| Product Name | Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Detection Kit |
| Description |
Quantitative colorimetric measurement of urea nitrogen |
| Species Reactivity | Species Independent |
| Platform | Microplate |
| Sample Types | Plasma, Saliva, Serum, Tissue Culture Media, Urine |
| Detection Method | Colorimetric Assay |
| Assay Type | Direct Quantitative Assay |
| Utility | Colorimetric assay used to quantitatively measure urea nitrogen in a variety of samples. |
| Sensitivity | 0.042 mg/dl |
| Assay Range | 0.156 - 10 mg/dl |
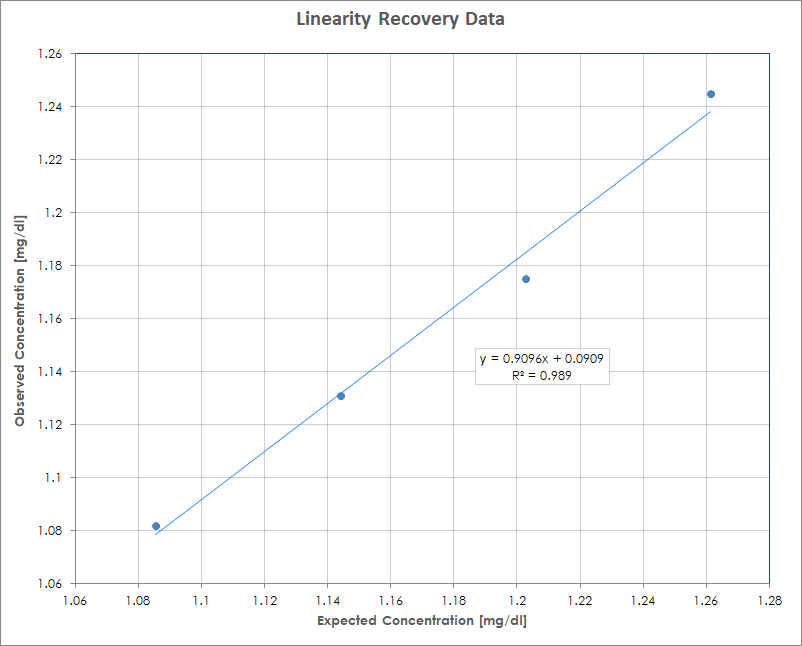
| Precision | Intra-Assay Precision (Within Run Precision) To determine Intra-Assay Precision, three samples of known concentration were assayed at different times, with different operators. The intra-assay coefficient of variation of the BUN within assays was determined to be <10%. Inter-Assay Precision (Between Run Precision) To determine Inter-Assay Precision, three samples of known concentration were assayed at different times, with different operators. The inter-assay coefficient of variation of the BUN between assays was determined to be <20%. |
| Incubation Time | 30 minutes |
| Number of Samples | 88 samples in duplicate |
| Other Resources | Kit Booklet Lot No. SU188700 , MSDS |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | 4ºC and -20ºC | ||||||||||||||||||
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice | ||||||||||||||||||
| Product Type | Detection Kits | ||||||||||||||||||
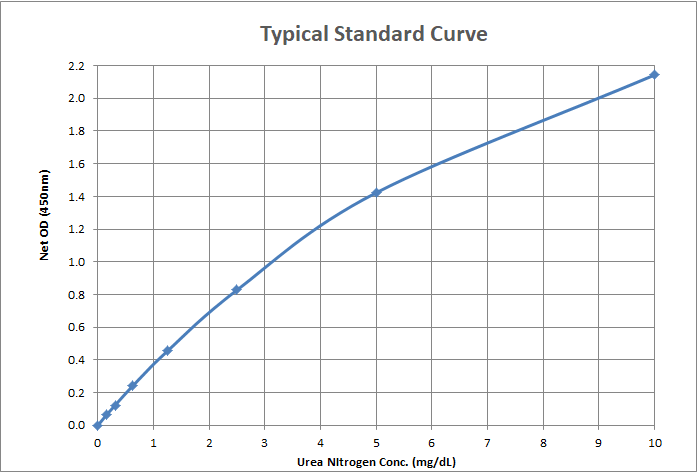
| Assay Overview | The Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure urea nitrogen in a variety of samples. A urea nitrogen standard is provided to generate a standard curve for the assay and all samples should be read off the standard curve. Samples are mixed with Color Reagents A and B and incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes. The colored product is read at 450 nm. The concentration of urea nitrogen in the sample is calculated, after making a suitable correction for any dilution, using software available with most plate readers. The results are expressed in terms of mg/dL urea nitrogen. If samples are to be expressed in terms of mg/dL urea, the data can be converted using the multiplier 2.14. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kit Overview |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Cite This Product | Blood Urea Nitrogen Detection Kit (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SKT-213) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | BUN, Blood urea nitrogen |
| Research Areas | Cardiovascular System, Cell Signaling |
| Scientific Background |
Urea is a nitrogenous waste product formed in the liver during protein metabolism and excreted by the kidneys. Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) levels are commonly used to assess renal function, with normal adult values ranging from 7–21 mg/dL. Elevated BUN (azotemia) may indicate kidney dysfunction, dehydration, or systemic illness. In neuroscience, impaired renal clearance of urea and other metabolites can contribute to cognitive dysfunction and neuroinflammation. Uremic toxins have been implicated in the development of encephalopathy and may exacerbate neurodegenerative conditions. Non-invasive sampling of urea in urine or saliva, alongside serum creatinine, provides a valuable tool for monitoring systemic health in neurological research. |
| References |
1. Laboratory reference values. Urea nitrogen (BUN). Rochester, Minn.: Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research; Nov. 2010. 2. Waiker, SS and JV Bonventre. (2008) Nephron Clin. Pract. 109:c192-c197. 3. Al Mofleh, IA. World J. Gastroent. (2008) Congestive heart failure. 14(5):675-684. 4. Iglesiase, J. et al. (2006) Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 21:3458-3465. 5. Mayo Clinic. “Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) tests.” http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/blood-urea-nitrogen/MY00373/DSECTION=results 6. Lum, G and S Leal-Khouri. (1989) Clin. Chem. 35(4):639-640. 7. Akai, T, et al. (1983) Clin. Chem. 1983. 29(10):1825-1827. |


StressMarq Biosciences :
Based on validation through cited publications.