| Product Name | Tranilast |
| Description |
Angiogenesis inhibitor |
| Purity | >95% (HPLC) |
| CAS No. | 53902-12-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C18H17NO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 327.33 |
| Field of Use | Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For in vitro research use only. |
Properties
| Storage Temperature | -20ºC |
| Shipping Temperature | Shipped Ambient |
| Product Type | Inhibitor |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO. |
| Source | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Off-white to yellow powder. |
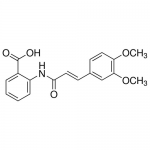
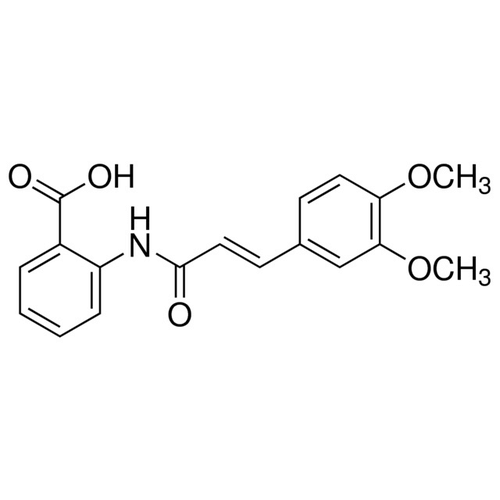
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)/C=C/C(=O)NC2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)O)OC |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C18H17NO5/c1-23-15-9-7-12(11-16(15)24-2)8-10-17(20)19-14-6-4-3-5-13(14)18(21)22/h3-11H,1-2H3,(H,19,20)(H,21,22)/b10-8+ |
| InChIKey | NZHGWWWHIYHZNX-CSKARUKUSA-N |
| Safety Phrases |
Classification: Caution: Substance not yet fully tested. Safety Phrases: S22 - Do not breathe dust S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection Hazard Phrases: H302 – Harmful if swallowed. H312 – Harmful in contact with skin. H332 – Harmful if inhaled. Precautionary Phrases: P261 – Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray P280 – Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+ P312 IF SWALLOWED: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician if you feel unwell. P304+P340 – IF INHALED: remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P501 – Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local/regional/national/ international regulations. |
| Cite This Product | Tranilast (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SIH-369) |
Biological Description
| Alternative Names | 2-{[(2E)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2- enoyl]amino}benzoic acid |
| Research Areas | Cancer, Cardiovascular System, Cell Signaling, Neuroscience |
| PubChem ID | 5282230 |
| Scientific Background | Tranilast is an antiallergic, antifibrotic drug that inhibits collagen synthesis, when administered in a dose –dependent manner for a 48 h treatment (1). As an antifibrotic agent, studies shown an effect on the growth of metastasis of mammary carcinoma. It is associated with the inhibition of the growth factor –beta. (TGF-beta) (2). |
| References |
1. Yamada H., Tajima S., Nishikawa T., Murad S., and Pinnell S., (1999) The Journal of Biochemistrystry. 116(4): 892-897. 2. Chakrabarti R., Subramanian V., Abadalla J., Jothy S., Predhomme GJ. (2009) Anticancer Drugs. 20(5): 334-45. |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.