Multiple System Atrophy (MSA)
What is Multiple System Atrophy?
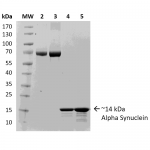
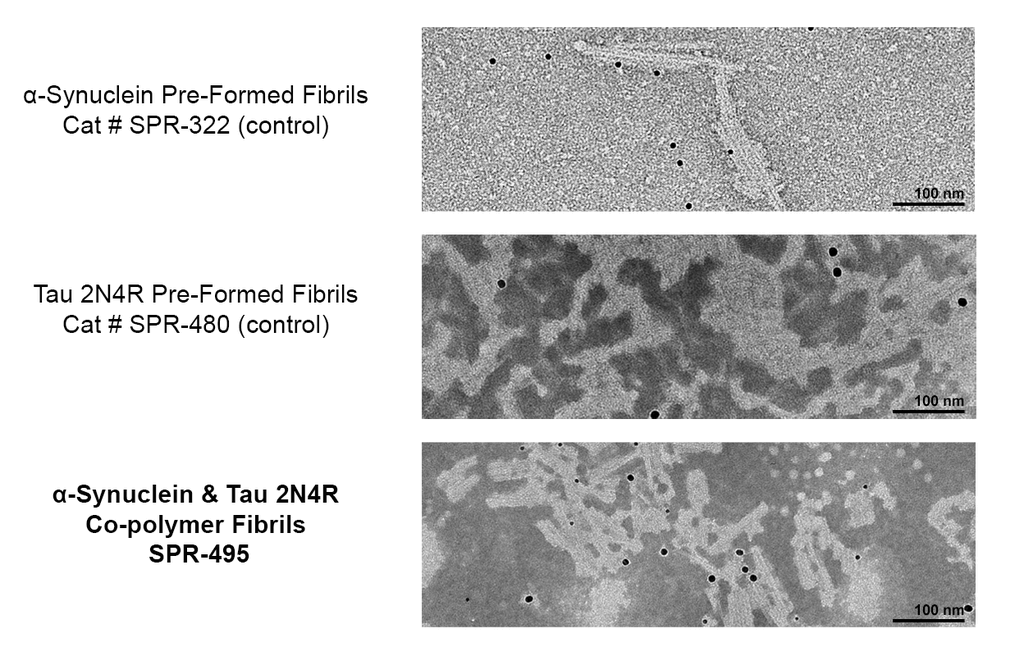
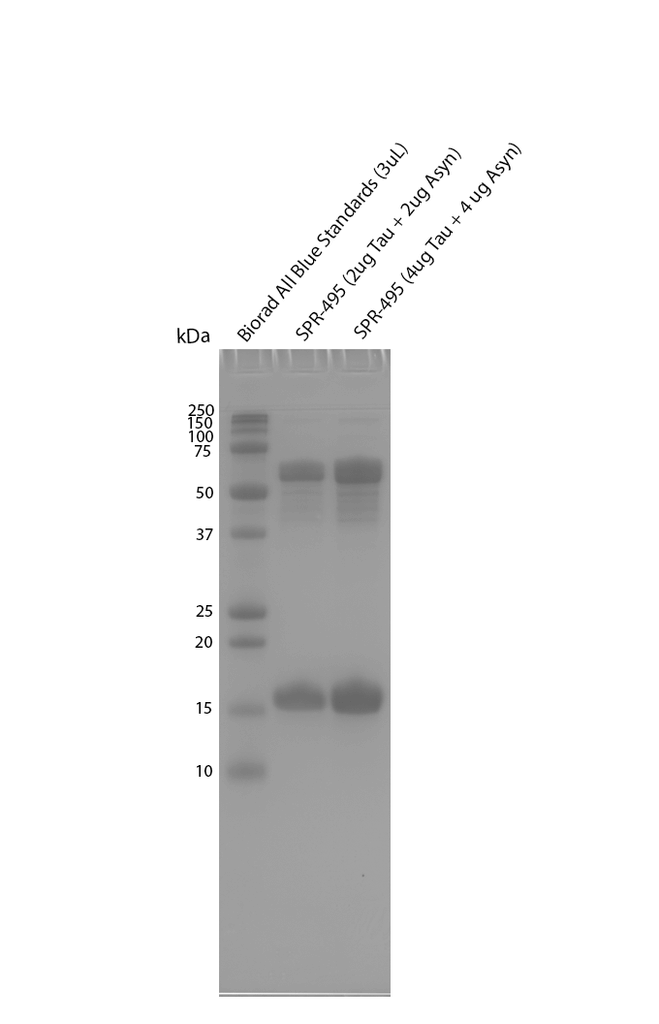
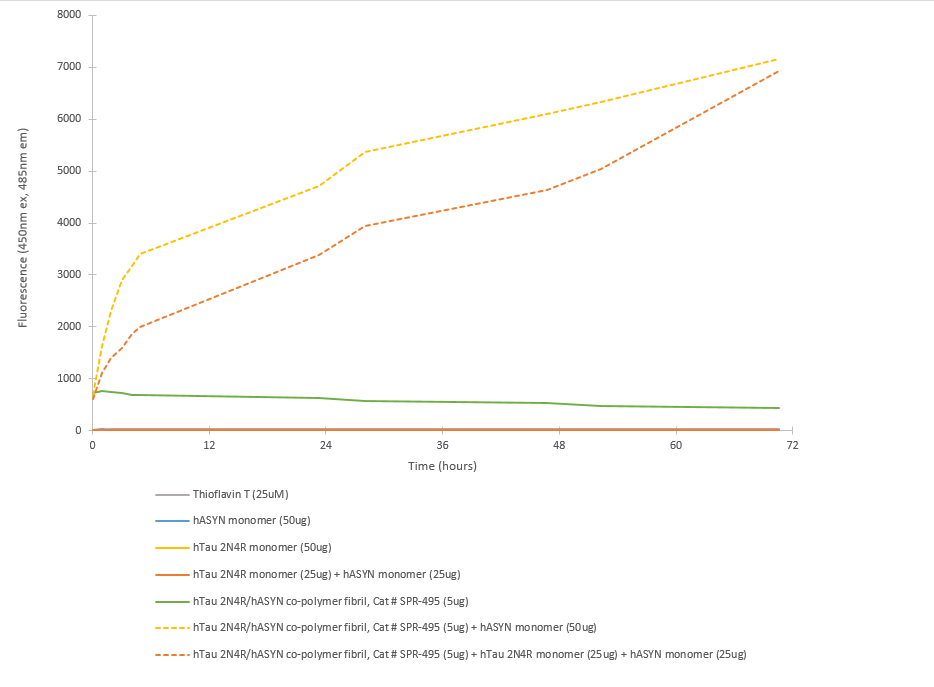
Multiple System Atrophy (MSA) is a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative disease belonging to the family of amyloid related diseases. MSA is defined by the misfolding and accumulation of amyloid alpha synuclein deposits in oligodendrocytes, to form Glial Cytoplasmic Inclusions (GCIs).
MSA was originally defined by parkinsonian features with a poor response to Levodopa, (when generally PD patients show good Levodopa responses), in the early disease stages, and cerebellar ataxia in combination with autonomic dysfunctions such as orthostatic hypotension or autonomic urinary abnormalities. There are currently no therapies available for MSA patients that address the root cause of the disease.
The identification of alpha synuclein in the GCIs of MSA patients’ oligodendrocytes was complemented with the identification of alpha synuclein accumulation in the Lewy Bodies present in patients suffering Parkinson’s Disease with Dementia (PDD) or Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB). These discoveries resulted in the classification of PD, PDD, DLB, and MSA as synucleinopathies, all defined by the accumulation of the alpha synuclein aggregates.
VIEW ALL MULTIPLE SYSTEM ATROPHY PRODUCTS
![Mouse Anti-LRRK2/Dardarin Antibody [N138/6] used in Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence (ICC/IF) on Human Neuroblastoma cell line (SK-N-BE) (SMC-446)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-446_LRRK2-Dardarin_Antibody_N138-6_ICC-IF_Human_Neuroblastoma-cell-line-SK-N-BE_60X_Composite-1.png)
![Mouse Anti-LRRK2/Dardarin Antibody [N138/6] used in Western Blot (WB) on Rat Brain Membrane (SMC-446)](https://www.stressmarq.com/wp-content/uploads/SMC-446_LRRK2-Dardarin_Antibody_N138-6_WB_Rat_Brain-Membrane_1.png)