and expressed as a percentage of control.
Human Amyloid Beta Pyroglutamate 3-42 Pre-formed Fibrils: StressMarq’s Aβ Pyroglutamate 3-42 Pre-formed Fibrils are generated from amyloid beta peptide 3-42. These fibrils present as primarily long strands when observed under TEM and AFM and have a unique high molecular weight signal on a Western Blot with an anti-amyloid beta antibody.
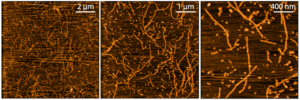
AFM of Human Amyloid Beta Pyroglutamate 3-42 Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-492).
Rigorous Quality Control
StressMarq’s quality control testing for neurodegenerative disease proteins includes:
- Sedimentation assays to ensure that most of the monomer was converted to fibril
- TEM/AFM imaging to verify fibril formation
- Thioflavin T assay to assess seeding capability of the fibrils
- SDS-PAGE to ensure protein purity
- Sterility check
- Endotoxin testing
Product Citations
StressMarq’s monomeric, fibrillar and oligomeric amyloid beta preparations have been cited in recent scientific research publications. Some products have also been validated in various applications by StressMarq collaborators.


Leave a Reply