FTY720/Fingolimod: A Potential Parkinson’s Disease Treatment
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is a common age-related neurodegenerative disorder that mainly affects movement. It is characterized by progressive degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) of the brain and the formation of Lewy Bodies. Alpha synuclein protein and its aggregation have been strongly implicated in PD pathology. Targeting alpha synuclein is considered a potential therapeutic strategy in PD. There is currently no cure but the existing treatments can only relieve some symptoms and improve quality of life in PD patients.
What is FTY720/fingolimod?
FTY720/fingolimod is an agonist of sphingosine‐1 phosphate receptors and an FDA approved drug for relapsing Multiple Sclerosis (MS). The drug can cross the blood-brain barrier and has some protective benefits in neurological disorders. It has been shown to increase brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression and improve myelination in MS patients.
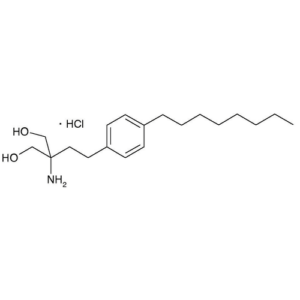
Chemical Structure of FTY720, Gilenya, 2-Amino-2-[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]-1,3-propanediol, hydrochloride.
FTY720/Fingolimod in Parkinson’s Disease
BDNF is a major neurotrophin which is involved in growth and differentiation of dopaminergic neurons. FTY720/ Fingolimod can increase BDNF expression which is abnormally low in PD patients and thus has potential in PD treatment. The drug has also been shown to stimulate the activity of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), an important serine/threonine phosphatase associated with PD1. Alpha synuclein normally interacts with PP2A enhancing its activity. In PD brain alpha synuclein is extensively phosphorylated at Ser129 which leads to its aggregation. Alpha synuclein aggregation has been shown to impair PP2A activity which can be enhanced pharmacologically by FTY7202.
Several other studies demonstrated the neuroprotective effects of FTY720/Fingolimod in different PD mouse models:
- In 6-OHDA- and rotenone-induced PD mouse models, fingolimod reduced motor deficits and the loss of nigral dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra3.
- In parkinsonian GM2+/- mouse models which develop motor deficits, low dose of Fingolimod significantly improved movement and reduced pathological alpha synuclein aggregation in brachial plexus4.
- In A53T transgenic mice which develop progressive intestinal synucleinopathy, the drug reduced alpha synuclein aggregation in the enteric nervous system5.
These findings suggest that FTY/fingolimod has the potential to counteract PD pathology and slow disease progression. Further studies need to be conducted to examine the impact of the drug in alpha synuclein aggregation and pathology.
StressMarq recently launched FTY720/Fingolimod (SIH-523) and also offers a broad selection of alpha synuclein products for Parkinson’s Disease research.
REFERENCES
- Novel FTY720-based compounds stimulate neurotrophin expression and phosphatase activity in dopaminergic cells. Vargas-Medrano J. et al. (2014) ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 5:782–786.
- Lewy-like aggregation of α-synuclein reduces protein phosphatase 2A activity in vitro and in vivo. Wu J. et al. (2012) Neuroscience. 207:288-297.
- Neuroprotective effects of fingolimod in mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. Zhao P. et al. (2017) FASEB J. 31(1):172-179.
- FTY720 Improves Behavior, Increases Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels and Reduces α-Synuclein Pathology in Parkinsonian GM2+/− Mice. Vidal-Martinez G. et al. (2019) Neuroscience 411:1-10.
- FTY720/Fingolimod Reduces Synucleinopathy and Improves Gut Motility in A53T Mice. Vidal-Martinez G. et al. (2016) J Biol Chem. 291(39): 20811-20821.

What dosage were the mice given?
Thank you for your interest in the article. Please refer to the references listed in the article for further details on the experiments mentioned.