| Product Name | Autophagy Flux Detection Kit |
| Description |
Detection of autophagy |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Platform | Reagents |
| Sample Types | Cell lysates |
| Assay Type | Quantitative WB (Western Blot) |
| Utility | Detection kit used to identify and characterise autophagy modulators using established markers, and analyse the effect of autophagy using western blotting techniques. |
| Number of Samples | 10 samples |
| Other Resources | Kit Booklet , MSDS |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Product Type | Detection Kits | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Assay Overview | The Autophagy Flux Detection kit facilitates the simple measurement of autophagy in cells. The kit utilises highly characterised antibodies to key autophagy biomarkers, LC3-II and p62, together with application of specific high purity control inhibitor for the accurate assessment of autophagic flux by Western blotting methods. Contains sufficient materials to run 10 Western blot analyses for each marker under specified conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Kit Overview |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Cite This Product | Autophagy Flux Detection Kit (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SKT-135) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | LC3-II and p62 Detection Kit |
| Research Areas | Autophagy, Cancer, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience |
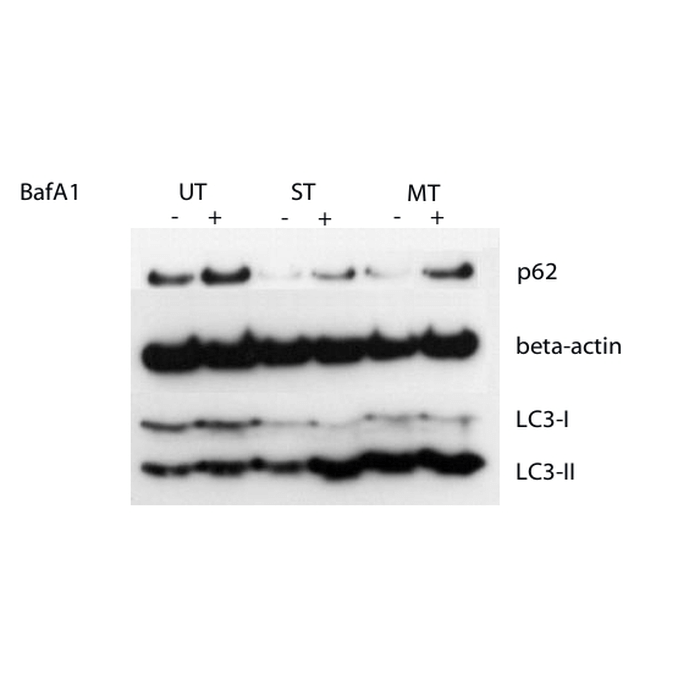
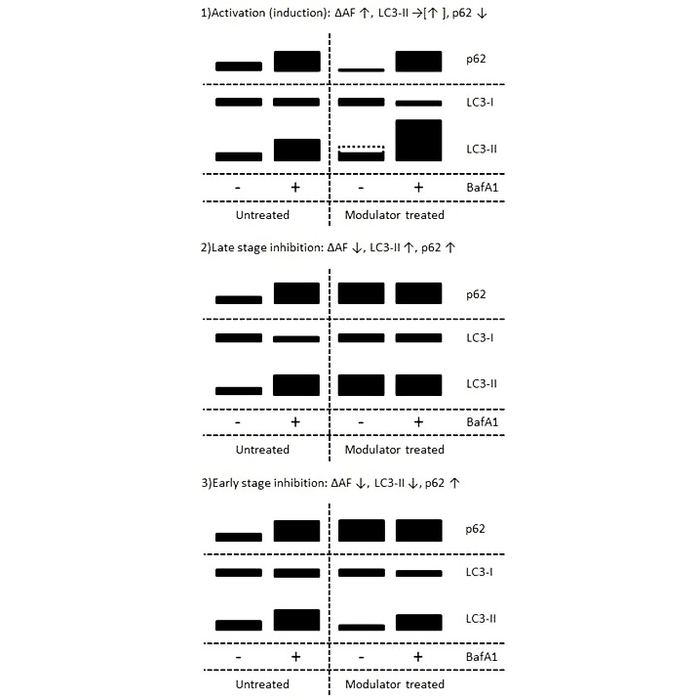
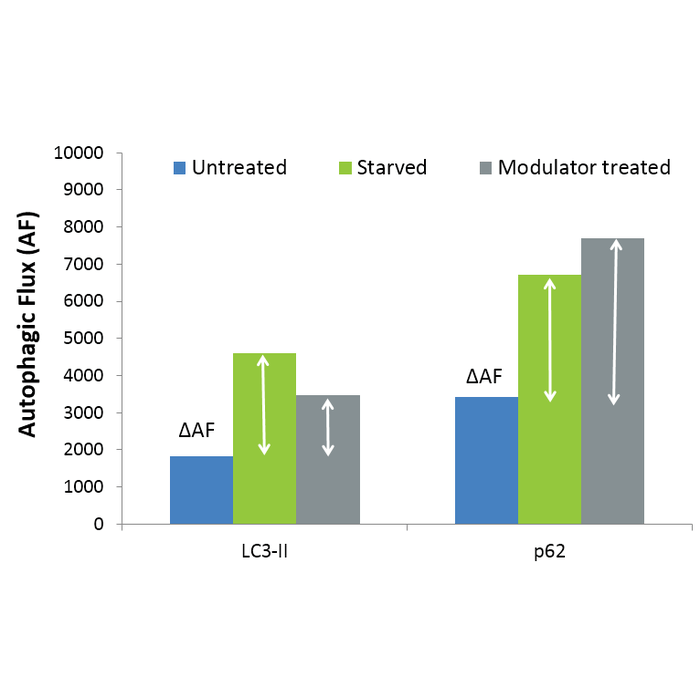
| Scientific Background | Autophagy is a lysosomal degradation pathway responsible for the removal of long-lived soluble proteins, misfolded and aggregated proteins, unwanted and damaged organelles (including mitochondria and peroxisomes) and intracellular pathogens (bacteria and viruses) (1,2). It is involved in various physiological or pathological processes, including promoting survival under starvation conditions, development, host defence response and immunity, cancer and neurodegenerative diseases in addition to maintenance of cellular proteostasis (3-5). Autophagy involves concerted action of more than 20 specific autophagy (ATG) proteins that mediate the formation of a double-membrane vesicle, the autophagosome, which engulfs its substrates and delivers them to the lysosome for degradation. Autophagy can be accurately assessed by measurement of autophagic flux, the complete process of autophagy from phagophore formation to substrate degradation and release of breakdown products. Changes in the flux or ‘turnover’ of the autophagy system upon intervention (e.g. drug treatment, gene knockdown, plasmid transfection) provide an excellent indication of its effect on autophagy and offers significant advantages over the static analysis of individual biomarkers levels often employed6. LC3-II (lipidated / autophagosome membrane associated form of LC3) and p62 (ubiquitin binding autophagy substrate receptor) proteins can be utilised as markers for measurement of autophagic flux. Differences in marker levels in the presence and absence of lysosomal degradation (inhibited by bafilomycin A1) represent the amount of LC3-II or p62 degraded and are a measure of autophagic flux (6-9). Use of a combination of autophagy markers to assess autophagic flux helps overcome the limitations of any one single marker in assessing such a complex system, facilitating accurate interpretation of results (6). For example LC3-II can associate with non-autophagic membranes and p62 can be degraded by the proteasome. Measurement of changes in autophagic flux following specific interventions such as drug treatment, gene knockdown or transfection, can be used to assess the effect of the intervention upon autophagy (10). |
| References |
1. Wang, K. & Klionsky, D. J. Autophagy 7, 297–300 (2011). 2. Wong, E. & Cuervo, A. M. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 2, a006734 (2010). 3. Rosenfeldt, M. T. & Ryan, K. M. Carcinogenesis 32, 955–63 (2011). 4. Galluzzi, L., Kepp, O. & Kroemer, G. The EMBO journal 30, 3213–4 (2011). 5. Metcalf, D. J., García-Arencibia, M., Hochfeld, W. E. & Rubinsztein, D. C. Experimental neurology 238, 22–8 (2012). 6. Klionsky, D. J. et al. Autophagy 8, 445–544 (2012). 7. Mizushima, N., Yoshimori, T. & Levine, B. Cell 140, 313–26 (2010). 8. Mizushima, N. & Yoshimori, T. Autophagy 3, 542–5 (2007). 9. Rubinsztein, D. C. et al. Autophagy 5, 585–9 (2009). 10. Menzies, F. M., Moreau, K., Puri, C., Renna, M. & Rubinsztein, D. C. Current protocols in cell biology. 15, 15.16 (2012). |
Product Images
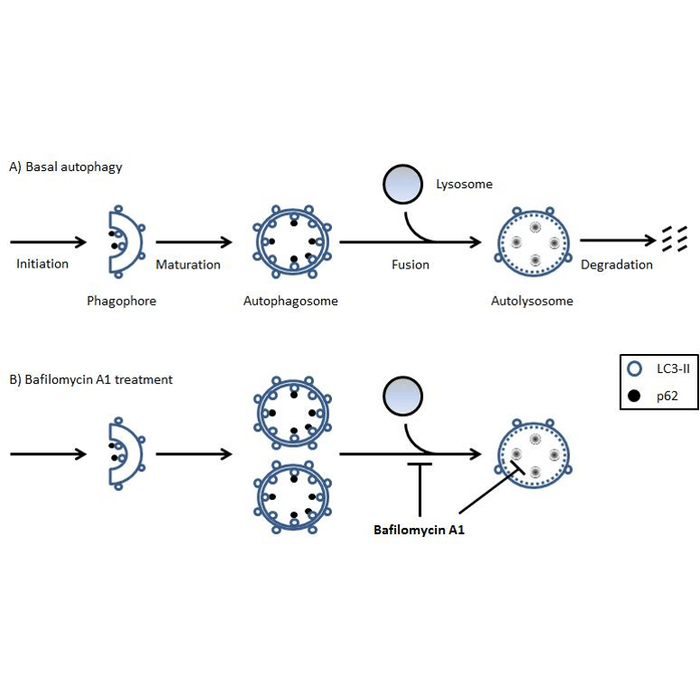
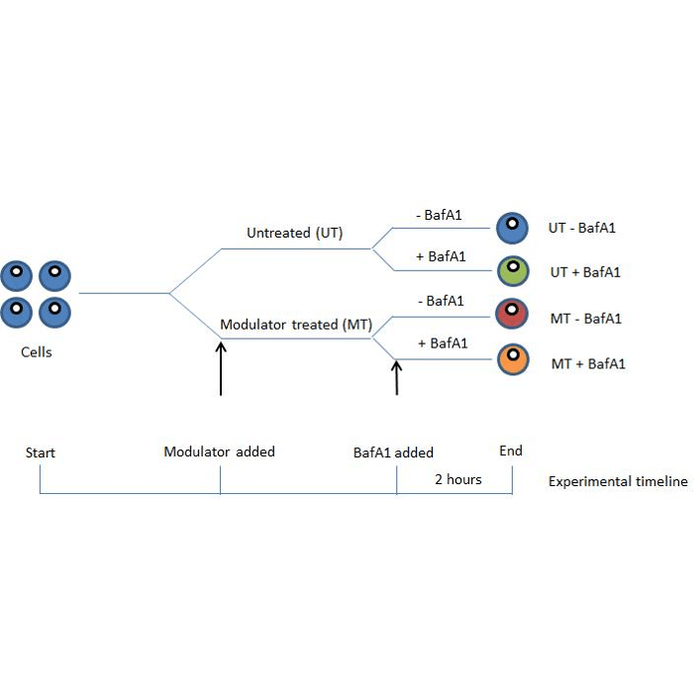
Schematic showing basal autophagy in cells and the effect of bafilomycin A1 (BafA1) treatment. Difference between LC3-II or p62 marker levels with and without BafA1 treatment represents the autophagic flux/turnover of the system and can be used to assess changes in autophagy upon experimental investigation.




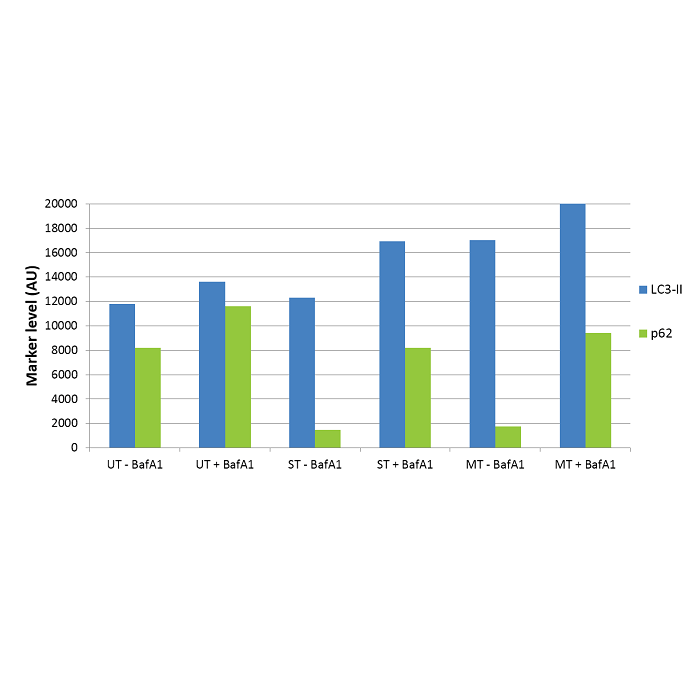
HXW :
I purchased this kit last year and very disappointed with it. The protocol is really poorly written and the ditailes are not adequately manefasted.
StressMarq Biosciences :
Thank you for your review. We are sorry to hear that you were not happy with this product and you found the protocol in the kit booklet difficult to follow. This product is undergoing redevelopment and when it relaunches we will ensure that the protocol is improved using your feedback.
For any future purchases, please contact us with your questions or concerns as our tech support team would be more than happy to assist you.