| Product Name | Alpha Synuclein Protein | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description |
Human Recombinant A53T Mutant Alpha Synuclein Protein Pre-formed Fibrils (Type 1) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | WB, SDS-PAGE, In vivo assay, In vitro assay | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conjugates |
No tag
StreptavidinProperties:
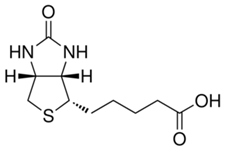
Biotin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
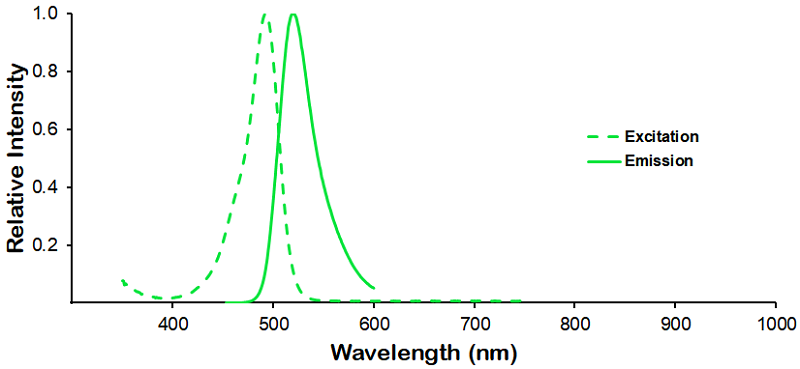
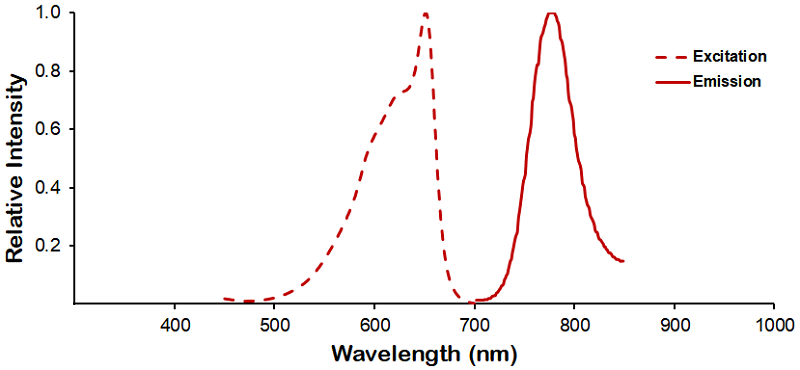
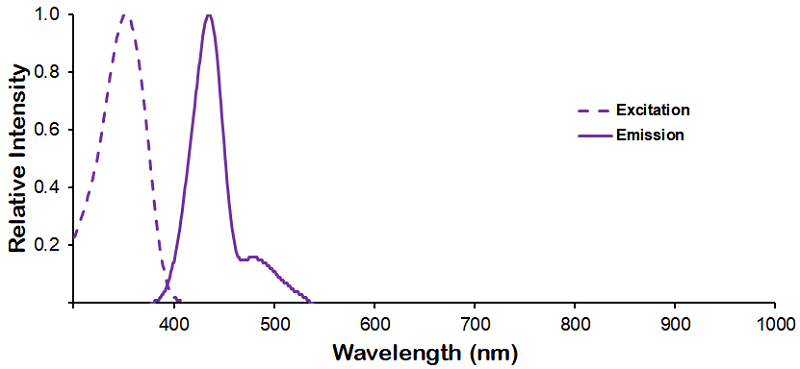
| R-PE (R-Phycoerythrin) | ||
| Overview: | 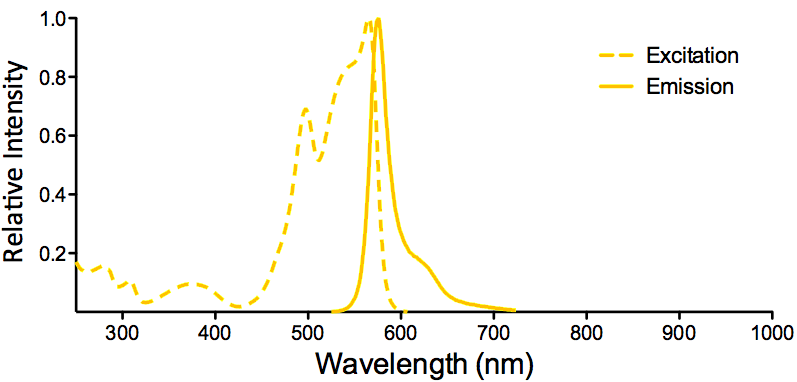 |
Optical Properties:
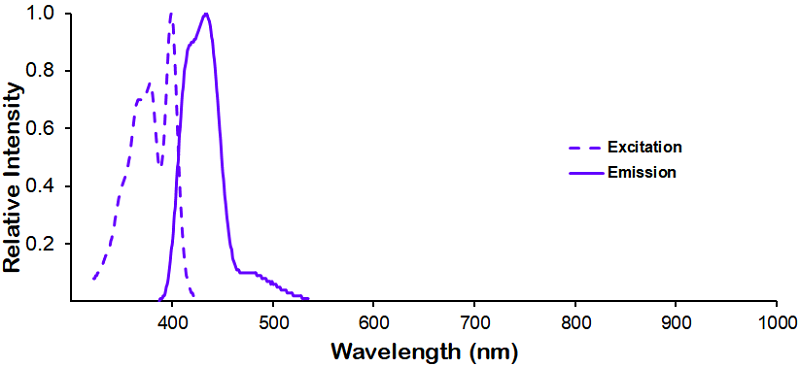
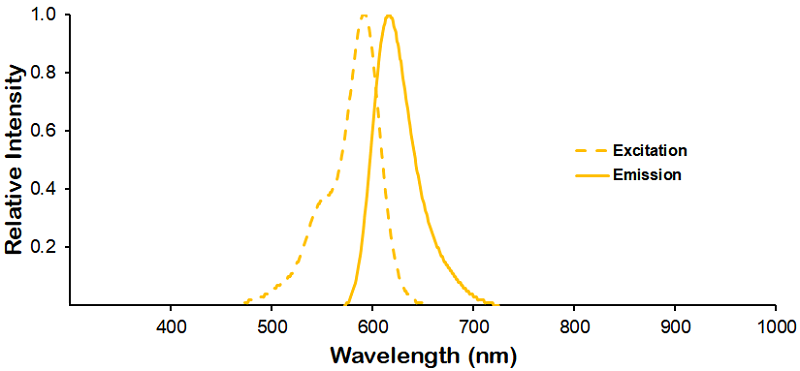
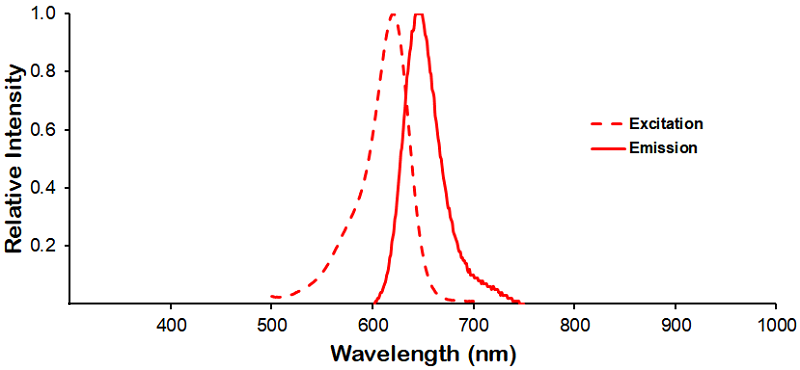
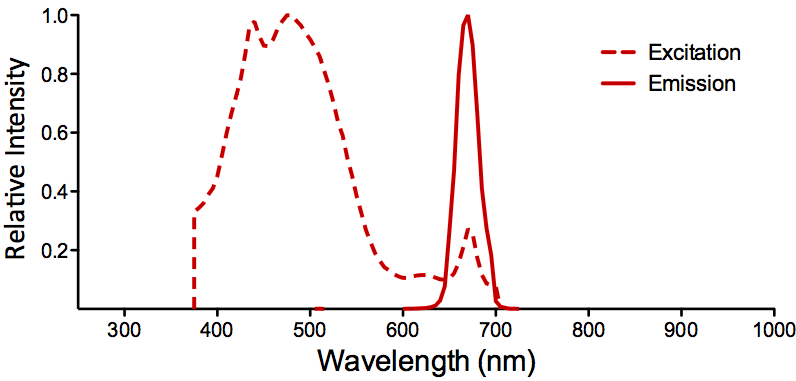
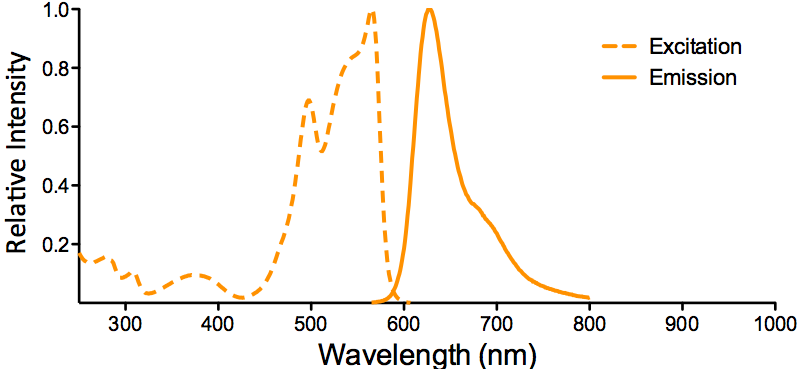
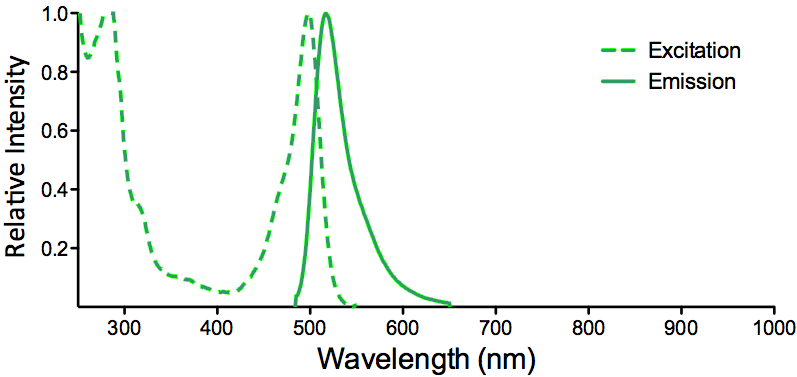
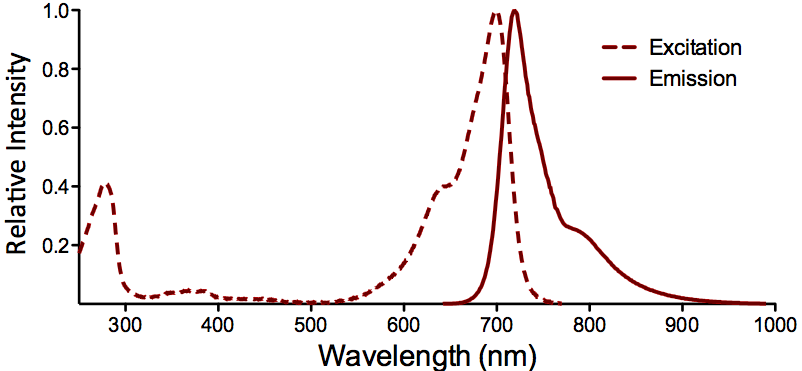
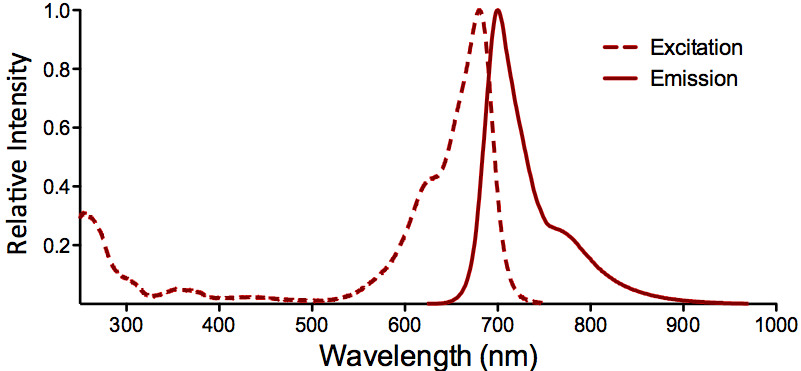
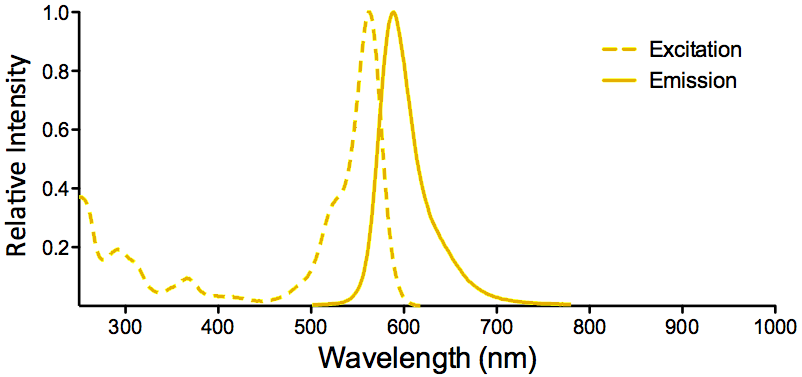
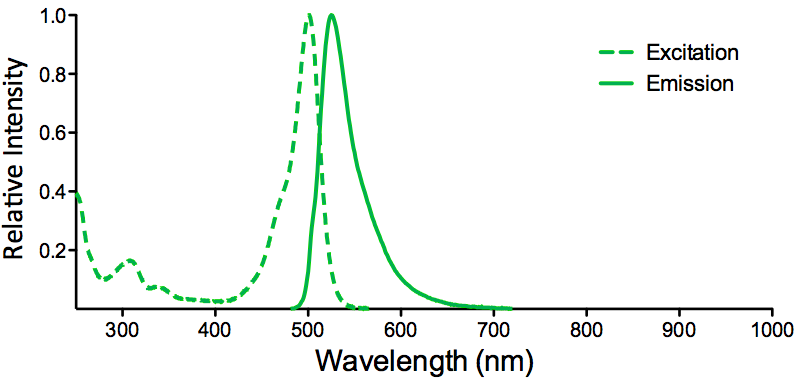
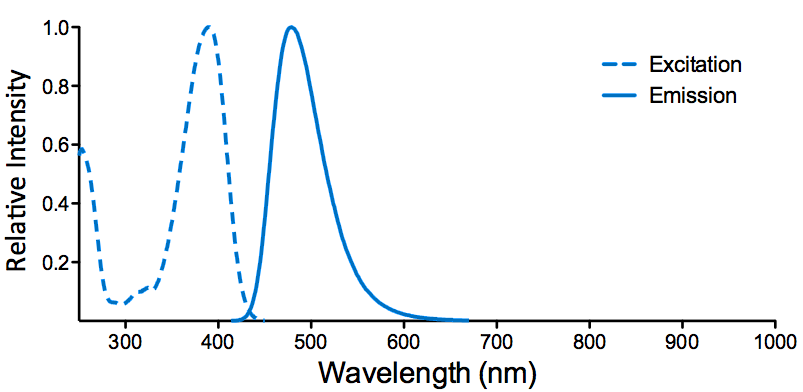
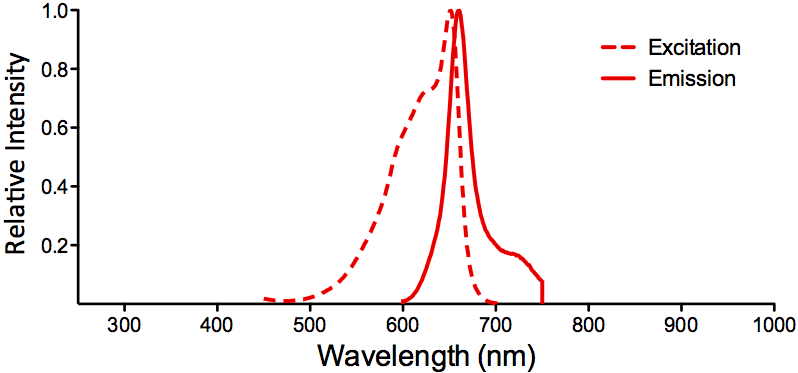
λex = 565 nm λem = 575 nm εmax = 2.0×106 Φf = 0.84 Brightness = 1.68 x 103 Laser = 488 to 561 nm Filter set = TRITC |
Properties
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH 7.4 |
| Storage Temperature | -80ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Dry Ice. Shipping note: Product will be shipped separately from other products purchased in the same order. |
| Purification | Ion-exchange Purified |
| Cite This Product | Human Recombinant A53T Alpha Synuclein Protein PFFs (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SPR-326) |
| Certificate of Analysis | Certified >95% pure using SDS-PAGE analysis. Low endotoxin <5 EU/mL @ 2mg/mL. |
| Other Relevant Information | For best results, sonicate immediately prior to use. Refer to the Neurodegenerative Protein Handling Instructions on our website, or the product datasheet for further information. Monomer source is catalog# SPR-325. |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | A53T mutant alpha synuclein, A53T mutated SNCA, A53T Alpha synuclein PFFs, Alpha synuclein PFF, Ala53thr mutant alpha synuclein, Alpha synuclein pre-formed fibrils, Alpha synuclein aggregates, Alpha synuclein protein aggregates, Alpha synuclein aggregates, Alpha-synuclein protein, Non-A beta component of AD amyloid protein, Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor protein, NACP protein, SNCA protein, NACP protein, PARK1 protein, SYN protein, Parkinson disease familial 1 Protein |
| Research Areas | Alzheimer's Disease, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience, Parkinson's Disease, Synuclein, Tangles & Tau, Multiple System Atrophy |
| Cellular Localization | Cytoplasm, Membrane, Nucleus |
| Accession Number | NP_000336.1 |
| Gene ID | 6622 |
| Swiss Prot | P37840 |
| Scientific Background | Alpha-Synuclein (SNCA) is expressed predominantly in the brain, where it is concentrated in presynaptic nerve terminals (1). Alpha-synuclein is highly expressed in the mitochondria of the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, striatum and thalamus (2). Functionally, it has been shown to significantly interact with tubulin (3), and may serve as a potential microtubule-associated protein. It has also been found to be essential for normal development of the cognitive functions; inactivation may lead to impaired spatial learning and working memory (4). SNCA fibrillar aggregates represent the major non A-beta component of Alzheimers disease amyloid plaque, and a major component of Lewy body inclusions, and Parkinson's disease. Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive accumulation in selected neurons of protein inclusions containing alpha-synuclein and ubiquitin (5, 6). The A53T mutation is a missense point mutation where alanine is replaced by threonine at the 53rd amino acid. This mutation has been linked to early-onset Parkinson's Disease (7) and increased rates of alpha synuclein fibrillization (8). |
| References |
1. “Genetics Home Reference: SNCA”. US National Library of Medicine. (2013). 2. Zhang L., et al. (2008) Brain Res. 1244: 40-52. 3. Alim M.A., et al. (2002) J Biol Chem. 277(3): 2112-2117. 4. Kokhan V.S., Afanasyeva M.A., Van'kin G. (2012) Behav. Brain. Res. 231(1): 226-230. 5. Spillantini M.G., et al. (1997) Nature. 388(6645): 839-840. 6. Mezey E., et al. (1998) Nat Med. 4(7): 755-757. 7. Polymeropoulos, M. H. (1998). Science. 276(5321), 2045–2047 8. Conway, K.E., et al. (1998). Nat Med. 4(11):1318-20 |
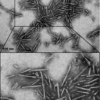
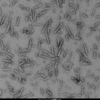
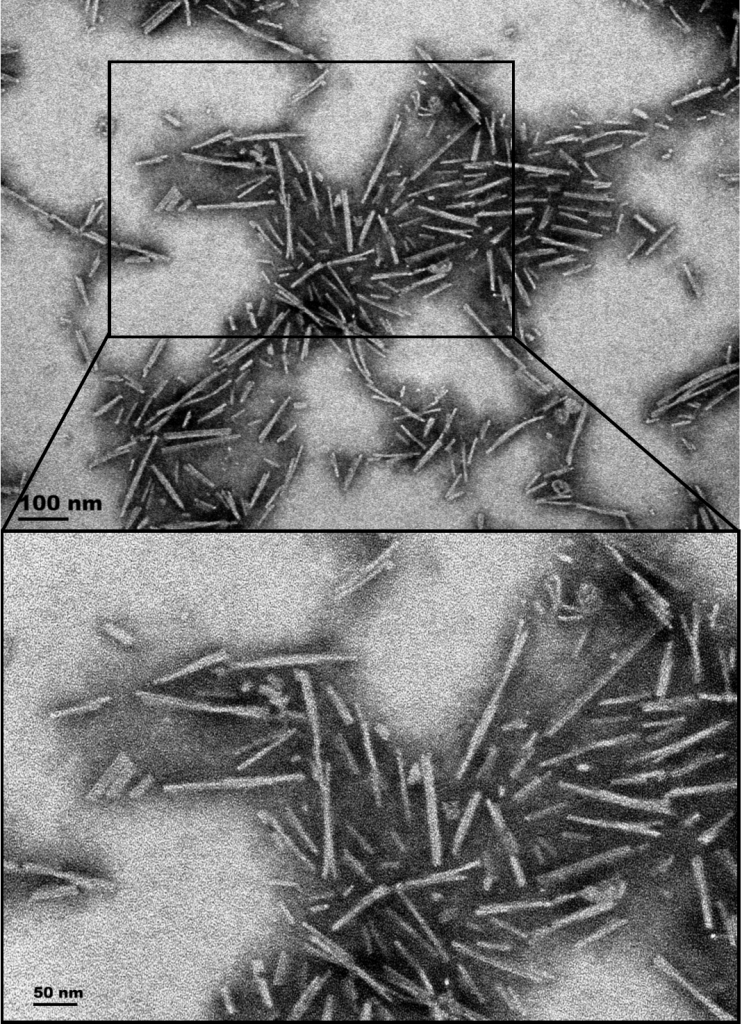
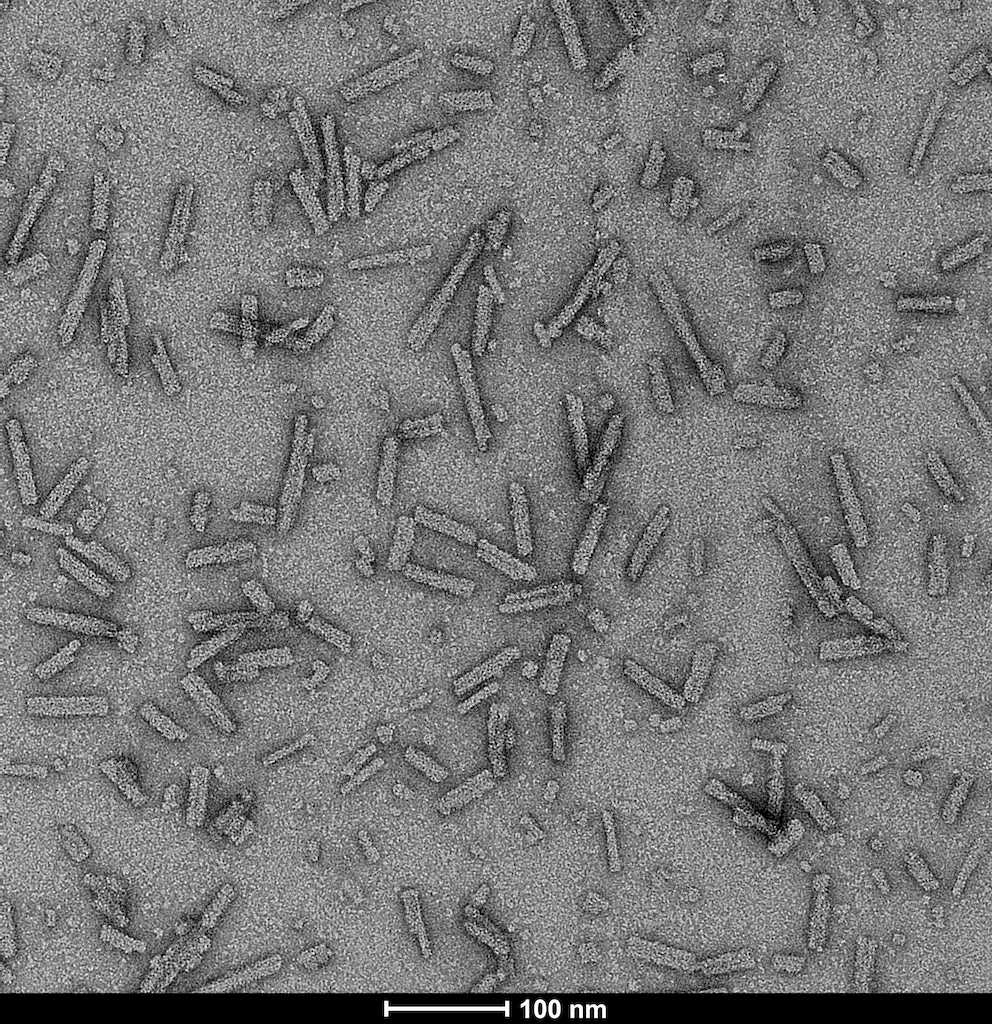
Product Images
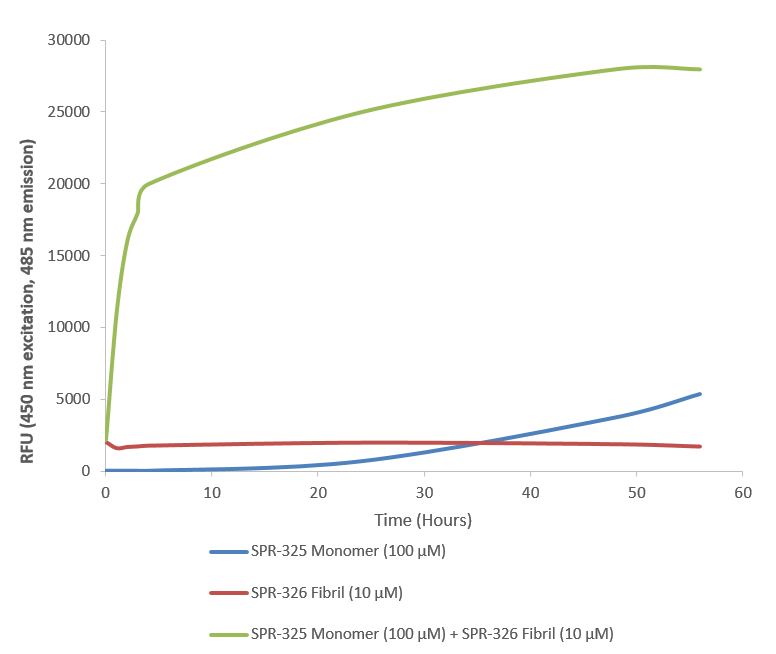
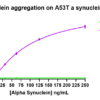
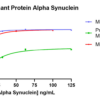
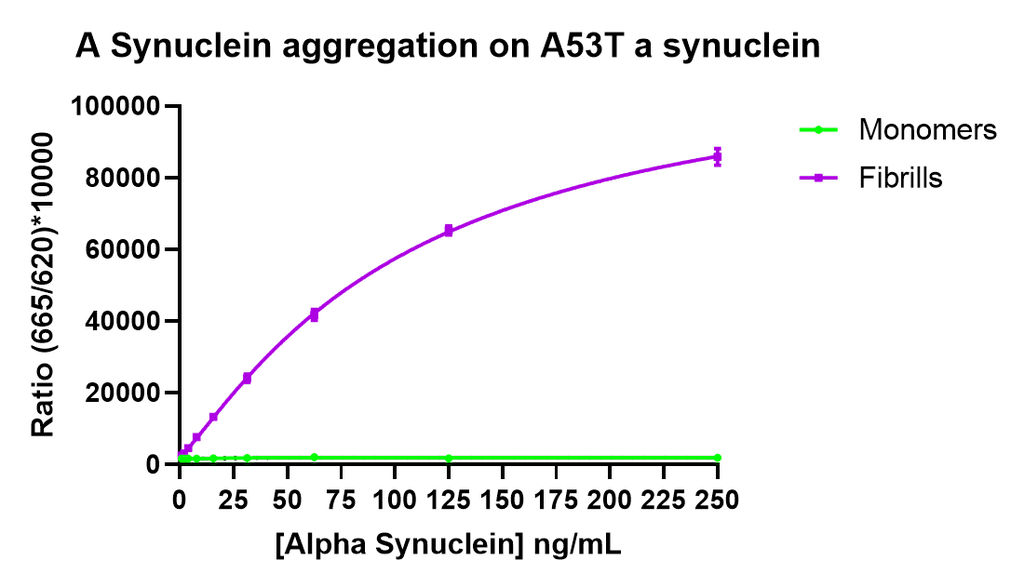
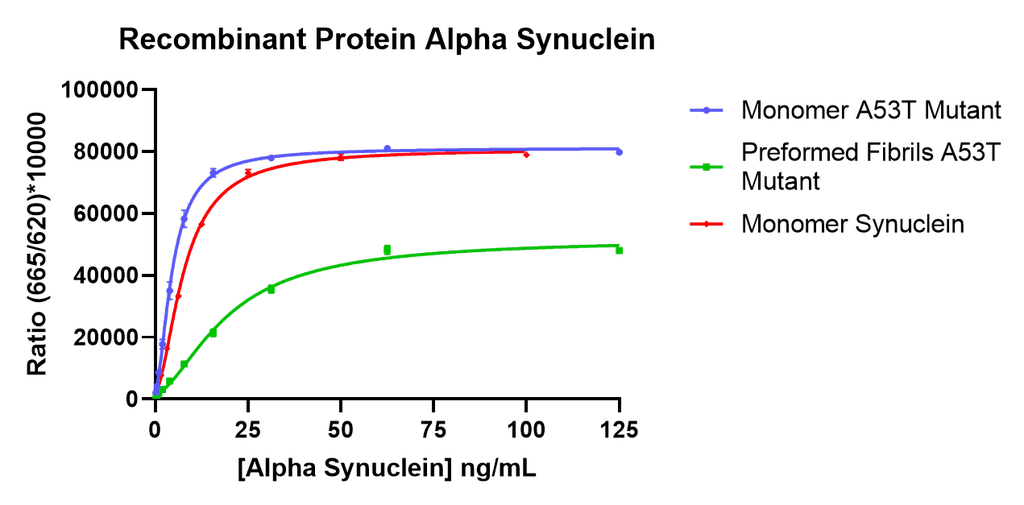
Thioflavin T is a fluorescent dye that binds to beta sheet-rich structures such as those in alpha synuclein fibrils. Upon binding, the emission spectrum of the dye experiences a red-shift and increased fluorescence intensity. Thioflavin T emission curves show a limited increase in fluorescence (correlated to alpha synuclein aggregation) over time in A53T alpha synuclein monomers (SPR-325). A much greater increase in fluorescence is seen when 100 µM monomer (SPR-325) is combined with 10 µM of fibrils (SPR-326) as the fibrils seed the formation of new fibrils from the pool of active monomers. Thioflavin T ex = 450 nm, em = 485 nm. Note: We use molecular weight of 14.46 kDa for both alpha synuclein monomer and fibril in calculations. We load 100µL/well for Thioflavin T assay so 100 µM is 144.6µg/well and 10 µM is 14.46 µg/well.
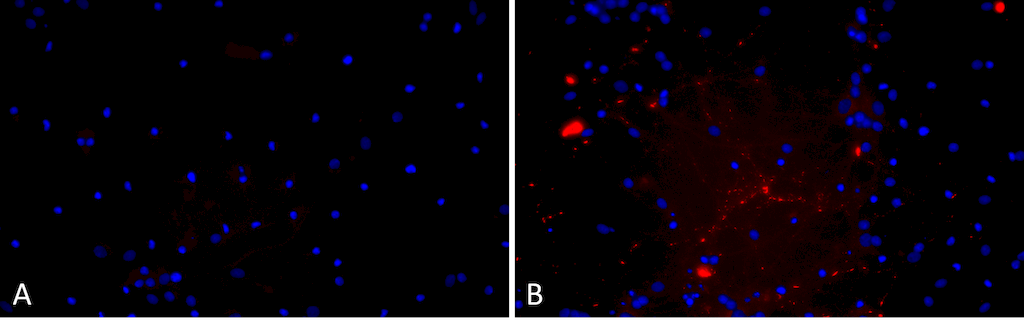
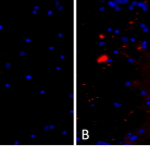
Primary rat hippocampal neurons show lewy body inclusion formation when treated with A53T mutant Alpha Synuclein Protein Pre-formed Fibrils (SPR-326) (B) but not when treated with a media control (A). Tissue: Primary hippocampal neurons. Species: Sprague-Dawley rat. Primary Antibody: Rabbit anti-pSer129 Antibody. Fibrils were diluted to 1 ug/uL in neuronal media consisting of B27, Glutamax, penicillin/strip, and neurobasalA and sonicated for 1 hour in a water bath. The sonicated stock was then used to achieve the final concentration of 1 ug/mL in the wells.
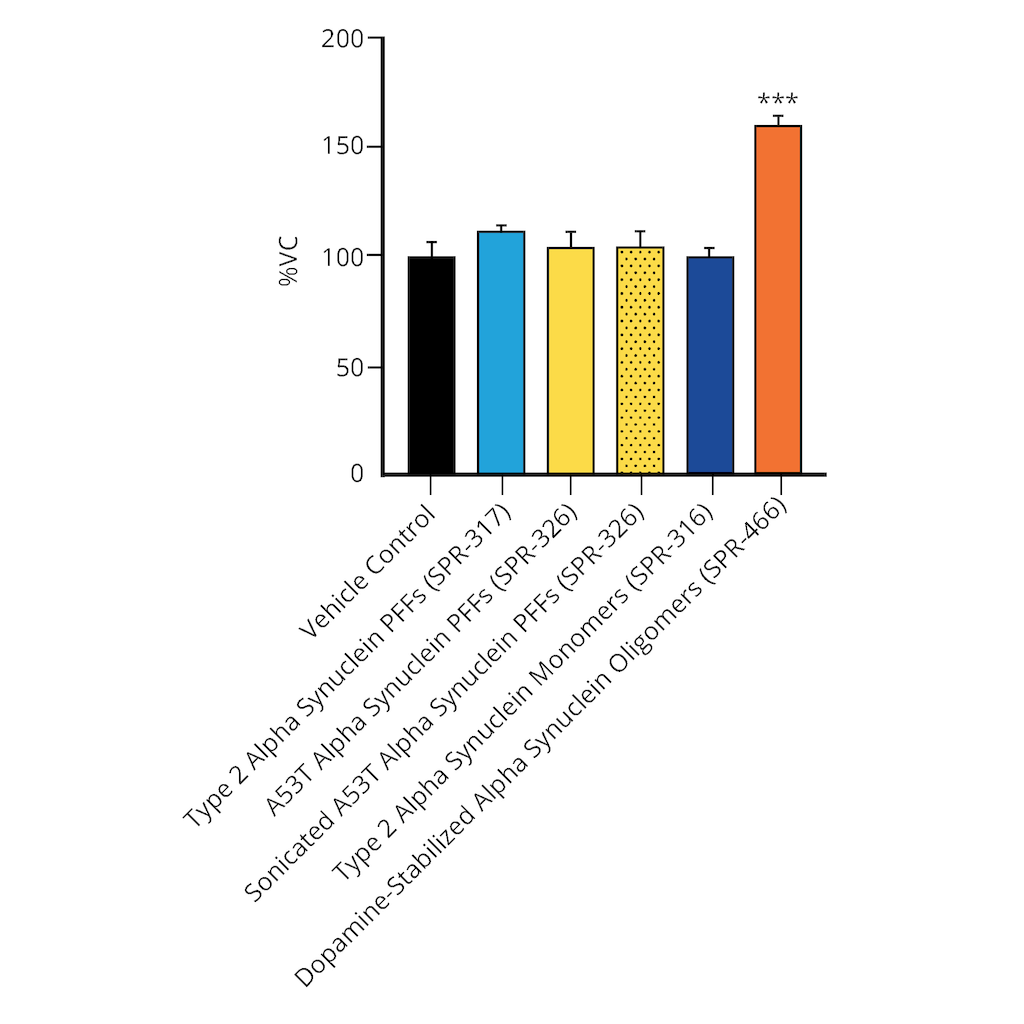
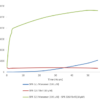
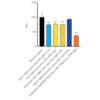
Evaluation of a-syn toxicity on primary mouse cortical neurons. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is a soluble enzyme present in the cytosol that is released upon cell death. Toxicity was assessed with an LDH assay and displayed as % of vehicle control (VC). Data are presented as bar graphs and standard deviation. For statistical analysis One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test (vs VC) was used. *** p<0.001. Treatment with A53T PFFs (sonicated or unsonicated) did not significantly impact LDH release. Data courtesy of QPS.
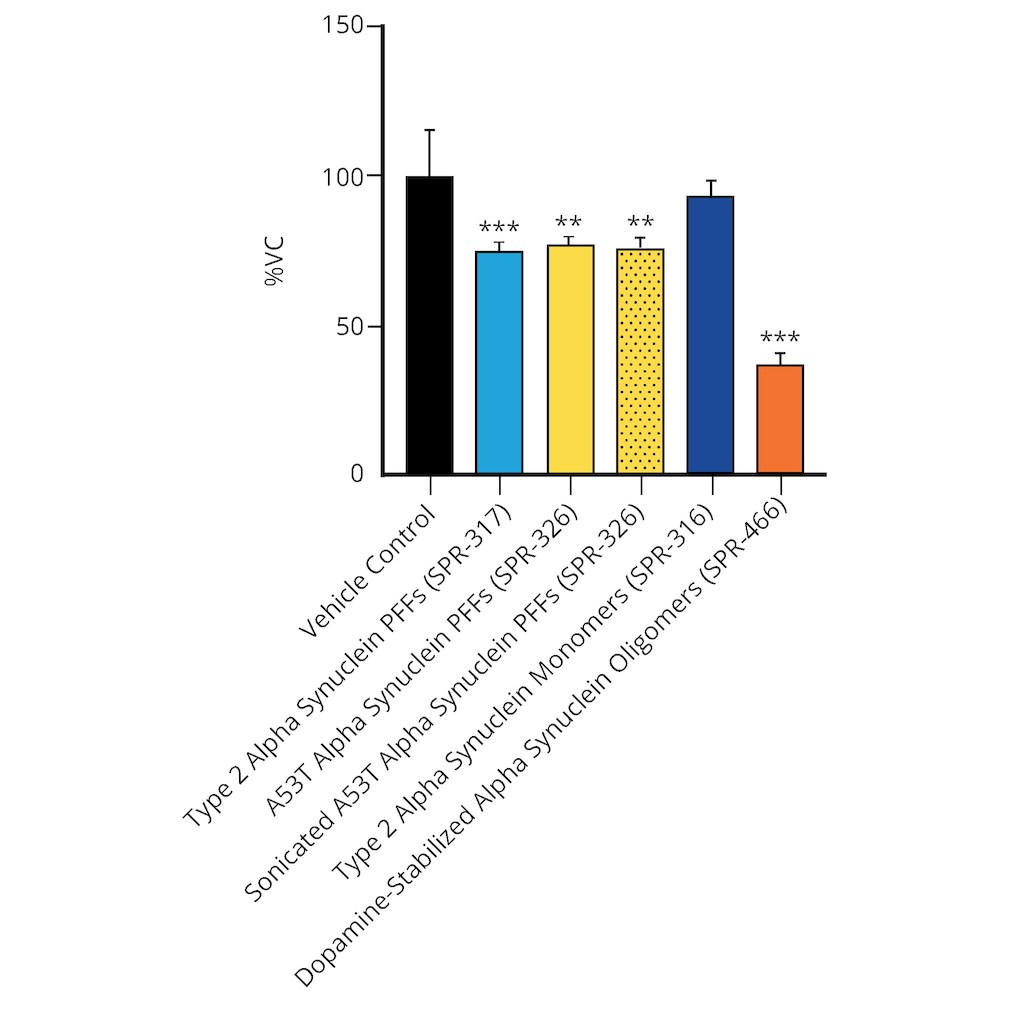
Evaluation of a-syn toxicity on primary mouse cortical neurons. Mitochondrial dehydrogenase activity reduces yellow MTT to dark blue formazan crystals, a reaction catalyzed in living cells. Cell viability was assessed with an MTT assay and displayed as % of vehicle control (VC). Data are presented as bar graphs and standard deviation. For statistical analysis One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test (vs VC) was used. ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. Treatment with A53T alpha synuclein PFFs (sonicated and unsonicated) reduced cell viability (p<0.01). Data courtesy of QPS.

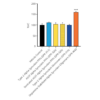
StressMarq Biosciences :
Based on validation through cited publications.