Properties
| Storage Buffer | PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide *Storage buffer may be subject to change |
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC, Conjugated antibodies should be stored according to the product label |
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice or 4ºC |
| Purification | Protein G Purified |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Number | 15A3 |
| Isotype | IgG2b |
| Specificity | Recognizes markers of oxidative damage to DNA (8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine, 8-hydroxyguanine and 8-hydroxyguanosine). |
| Cite This Product | StressMarq Biosciences Cat# SMC-155, RRID: AB_889490 |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 8-Hydroxy Guanine Antibody, 8-OH-dG Antibody, 8OHG Antibody, 80G Antibody, 8 hydroxyguanine Antibody, 8 hydroxy 2' deoxyguanosine Antibody, 8 hydroxyguanosine Antibody, 8 OHG Antibody, 8-OHG Antibody, 8OHdG Antibody |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Cell Signaling, DNA Damage and Repair, DNA/RNA, Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling, Oxidation, Oxidative Stress, Post-translational Modifications |
| Scientific Background | DNA or RNA damage is due to environmental factors and normal metabolic processes inside the cell, that then hinder the ability of the cell to carry out its functions. There are four main types of DNA due to endogenous cellular processes and they are oxidation, alkylation, hydrolysis and mismatch of the bases. During the oxidation of bases, highly reactive chemical entities collectively known as RONS, occurs. RONS stands for reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and includes nitric oxide, superoxide, hydroxyl radical, hydrogen peroxide and peroxynitrite. Numerous studies have shown that RONS causes a variety of issues including DNA damage(1). 8-hydroxyguanine, 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanonsine and 8- hydroxyguanosine are all RNA and DNA markers of oxidative damage. 8-hydroxy-2'-guanosine is produced by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species including hydroxyl radical and peroxynitrite. Specifically its high biological relevance is due to its ability to induce G to T transversions, which is one of the most frequent somatic mutations (2). 8-hydroxy-guanine has been the most frequently studied type of DNA base damage, with studies in diabetes, and cancer. Base modifications of this type arise from radical-induced hydroxylation and cleavage reactions of the purine ring (3, 4). And finally, 8-hydroxy-guanosine, like 8-hydroxy-2'-guanosine, induces a mutagenic transversion of G to T in DNA. Its role has specifically been tested in the development of diabetes, hypertension and strokes (5, 6, and 7). |
| References |
1. Kim H.W., Murakami A., Williams M.V., and Ohigashi H. (2003) Carcinogenesis 24(2): 235-241. 2. Pilger A. and Rudiger H.W. (2006) Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 80(1): 1-15. 3. Malins D.C. and Haimanot R. (1991) Cancer Res. 51(19): 5430-5432. 4. Kvam E. and Tyrrell R.M. (1997) Carcinogenesis 18(11): 2281-2283. 5. Kowluru R.A., Atasi L., and Ho Y.S. (2006) Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47(4): 1594-9. 6. Bowers R. et al. (2004) Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 169(6): 764-9. 7. Cui J., Holmes E.H., Greene T.G., and Liu P.K. (2000) Faseb J. 14(7): 955-67. |
Product Images
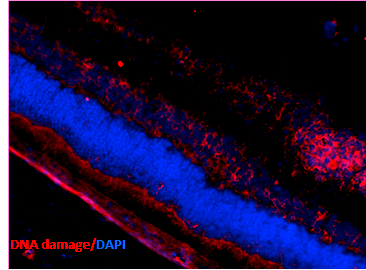
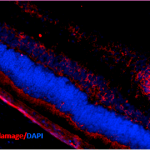
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-DNA Damage Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 15A3 (SMC-155). Tissue: Retinal Injury Model. Species: Mouse. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-DNA Damage Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-155) at 1:1000. Secondary Antibody: Alexa Fluor 594 Goat Anti-Mouse (red). Courtesy of: Dr. Rajashekhar Gangaraju, University of Indiana, Department of Ophthalmology, Eugene and Marilyn Glick Eye Institute.
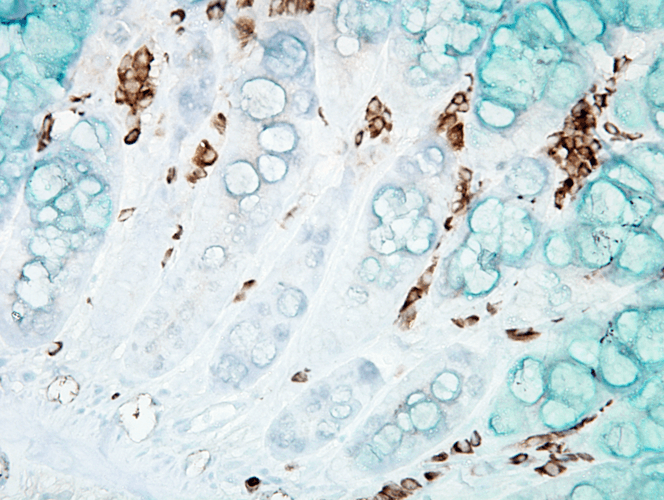
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-DNA Damage Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 15A3 (SMC-155). Tissue: inflamed colon. Species: Mouse. Fixation: Formalin. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-DNA Damage Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-155) at 1:1000000 for 12 hours at 4°C. Secondary Antibody: Biotin Goat Anti-Mouse at 1:2000 for 1 hour at RT. Counterstain: Mayer Hematoxylin (purple/blue) nuclear stain at 200 µl for 2 minutes at RT. Magnification: 40x. With anti-microbial. This image was produced using an amplifying IHC wash buffer. The antibody has therefore been diluted more than is recommended for other applications.
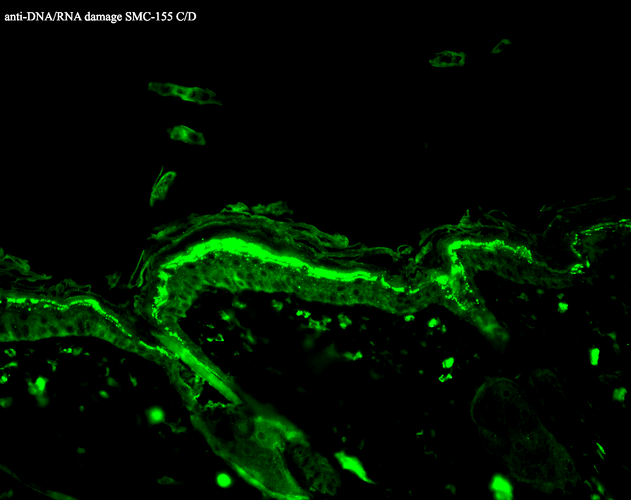
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-DNA Damage Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 15A3 (SMC-155). Tissue: backskin. Species: Mouse. Fixation: Bouin’s Fixative and paraffin-embedded. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-DNA Damage Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-155) at 1:100 for 1 hour at RT. Secondary Antibody: FITC Goat Anti-Mouse (green) at 1:50 for 1 hour at RT.
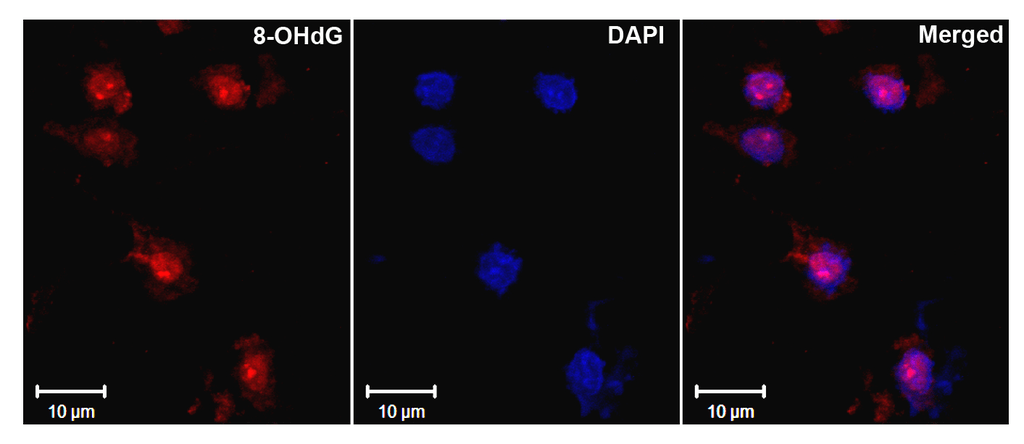
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-DNA Damage Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 15A3 (SMC-155). Tissue: Ischemic fresh brain tissue. Species: Rat. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-DNA Damage Monoclonal Antibody (SMC-155) at 1:1000 for 16 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Alexa Fluor 546 Goat Anti-mouse (Red) at 1:500 for 1 hour at RT. Localization: Cerebral Cortex. Courtesy of: Dr. Yi Yang, U. New Mexico.

![Mouse Anti-DNA Damage Antibody [15A3] used in Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on Mouse inflamed colon (SMC-155)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-155_DNA-Damage_Antibody_15A3_IHC_Mouse_inflamed-colon_40x_1-100x100.png)
![Mouse Anti-DNA Damage Antibody [15A3] used in Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on Mouse backskin (SMC-155)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-155_DNA-Damage_Antibody_15A3_IHC_Mouse_backskin_1-100x100.png)
![Mouse Anti-DNA Damage Antibody [15A3] used in Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on Rat Ischemic fresh brain tissue (SMC-155)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-155_DNA-Damage_Antibody_15A3_IHC_Rat_ischemic-fresh-brain-tissue_1-100x100.png)
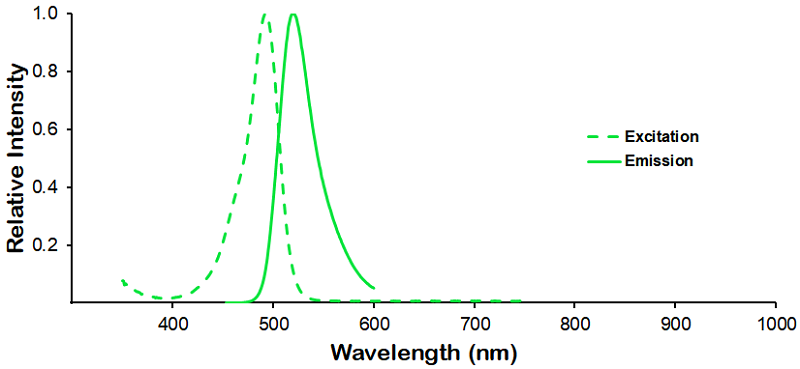
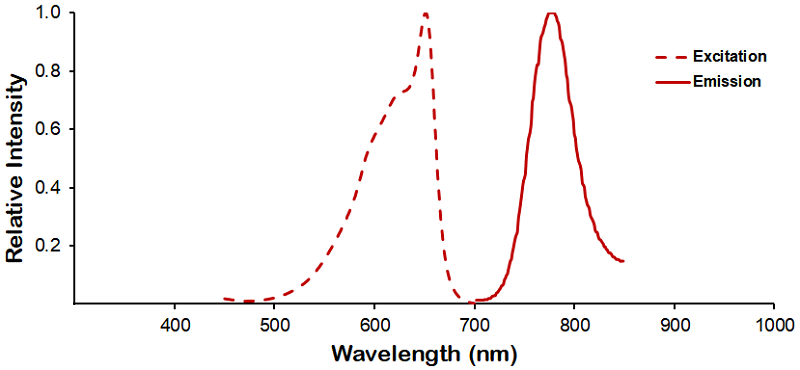
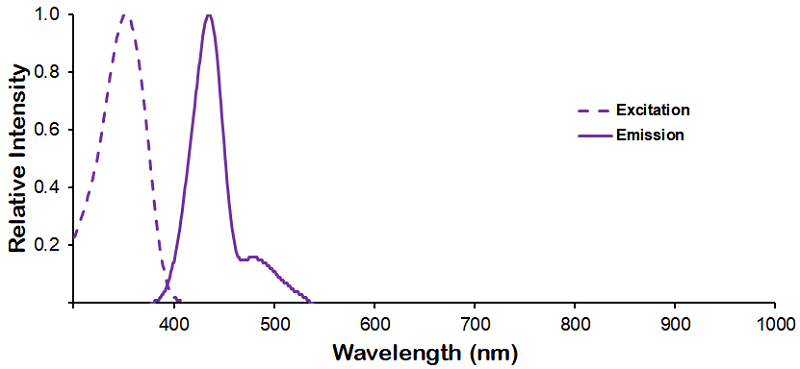
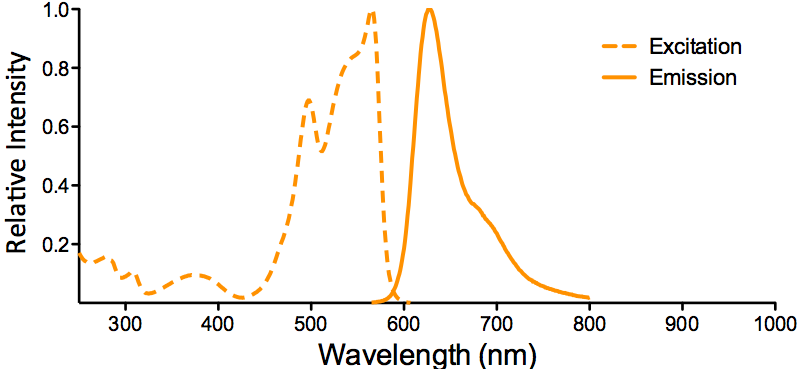
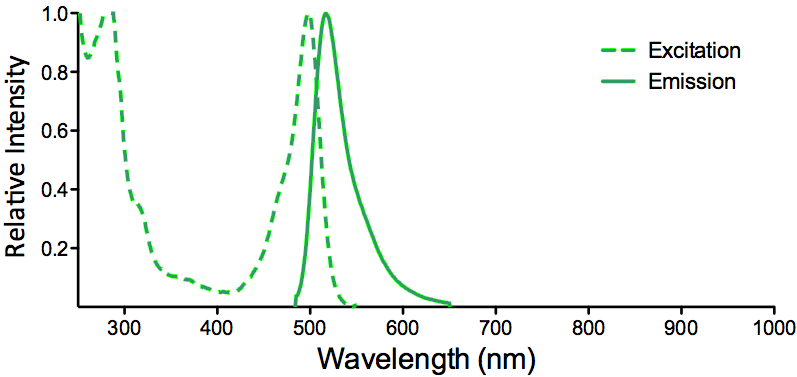
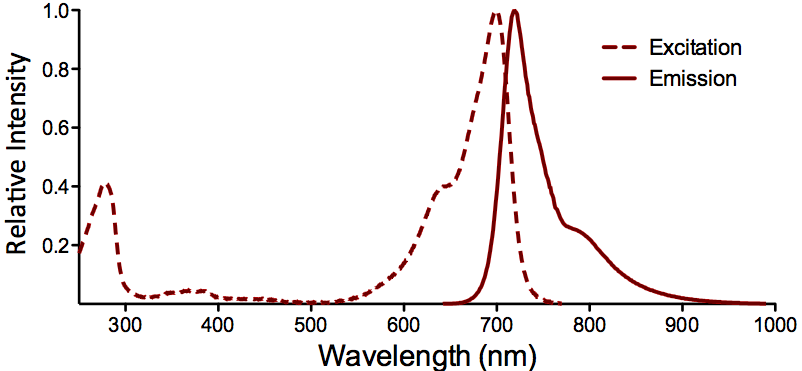
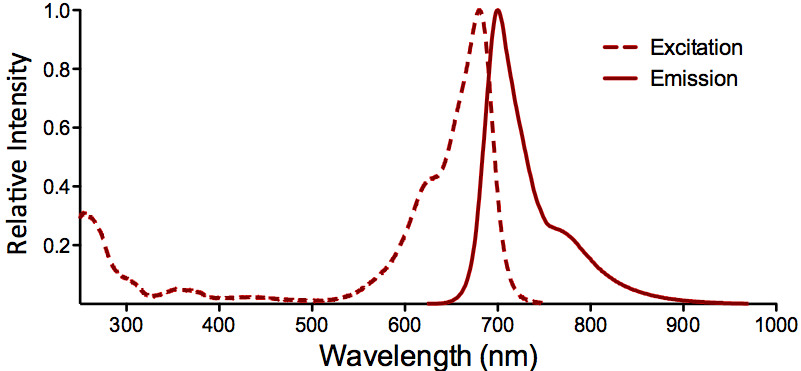
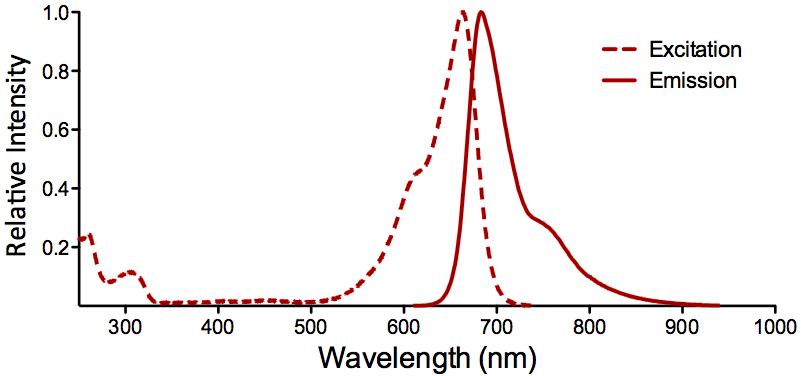
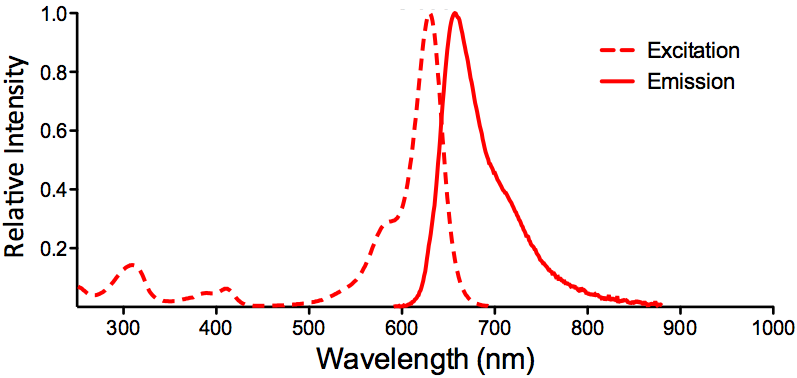
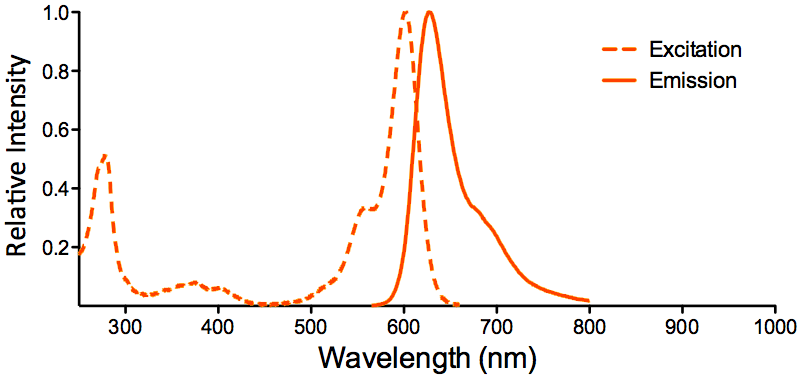
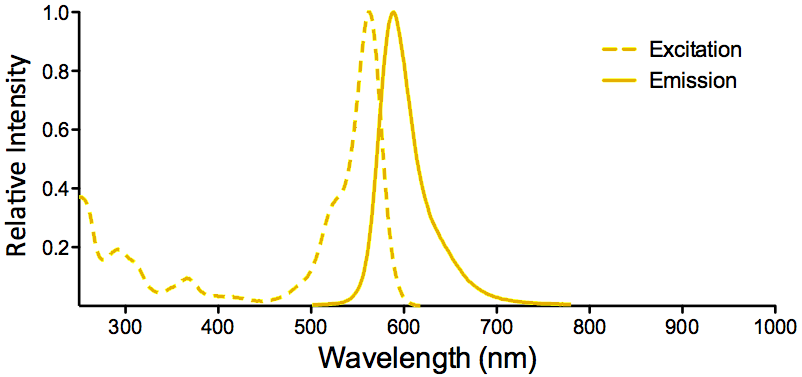
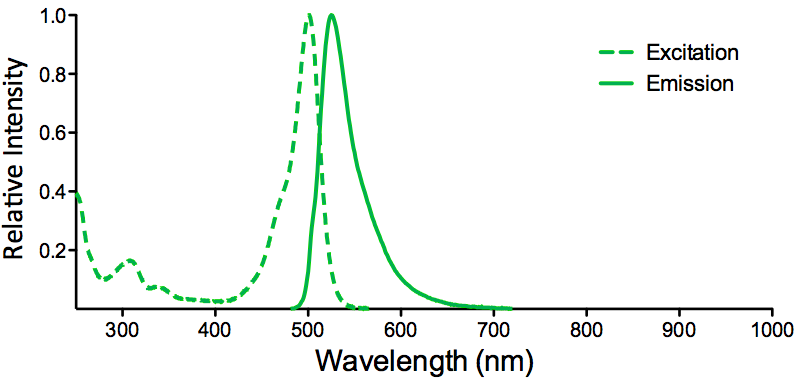
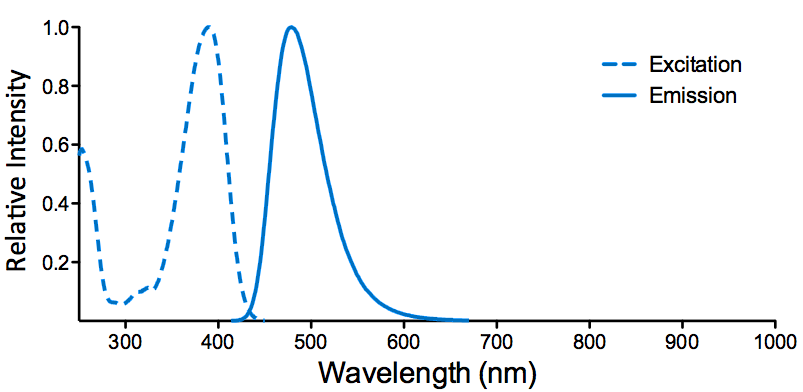
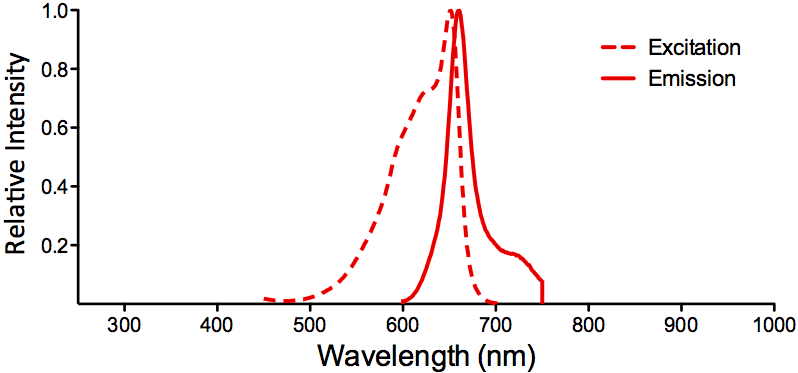
StressMarq Biosciences :
Based on validation through cited publications.