| Product Name | Alpha Synuclein S87N Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description |
Human Recombinant Alpha Synuclein S87N Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | WB, SDS PAGE, In vitro Assay | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentration | 2 mg/ml or 5 mg/ml | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conjugates |
No tag
StreptavidinProperties:
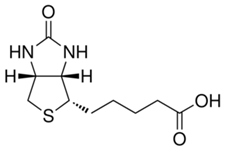
Biotin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| R-PE (R-Phycoerythrin) | ||
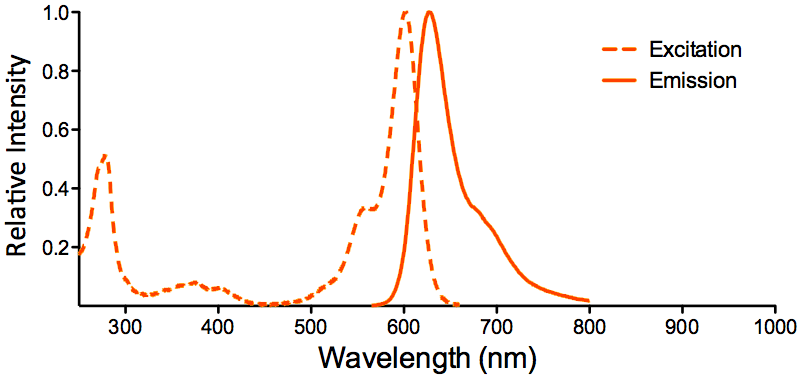
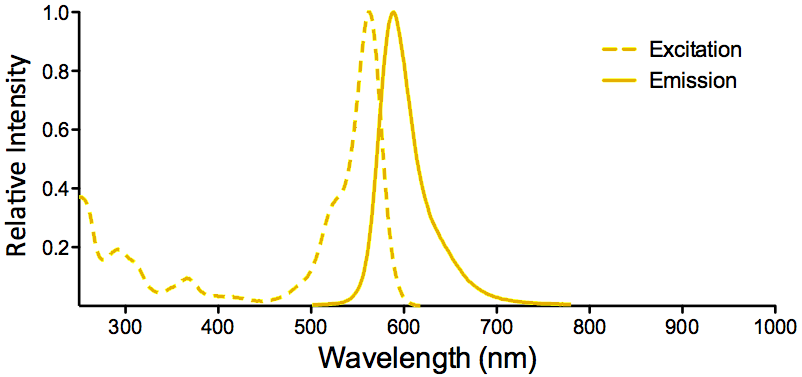
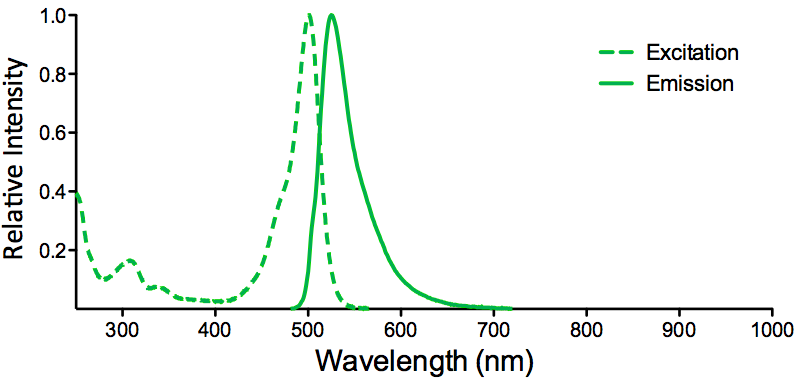
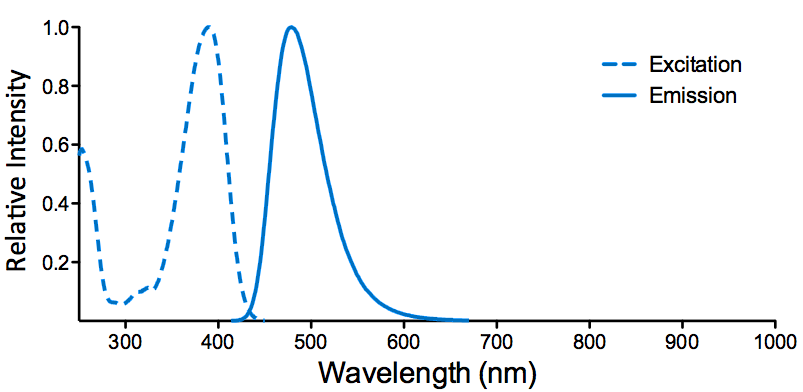
| Overview: | 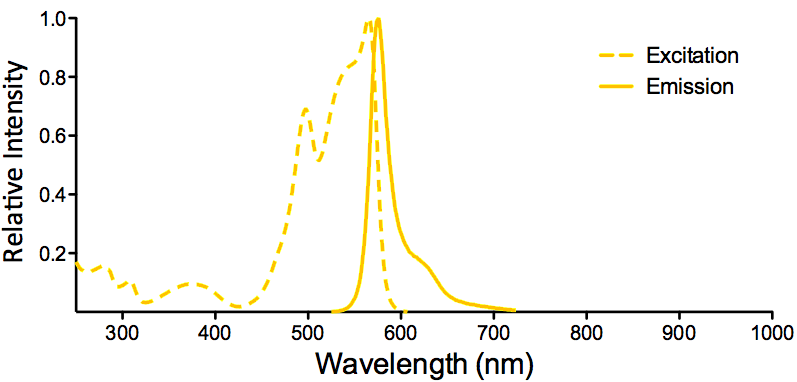 |
Optical Properties:
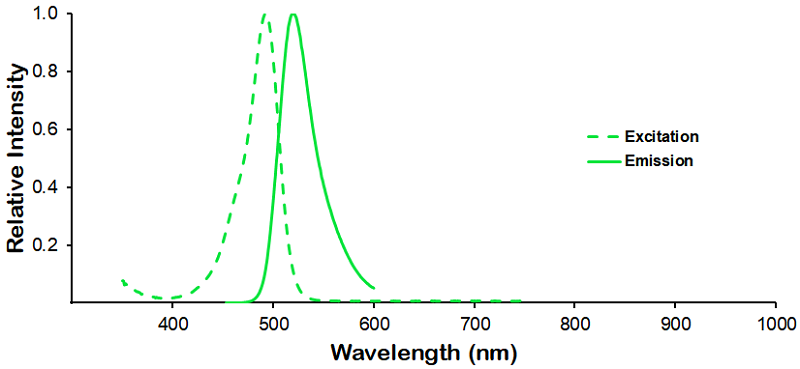
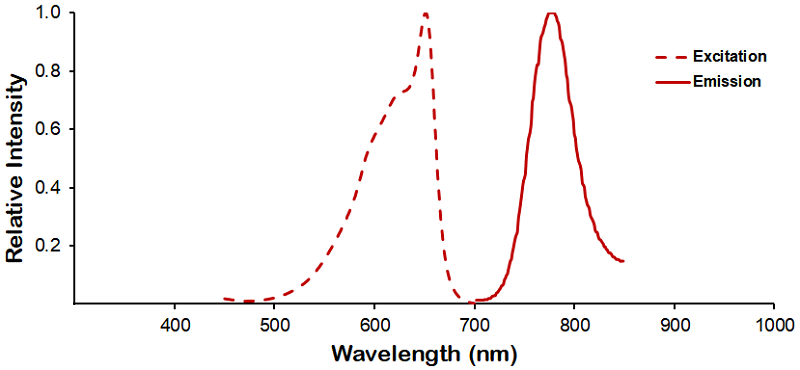
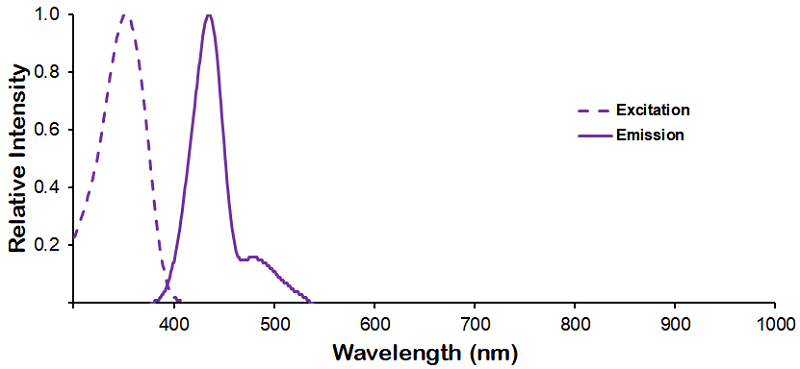
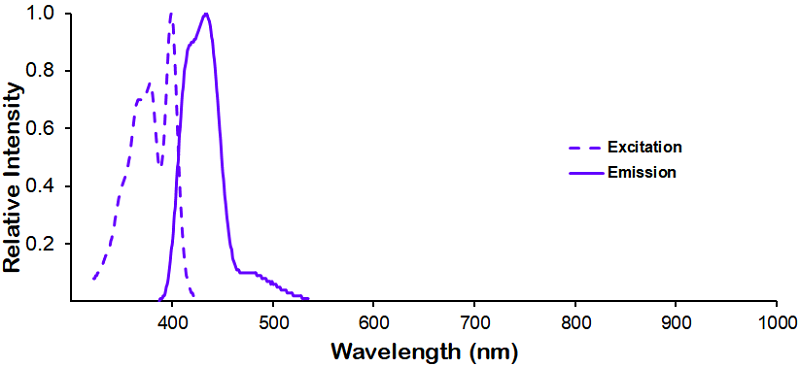
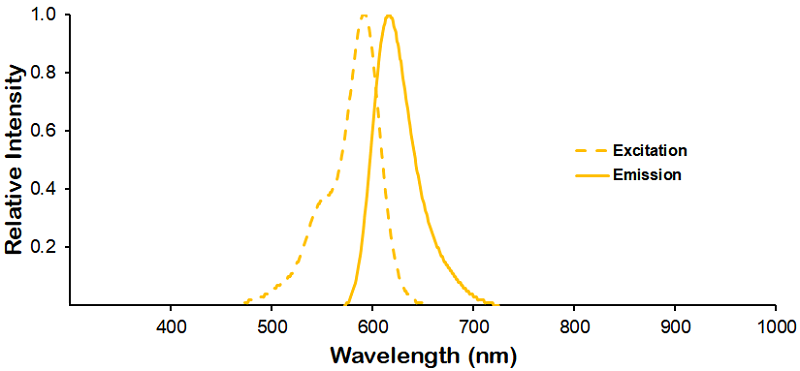
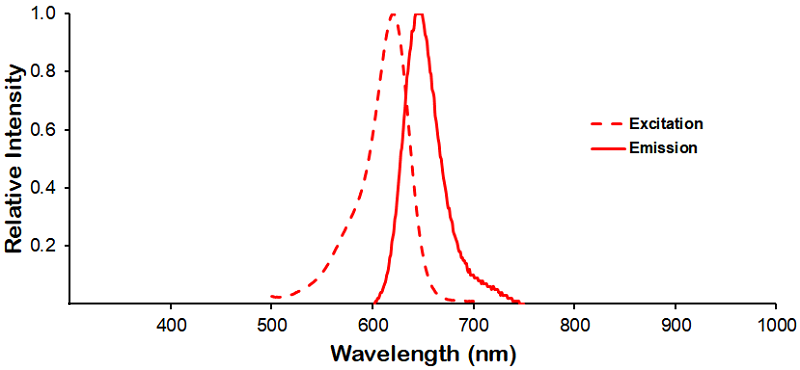
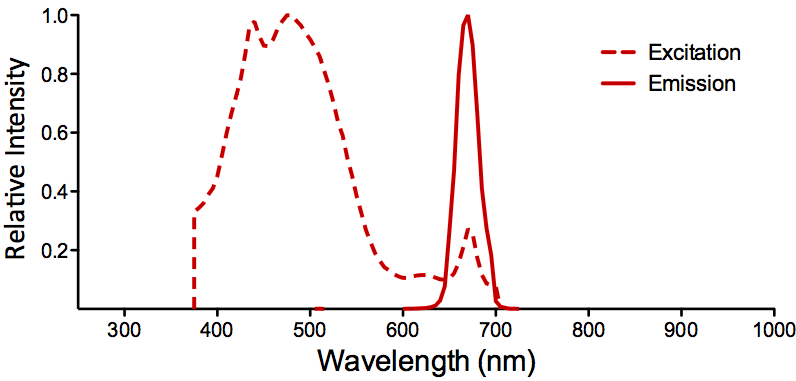
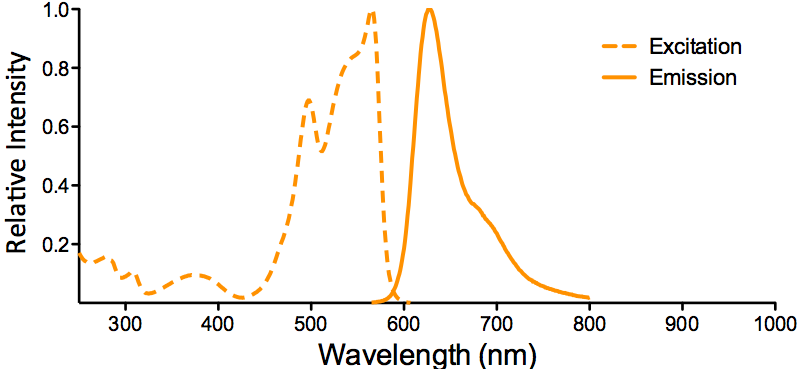
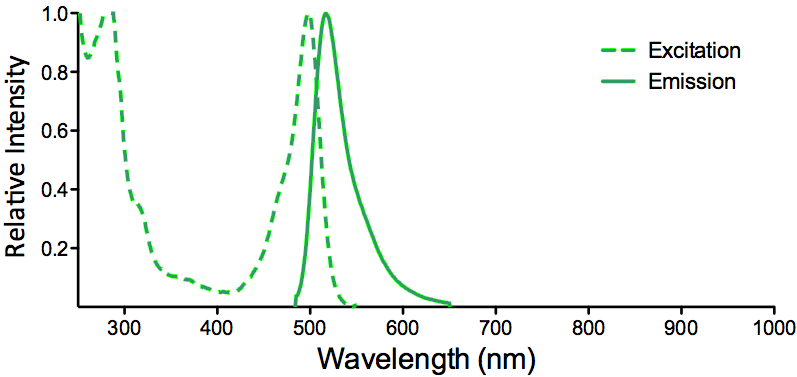
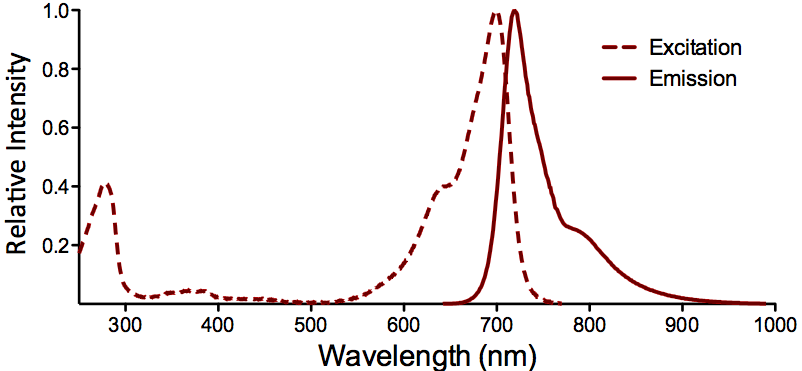
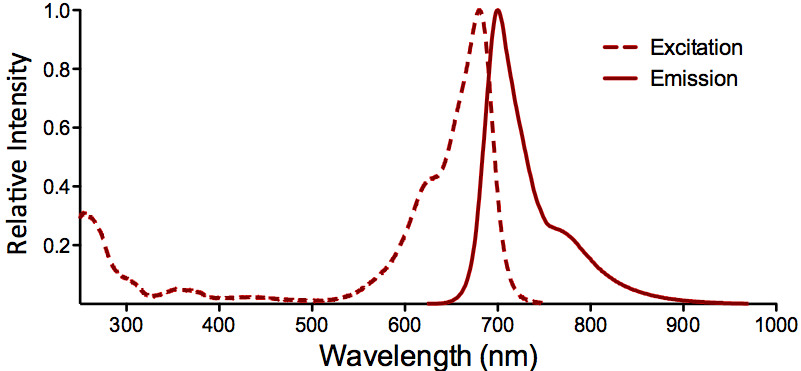
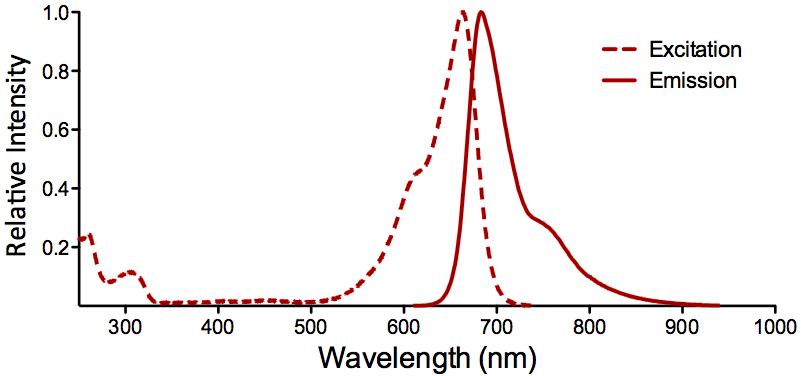
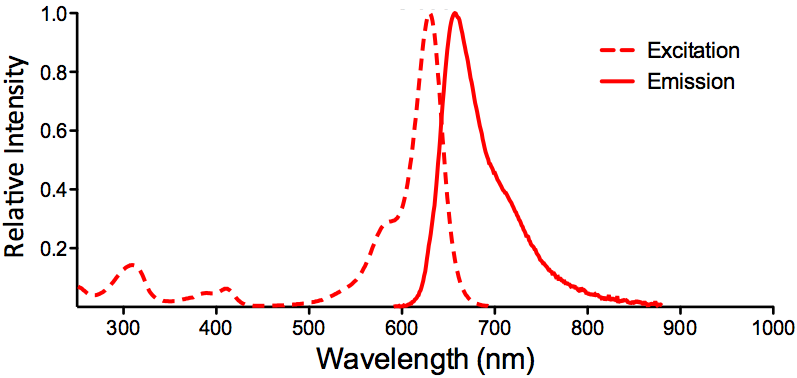
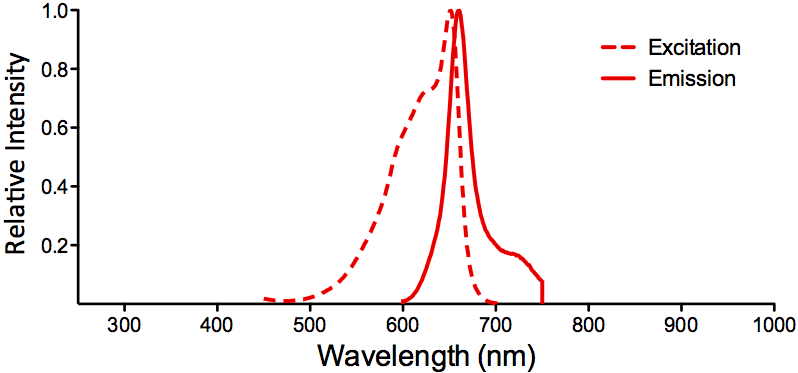
λex = 565 nm λem = 575 nm εmax = 2.0×106 Φf = 0.84 Brightness = 1.68 x 103 Laser = 488 to 561 nm Filter set = TRITC |
Properties
| Storage Buffer | 1X PBS pH 7.4 |
| Storage Temperature | -80ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Dry Ice. Shipping note: Product will be shipped separately from other products purchased in the same order. |
| Purification | Ion-exchange Purified |
| Cite This Product | Human Recombinant Alpha Synuclein S87N Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SPR-500) |
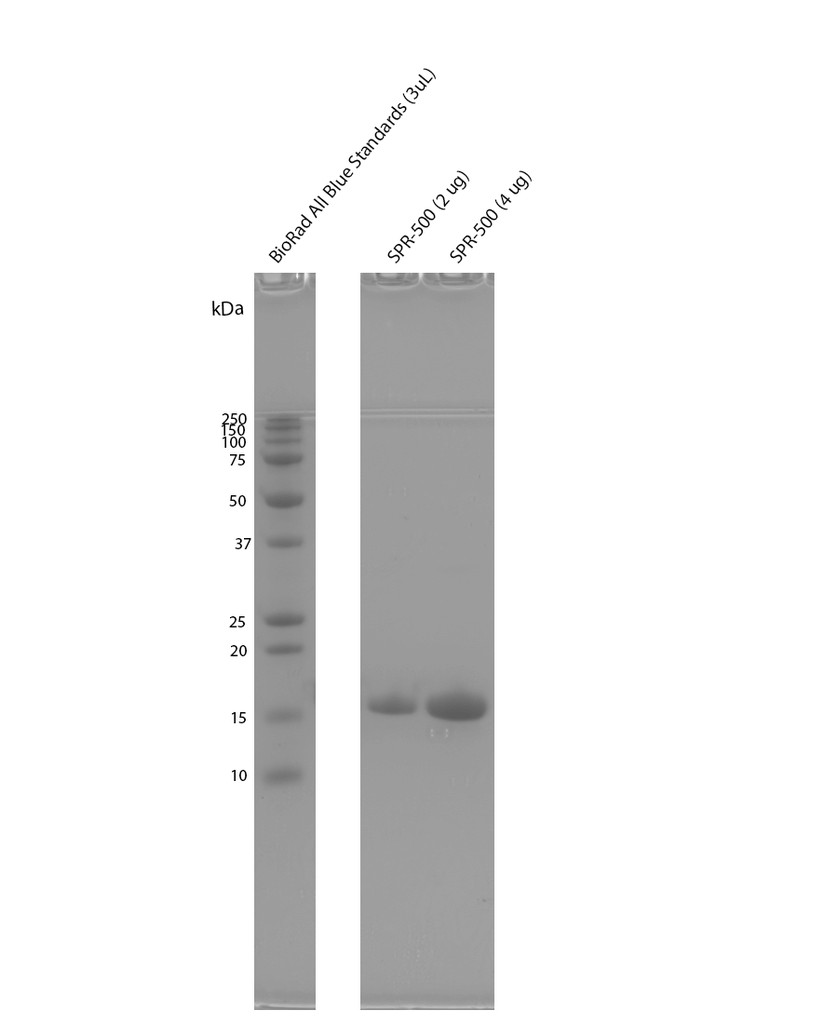
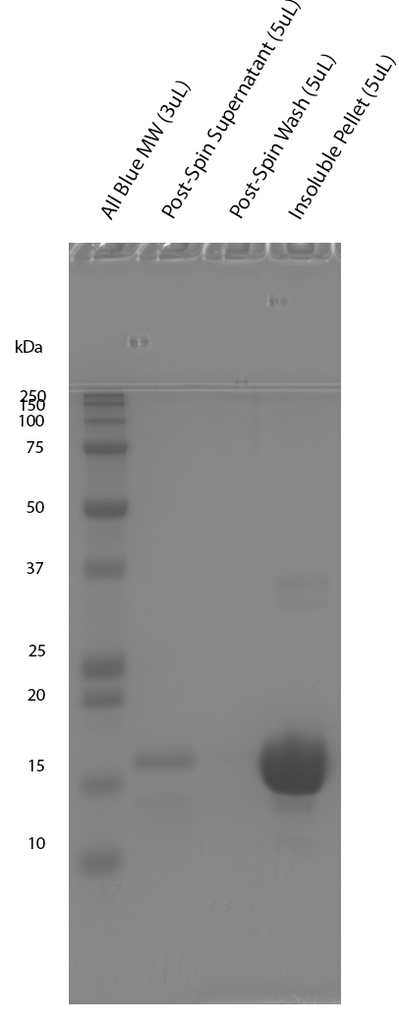
| Certificate of Analysis | Protein certified >95% pure on SDS-PAGE & Nanodrop analysis. Low endotoxin <5 EU/mL @ 2mg/mL. |
| Other Relevant Information | For best results, sonicate immediately prior to use. Refer to the Neurodegenerative Protein Handling Instructions on our website, or the product datasheet for further information. Monomer source is catalog# SPR-499. |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | MAPT, 2N4R, Tau40 neurofibrillary tangle protein, paired-helical filament, PHFs, SNCA, NACP, PARK1, asyn, alpha-synuclein, pre-formed fibril, PFFs, mixed fibrils |
| Research Areas | Alzheimer's Disease, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience, Parkinson's Disease, Synuclein, Tangles & Tau, Multiple System Atrophy |
| Accession Number | NP_000336.1 |
| Gene ID | 6622 |
| Swiss Prot | P37840-1 |
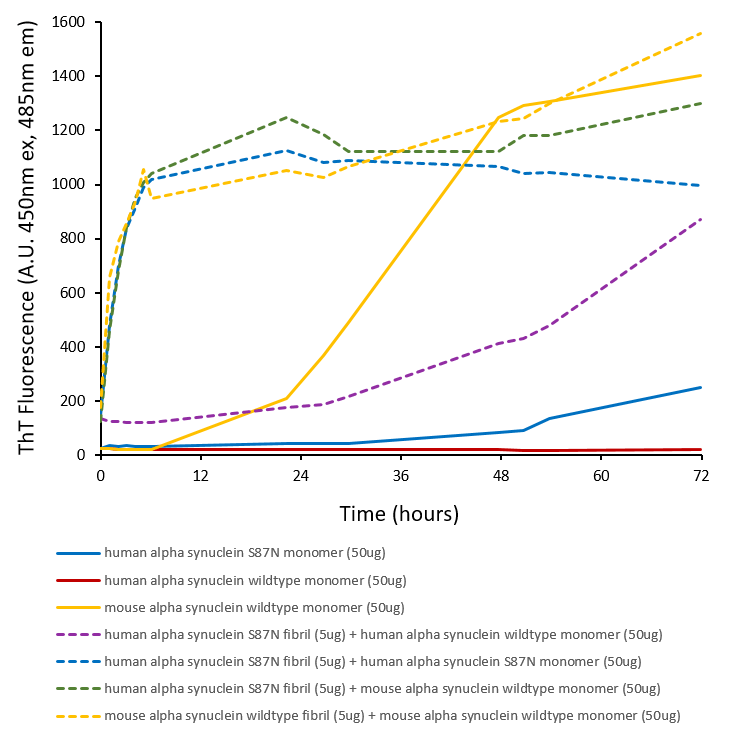
| Scientific Background | Human alpha synuclein S87N mutant (HuS87N) has Ser87 mutated to the equivalent mouse residue Asn87, effectively making it a human-mouse chimeric protein. Despite sequence differences at only seven residues, or 5% of the total 140 amino acids, the aggregation rate of wild-type mouse α-syn (MsWT) is faster than wild-type human α-syn (HuWT) in vitro. In wild-type mouse models, MsWT fibrils are more efficient than HuWT fibrils at inducing endogenous mouse α-syn pathology (1). A53T or S87N substitutions in human α-syn substantially accelerate fibrilization rates in vitro (2,3). Chimeric HuS87N fibrils show enhanced induction of α-syn pathology greater than both HuWT and MsWT fibrils in mice neuron cultures (4). Therefore, HuS87N is a good construct for inducing robust endogenous α-syn seeding and pathology in wild-type mice/cultures. |
| References |
1. Masuda-Suzukake et al. 2013. Prion-like Spreading of Pathological α-synuclein in Brain. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awt037 2. Kang, K. et al. 2011. The A53T Mutation is Key in Defining the Differences in the Aggregation Kinetics of Human and Mouse α-synuclein. JACS. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja203979j 3. Ohgita, T. et al. 2023. Intramolecular Interaction Kinetically Regulates Fibril Formation by Human and Mouse Alpha-Synuclein. Sci Rep https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-38070-4 4. Luk, K., C. et al. 2016. Molecular and Biological Compatibility with Host Alpha-Synuclein Influences Fibril Pathogenicity. Cell Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.053 |
Product Images
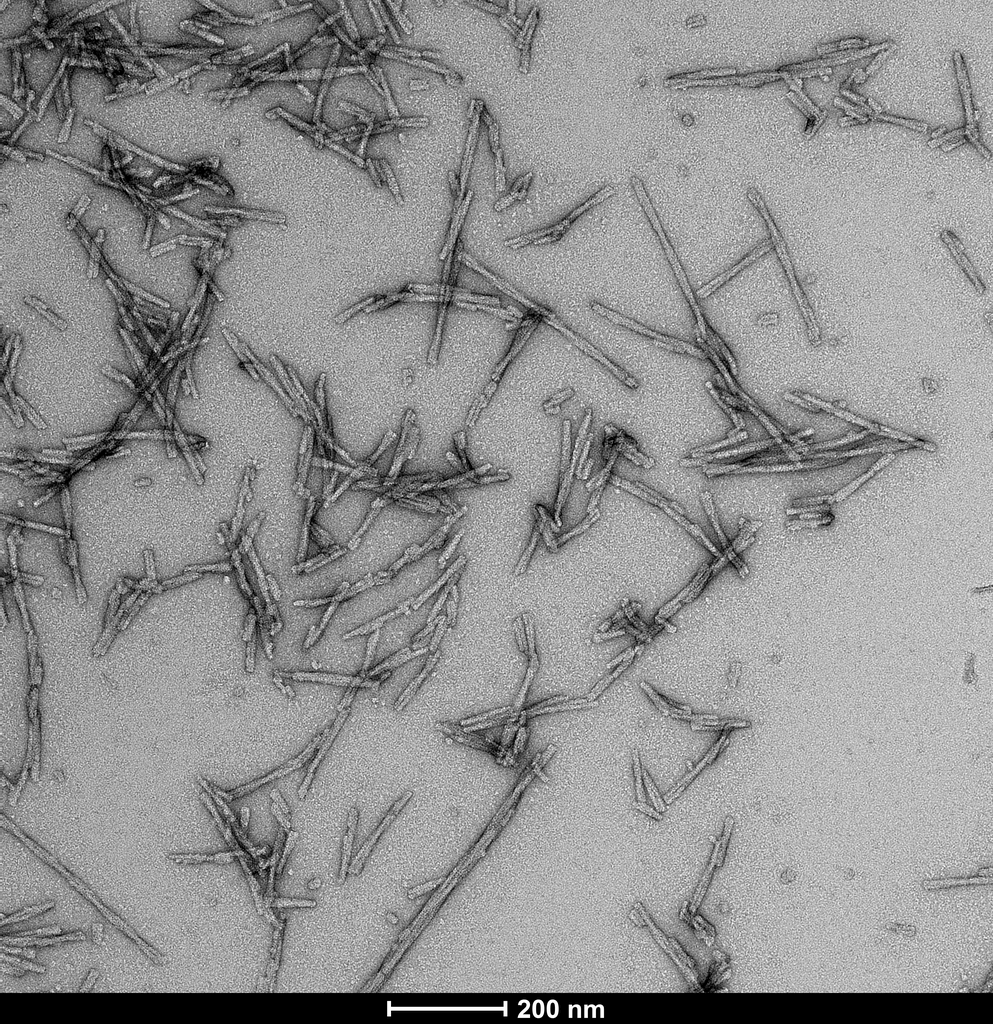
TEM of human alpha synuclein S87N fibrils (SPR-500). Negative stain transmission electron microscopy images acquired at 80 Kv on carbon coated 400 mesh copper grids using phosphotungstic acid and uranyl acetate stain. Scale bar = 200 nm. Method: Samples were prepared for examination in the transmission electron microscope using the ‘direct application method’ (Doane and Anderson 1987).
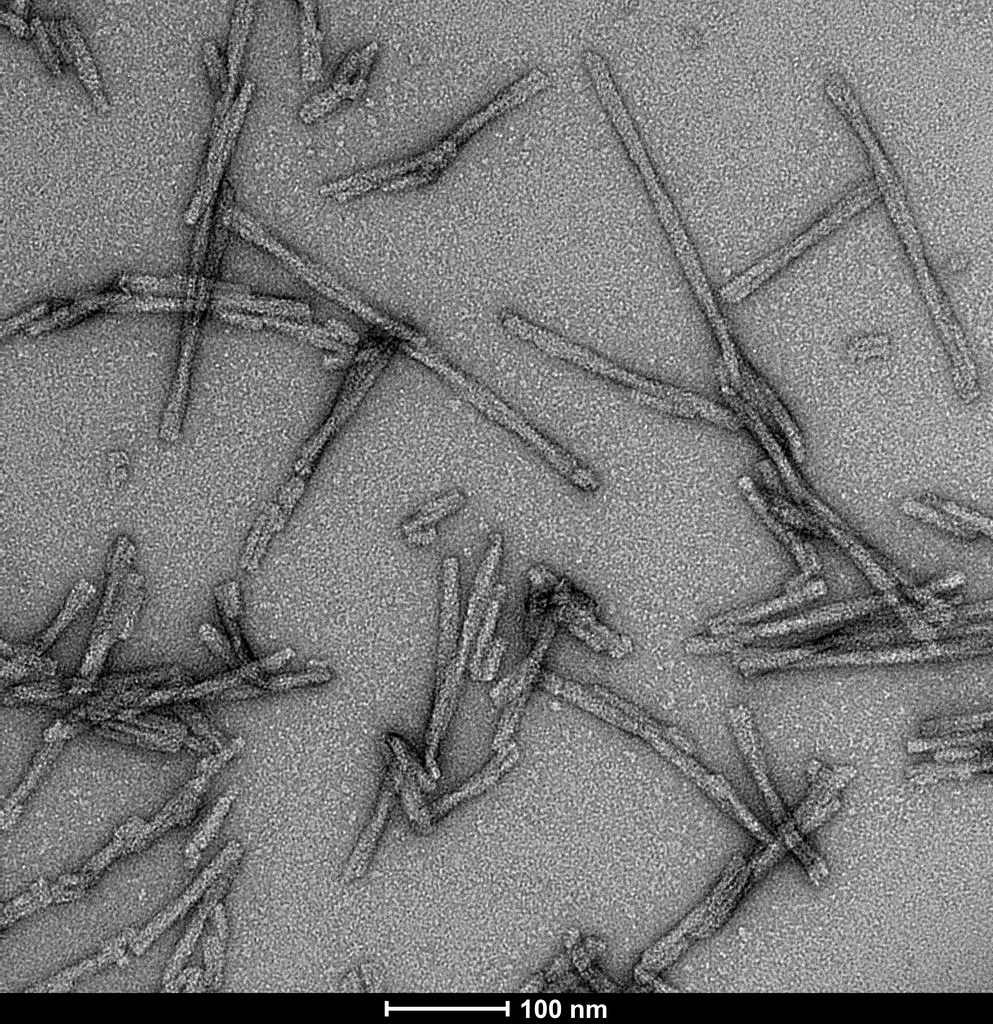

TEM of human alpha synuclein S87N fibrils (SPR-500). Negative stain transmission electron microscopy images acquired at 80 Kv on carbon coated 400 mesh copper grids using phosphotungstic acid and uranyl acetate stain. Scale bar = 100 nm. Method: Samples were prepared for examination in the transmission electron microscope using the ‘direct application method’ (Doane and Anderson 1987).
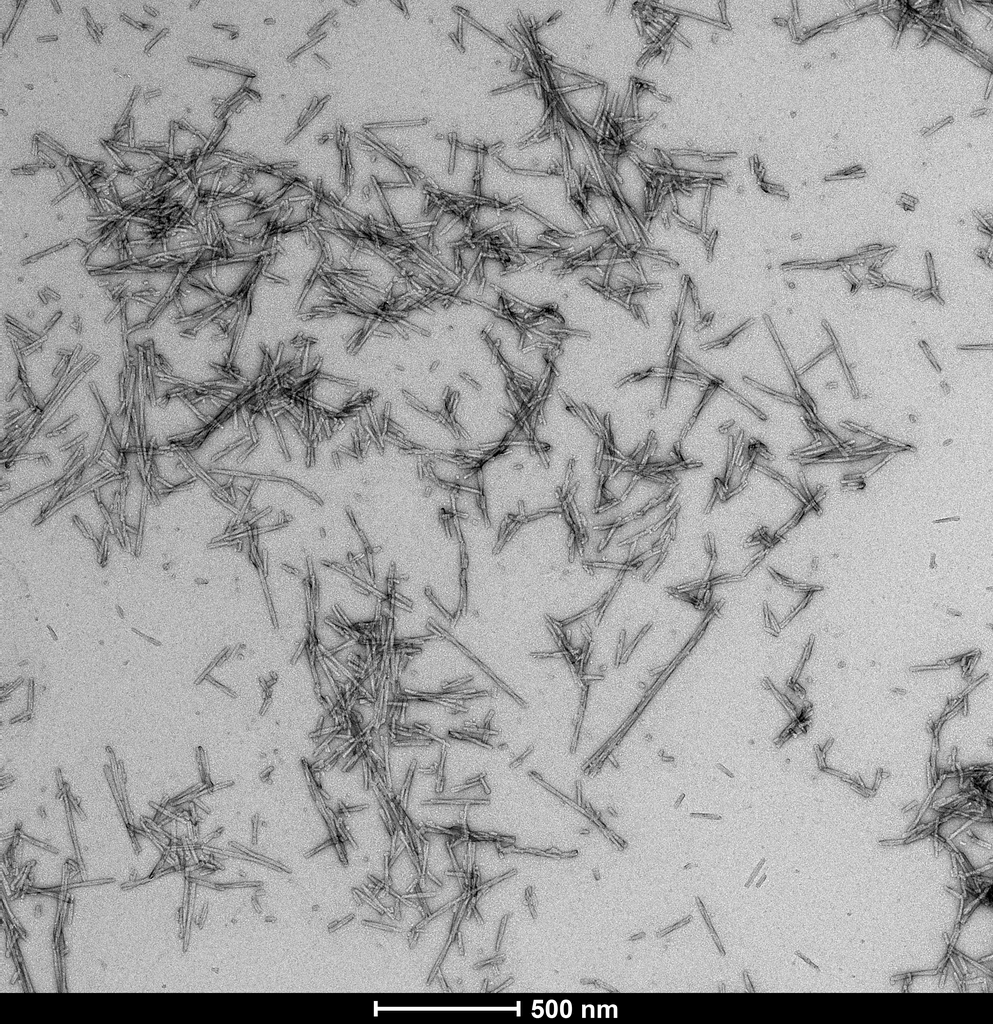
TEM of human alpha synuclein S87N fibrils (SPR-500). Negative stain transmission electron microscopy images acquired at 80 Kv on carbon coated 400 mesh copper grids using phosphotungstic acid and uranyl acetate stain. Scale bar = 500 nm. Method: Samples were prepared for examination in the transmission electron microscope using the ‘direct application method’ (Doane and Anderson 1987).

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.