Creating Reproducible Neurodegenerative Disease Models
Neurodegenerative diseases are currently estimated to be the second highest cause of death globally. New findings from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2023 propose that the number of people living with neurological disorders is expected to double as the average lifespan increases worldwide. Although differences exist in the etiology of neurodegenerative diseases, many diseases belonging to this category exhibit comparable characteristics. These include an increased buildup of misfolded proteins, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation, which ultimately contribute to neuronal dysfunction and cell death.
The recent approval of the drug Lecanemab by the FDA in 2023, which slows Alzheimer’s disease progression by aiding in plaque clearance, is a testament to the potential of disease-modifying drugs. There are currently no medications that slow disease progression in Parkinson’s, as existing therapeutic interventions only target the disease’s motor symptoms. Research models enabling the screening of potentially active compounds are critical for developing therapeutics that may reduce the severity of neurodegenerative diseases in the aging population. Current models using primary neuronal cells, human induced pluripotent stem cells, and neuronal organoids are promising but remain expensive, labour-intensive, and challenging to reproduce.
By assessing cell viability and microglial phagocytosis in neurodegenerative models induced by alpha synuclein, tau, and amyloid beta pre-formed fibril aggregation, Luykx et al., have overcome the limitations of current models and proposed effective, reproducible, and inexpensive assays to screen disease-modifying drugs. The models described in this work will support researchers in screening potential therapies that may slow disease progression of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Recapitulating the molecular features of Alzheimer’s & Parkinson’s disease
The molecular features of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s are complex and distinct. In Alzheimer’s disease, the formation of extracellular plaques of amyloid beta peptide, which produce neurotoxic oligomers and fibrils, is the initial causative factor. Subsequently, neurofibrillary tangles made up of abnormally hyperphosphorylated and misfolded forms of tau protein begin to accumulate. The accumulation of amyloid beta precedes the conversion of tau from a normal to a toxic state. StressMarq’s Human Amyloid Beta 1-42 Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-487) and Human Tau (K18) P301L Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-330) were used in this study to mimic this disease process in cellular assays.
The pathological hallmark of Parkinson’s disease is the formation of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites. Alpha synuclein is the main constituent of Lewy bodies, an endogenous protein that, when existing in oligomeric or fibrillar forms, gives rise to neuroinflammation and other effects that are detrimental to normal cellular function. Researchers from the neurology research group at Universiteit Hasselt in Diepenbeek (Belgium) collaborated with the contract research organization (CRO), InnoSer (the Netherlands) to generate a Parkinson’s disease model utilizing StressMarq’s Human Alpha Synuclein Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-322).
Reduction in cell viability in neurodegenerative cellular models
Cell viability has been shown to be reduced in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and corresponding neurodegenerative disease models. Thus, the researchers investigated whether the readout of cell viability in the human neuroblastoma cell model SH-SY5Y could serve as a marker of disease progression – a characteristic which may also increase functionality in a drug screening model.
Measurement of cell viability was determined in response to previously identified inducers of neurodegenerative disease. The neurotransmitter glutamate is known to cause excitotoxicity in excess, resulting in overstimulation of neuronal receptors that consequently enables the progression of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. As hypothesized, a reduction in cell viability was observed post-glutamate treatment of SH-SY5Y cells. Specifically, a concentration-dependent decrease in cell viability was observed in the Alzheimer’s disease model induced with StressMarq’s Human Amyloid Beta 1-42 Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-487).
Another Alzheimer’s disease model induced with StressMarq’s Human Tau (K18) P301L Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-330) corroborated the decrease in cell viability. Induction of Parkinson’s disease using StressMarq’s Human Alpha Synuclein Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-322) also demonstrated a significant reduction in cell viability.
Assessing microglial activation & phagocytosis
Next, the researchers examined whether microglial phagocytosis could be used as a tool to assess the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. The activation of the central nervous system’s (CNS) resident phagocytes and microglia in response to the accumulation of amyloid beta and alpha synuclein around damaged areas is one of the hallmarks of neuroinflammation observed in Alzheimer’s disease.
To visualise the phagocytic process, pre-formed fibrils were labelled with a rhodamine-based pH dye, followed by cellular imaging analysis. During phagocytosis, proteins on the microglial cell surface recognize and engulf target substrates into intracellular compartments called phagosomes. The rhodamine-based pH dye is sensitive to pH changes – a quality that may be exploited to monitor phagocytotic process progression. As phagosomes mature by fusing with lysosomes to form highly acidic phagolysosomes that degrade their contents, the overall pH decreases and becomes acidic. When this occurs, the fluorescent signal emitted by the pHrodo dyes increases, rendering this technique extremely useful for identifying phagocytic microglial activation.
In the human microglial HMC3 cell line, treatment with pHrodo-labelled Human Amyloid Beta 1-42 Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-487) and Alpha Synuclein Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-322) from StressMarq revealed a significant increase in phagocytic capacity. The effect of monoclonal antibody treatment on microglial activation was then assessed. Aducanumab — which binds to amyloid beta, activates microglial phagocytosis, and enables clearance of amyloid beta plaques — produced a significant increase in phagocytosis following amyloid beta pre-formed fibril treatment compared to cells treated with the amyloid beta pre-formed fibrils alone.
Developing disease models with StressMarq’s neurodegenerative proteins
In this study, StressMarq’s fibrillar and oligomeric neurodegenerative protein constructs were critical in inducing Alzheimer’s & Parkinson’s disease pathology in the generated cellular models. StressMarq’s Human Amyloid Beta Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-487), Human Tau (K18) P301L Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-330) and Human Alpha Synuclein Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-322) were utilized to assess increases in phagocytic activity of microglia and a decrease in cell viability in neuronal cells. These insights highlight the pivotal role that StressMarq’s extensive portfolio of tools for neurodegenerative disease research may play in pre-clinical models, enabling high-throughput drug screening in the drug discovery process.
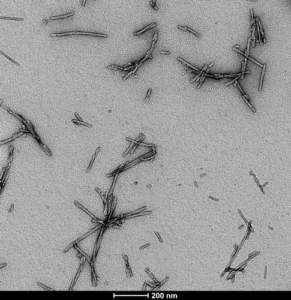
Figure 1. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) of Human Alpha Synuclein Pre-formed Fibrils (Type 1) (catalog# SPR-322)
Summary
Developing reproducible in vitro neurodegenerative disease models that can assess the ability of treatments to slow disease progression is indispensable in developing novel therapeutics. Although promising, current models remain expensive, labour-intensive, and challenging to reproduce. The findings by Luykx et al. demonstrate that microglial activation and cell viability data presented in neurodegenerative models induced by fibril aggregation can be used to monitor disease progression and screen disease-modifying drugs. These rapid, effective, and inexpensive neurodegenerative disease models have the potential to significantly accelerate the preclinical development of therapeutics.
Related StressMarq products
StressMarq is a market leader in the manufacturing of unique fibrillar, oligomeric, and monomeric protein preparations for neurodegenerative disease research. Visit our website for details on tau, amyloid beta, and alpha synuclein proteins, and a list of other scientific publications where our products have been used.
References
- Validation of preclinical cellular models to screen the effectiveness of drugs to slow down Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease progression. Luykx, A. Master’s thesis. Maastricht University.


Leave a Reply