Autoimmune Treatment using Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a promising treatment for many diseases. MSCs are multipotent – giving rise to several different cell types – and are easy to expand in vitro. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) produced by MSCs also have therapeutic properties. EVs do not self-replicate and can avoid controlled cell division and contamination risks of MSCs. This offers a promising cell-free therapeutic option. While both MSCs and their EVs can regulate inflammation and stimulate repair, it has been demonstrated that EVs are responsible for the immunosuppressive features of MSCs.
The therapeutic potential of MSCs and their EVs is pertinent for several diseases, including autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune diseases are defined by overactive immune systems that recognize healthy cells as foreign bodies. A study by Haghighitalab et al. shows that enriching MSCs with factors they already secrete can improve the immunomodulatory properties of MSCs and EVs1. This study supports the potential use of enriched preparations of EVs as a substitute for direct cell therapy.
Increased Gene Expression in MSCs and their EVs
Figure 1: Mesenchymal stem cells labelled with fluorescent molecules. Adobe Stock
MSCs can lose stemness and spontaneously differentiate, however, overexpressing human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) catalytic component can circumvent this2. The study employed this cellular model and demonstrated that the hTERT-MSCs displayed mesenchymal characteristics – they expressed the same MSC cell surface markers, CD44 and CD73 markers, without CD45 expression.
Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) can activate MSCs to produce immunomodulatory molecules, such as IDO1 (indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-1). Treating hTERT-MSCs with IFN-γ increased the expression of IDO1, along with PTGS2 (prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2), and TGF-β1 (transforming growth factor beta 1).
Other enhancers of immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory pathways produced the same effects as IFN-γ-stimulated cells. These included polyinosinic: polycytidylic acid poly (I:C) and StressMarq’s human recombinant Glucose-Regulated Protein 78 GRP78 (BiP) (catalog# SPR-119)3.
Enriched hTERT-MSCs and Cell-Free EV are Immunosuppressive
The researchers analyzed the upregulated genes. The hTERT-MSCs with overexpressed IDO1, PTGS2, and TGF-β1 retained their mesenchymal nature, as shown by CD44 and CD73 expression. The researchers then assessed lymphocyte inhibition to find effective immunomodulators. The individual overexpression of IDO1, PTGS2, or TGF-β1 reduced lymphocyte inhibition. A further reduction in lymphocyte inhibition was seen by overexpressing all three target genes. hTERT-MSCs stimulated with IFN-γ also showed inhibitory effects. Surprisingly, EVs from the parental MSCs overexpressing the target genes could mimic this inhibitory effect.
The cell-free EVs expressed the appropriate exosomal markers. Functionally, they displayed better immunosuppressive properties than MSCs primed using immunomodulatory enhancers. So, enriched EVs is a promising cell-free therapeutic for immunomodulatory treatment.
Study Implications
Inhibiting lymphocytes is required for the long-term treatment of autoimmune diseases or following transplant surgery. Haghighitalab et al. describe protocols for potential immunomodulatory therapy using cell-free enriched EVs. These products could serve as alternatives to immunosuppressive drugs, which can have multiple side effects.
StressMarq’s GRP78 (Bip) Protein Stimulates Modulatory and Anti-Inflammation Pathways
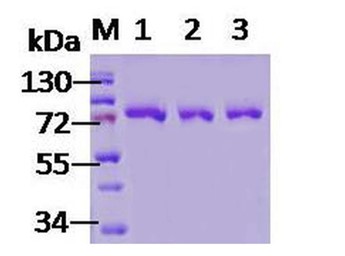
Figure 2: SDS-PAGE of Human Grp78 Protein (catalog# SPR-119)
In this study, StressMarq’s human recombinant GRP78 (BiP) protein (catalog# SPR-119) was shown to stimulate immunomodulatory and inflammation pathways. Defining MSCs using cell surface markers is critically important.
References
- Investigating the effects of IDO1, PTGS2, and TGF-β1 overexpression on immunomodulatory properties of hTERT-MSCs and their extracellular vesicles. Haghighitalab, A. et al. Sci Rep. 2021; 11.
- Overexpression of hTERT increases stem-like properties and decreases spontaneous differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cell lines. Tsai, C. C. et al. J Biomed Sci. 2010; 17.
- Inhibition of Antigen-Presenting Cell Function and Stimulation of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells to Express an Anti-inflammatory Cytokine Profile by the Stress Protein BiP: Relevance to the Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis. Corrigall, V. M et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50.


Leave a Reply