| Product Name | MCC-950 |
| Description |
NLRP3 inflammasome activation inhibitor |
| Purity | >98% (HPLC); NMR (conforms) |
| CAS No. | 256373-96-3 |
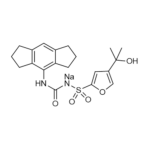
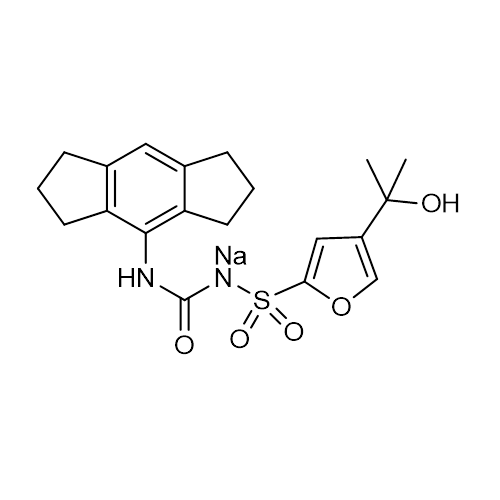
| Molecular Formula | C20H23N2O5S ∙ Na |
| Molecular Weight | 426.5 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | May be dissolved in water (30 mg/ml): or DMSO (40 mg/ml) |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | White powder |
| SMILES | COC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC(=O)NC2=CC(=CC=C2)O |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C15H15NO3/c1-19-14-7-5-11(6-8-14)9-15(18)16-12-3-2-4-13(17)10-12/h2-8,10,17H,9H2,1H3,(H,16,18) |
| InChIKey | OTXSEOHBMQFDBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Caution: Not a hazardous substance or mixture. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection |
| Cite This Product | MCC-950 (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-604) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | N-[[(1,2,3,5,6,7-Hexahydro-s-indacen-4-yl)amino]carbonyl]-4-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)-2-furansulfonamide sodium salt; CRID3; CP-456773 sodium salt |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Cell Signaling, Growth Factors, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience, Parkinson's Disease, Synuclein, TNF |
| PubChem ID | 1234617 |
| Scientific Background | MCC950 was originally found to act as a cytokine release inhibitory drug (CRID), arresting activated monocytes and preventing activation of caspase-1(1). Discovered to be a novel inhibitor of the NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasomes(2). Blocks canonical and noncanonical NLRP3 activation at nanomolar concentrations3. Inhibits interleukin 1β (IL-1β) secretion in vivo and attenuates the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (an MS disease model)(3). Disrupts the interaction between AIM2 and ASC in a reconstituted cell-free inflammasome(4). A valuable new tool for exploring the pathophysiology of NLRP3. It may contribute to additional alpha synuclein aggregation and cell loss in PD (5). |
| References |
1. Laliberte R.E. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278(19):16567-78. 2. Coll R.C., et al. (2011) PLoS One. 6(12):e29539. 3. Coll R.C., et al. (2015) Nat. Med. 21(3):248-255. 4. Kaneko N., et al. (2015) J. Immunol. Methods. 426:76-81. 5. Nguyen L., et al. (2022) J Parkinsons Dis. 12(7): 2117-2133. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.