| Product Name | Mycophenolate mofetil |
| Description |
Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% (TLC); NMR (Conforms) |
| CAS No. | 128794-94-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C23H31NO7 |
| Molecular Weight | 433.5 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | May be dissolved in DMSO (40 mg/ml); or ethanol (4 mg/ml) |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White powder |
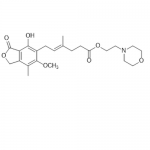
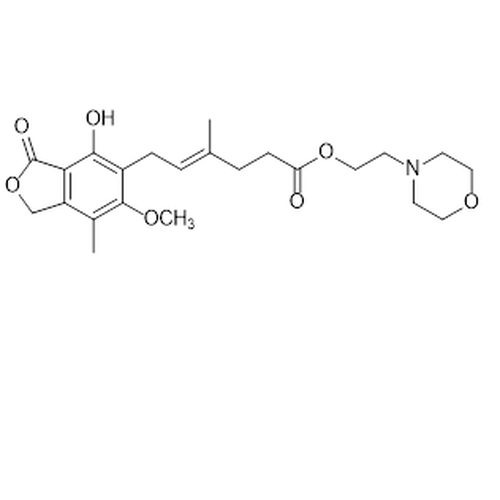
| SMILES | C/C(=CCc1c(c2c(COC2=O)c(C)c1OC)O)/CCC(=O)OCCN1CCOCC1 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C23H31NO7/c1-15(5-7-19(25)30-13-10-24-8-11-29-12-9-24)4-6-17-21(26)20-18(14-31-23(20)27)16(2)22(17)28-3/h4,26H,5-14H2,1-3H3/b15-4+ |
| InChIKey | RTGDFNSFWBGLEC-SYZQJQIISA-N |
| Safety Phrases | GHS Classifcation: GHS07 Acute toxicity (oral, dermal, inhalation), category 4, Skin irritation, category 2, Eye irritation, category 2, Skin sensitisation, category 1, Specific Target Organ Toxicity – Single exposure, category 3 AND GHSO9 Hazardous to the aquatic environment, Acute hazard, category1, Chronic hazard, categories 1,2 Hazard statement(s): H302-H400 Precautionary statement(s): P273 |
| Cite This Product | Mycophenolate mofetil (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-568) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 6-(1,3-Dihydro-4-hydroxy-6-methoxy-7-methyl-3-oxo-5-isobenzofuranyl)-4-methyl-4-hexenoic acid 2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl ester |
| Research Areas | Adaptive Immunity, Astrocyte Markers, Autoimmune, B Cells, Cell Markers, Glial Markers, Immunology, Microglia Markers, Neuroscience |
| PubChem ID | 5281078 |
| Scientific Background | Mycophenolate mofetil is an immunosuppressive agent useful in prevention of organ allograft rejection (1). It is metabolized to mycophenolic acid in vivo, which acts by inhibiting the biosynthesis of guanine nucleotides via inhibition of inosine 5’-monophosphate dehydrogenase, suppressing the production of proinflammatory cytokines, nitric oxide and LDH in macrophages (2,3). It also inhibits IL-2-dependent T cell proliferation (4), and microglial and astrocytic activation reducing cell death after neuronal injury (5). It also prevents neuroinflammation. |
| References |
1. Allison A.C., and Eugui, E.M. (1996) Clin. Transplant. 10:77. 2. Jonsson C.A., et al., (2002) Cell. Immunol. 216:93. 3. Allison A.C., et al., (1993) Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 696:63. 4. Quemeneur J., et al., (2002) J. Immunol. 169:2747 5. Ebrahimi F., et al., (2012) J. Neuroinflammation 9:89. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.