| Product Name | Dihydroceramide |
| Description |
Autophagy inducer |
| Purity | >98% |
| CAS No. | 13031-64-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C20H41NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 343.54 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inducer |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol (5 mg/ml) or DMSO (5 mg/ml: dissolve in hot DMSO, then cool to RT). |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White solid. |
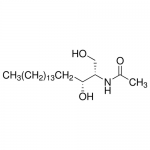
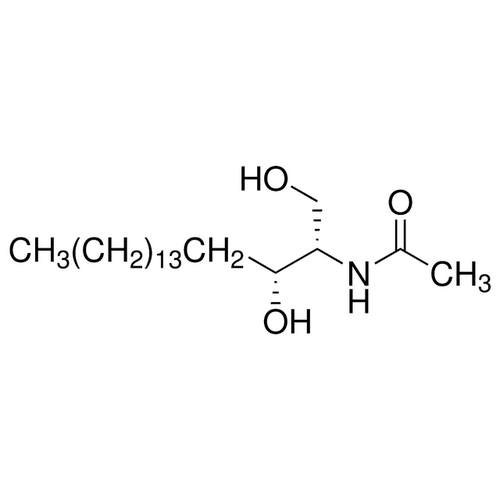
| SMILES | [C@@H](NC(=O)C)([C@H](O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)CO |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C20H41NO3/c1-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-20(24)19(17-22)21-18(2)23/h19-20,22,24H,3-17H2,1-2H3,(H,21,23)/t19-,20+/m0/s1 |
| InChIKey | CRJGESKKUOMBCT-VQTJNVASSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Not WHMIS controlled. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust. S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. |
| Cite This Product | Dihydroceramide (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-398) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | C2 Dihydroceramide, D-erythro-N-Acetylsphinganine |
| Research Areas | Autophagy, Cancer |
| PubChem ID | 6610273 |
| Scientific Background | Both in yeast and mammalian systems, dihydroceramide is the reaction intermediate found immediately prior to the final reaction product in the de novo synthesis of ceramide lipids. Recent studies have revealed that an accumulation of dihydroceramide will induce autophagy. Accumulation of dihydroceramide occurs due to inhibition of dihydroceramide desaturase, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of dihydroceramide into ceramide. |
| References |
1. Gagliostro, V. et al. (2012). Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 44(12): 2135-43. 2. Jiang, Q. et al. (2012). Int J Cancer, 130(3): 685-93. 3. Signorelli, P. et al. (2009). Cancer Lett, 282(2): 238-43. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.