Tau Fibrillar and Oligomeric Constructs
This is an updated version of a previously published article.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a very complex neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by the extracellular deposition of amyloid plaques and the intracellular accumulation of insoluble tau neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in the brain. Tau protein is implicated in AD progression, where tau hyper-phosphorylation and aggregation leads to the formation of NFTs, and ultimately to neuronal dysfunction and death. Alzheimer’s disease currently has no cure, however, scientists worldwide are currently focused on generating novel cellular and animal disease models that reproduce tau aggregation to assist in developing new therapeutic interventions.
StressMarq Biosciences offers a wide range of monomeric, filamentous and fibrillar tau constructs for AD research. These fibrillar preparations can be used to induce tau pathology and develop disease models.
Tau Monomers
Tau protein is primarily located in the axons of neurons and stabilizes microtubules. It has a natively unfolded structure and is highly soluble. Monomeric tau has a molecular weight of about 46 kDa and exists in different isoforms which are generated by alternative splicing of the tau gene. However, under certain pathological conditions, tau may undergo post-translational modifications such as hyper-phosphorylation. This process leads to the formation of larger, insoluble structures that are toxic to neurons. See our tau page for a complete list of tau monomers offered by StressMarq.
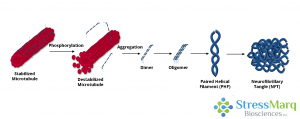
Tau dissociates from microtubules, leading to their destabilization. It then aggregates into oligomers, paired helical filaments, and ultimately neurofibrillary tangles.
Tau Paired Helical Filaments (PHFs) & Neurofibrillary Tangles (NFTs)
In Alzheimer’s disease tau hyper-phosphorylation results in the transformation of normal tau into paired helical filaments and neurofibrillary tangles. PHFs are soluble with a twisted double-helical structure. Tau found in the PHF conformation is more negatively charged than monomeric tau which affects its binding to microtubules and promotes the neurodegenerative process.
NFTs, a major hallmark of AD, are composed of PHFs. These filamentous, insoluble aggregates of tau have an increased beta sheet structure consisting of aggregated PHFs and may be toxic to cells.
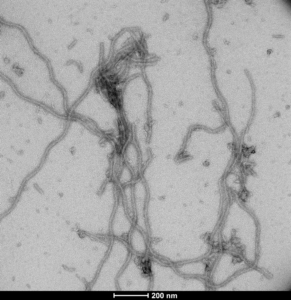
Human Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant Filaments: These tau filaments are soluble with a duplex twisted structure closely resembling brain-derived paired helical filaments. They do not appear to seed tau monomers and are fibrilized with a linear anionic scaffold (t-RNA).
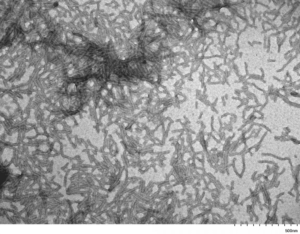
TEM of Human Recombinant Tau Protein Filaments (catalog# SPR-463)
Tau Pre-formed Fibrils (PFFs)
Tau pre-formed fibrils are formed through the polymerization of soluble tau monomers into insoluble fibrils. Tau PFFs induce endogenous tau phosphorylation and aggregation and can be used as tools to generate disease models that mimic Alzheimer’s pathophysiology. Injecting tau PFFs into animals generates tau pathology in a short period compared to transgenic models.
StressMarq offers several types of tau PFFs that can be used in Alzheimer’s disease research:
Escherichia coli-expressed Tau Pre-formed Fibrils
Human Tau-441 (2N4R) Wild-Type: A full length isoform of wild-type tau protein, using heparin as an induction scaffold. The PFFs are able to seed aggregation of monomers.
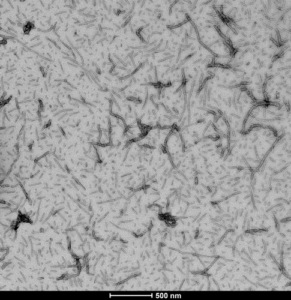
TEM of Human Recombinant Tau-441 (2N4R), Wild-Type PFFs (catalog# SPR-480)
Human Tau-441 P301S & Mouse Tau-430 P290S Mutants: A full-length isoform with a P301S mutation for the human tau and P290S for the mouse tau. Heparin has been used as an induction scaffold. Human and mouse tau PFFs are capable of seeding monomers and can induce tau aggregation.

TEM of Human Recombinant Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant PFFs (catalog# SPR-329).
Human Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant conjugated to ATTO 488 dye: Tau-441 PFFs can be conjugated to fluorescent dyes and tracked in vitro. ATTO 488-conjugated tau PFFs exhibit enhanced seeding compared to unconjugated fibrils.
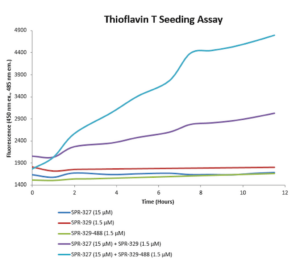
Thioflavin T seeding assay of ATTO 488-conjugated tau PFFs (catalog# SPR-329-A488).
Human Tau (K18) P301L Mutant: K18 is a truncated form of human tau containing 4 microtubule binding repeats. The P301L mutation has been linked to frontotemporal dementia. Heparin is used as an induction scaffold. P301L transgenic mice injected with StressMarq’s Tau (K18) P301L mutant PFFs show seeding of tau pathology at injection site nine weeks post-injection.
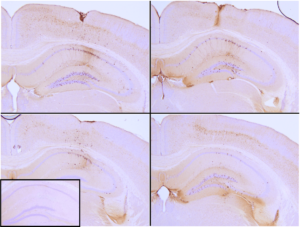
Immunohistochemistry analysis of P301L mouse hippocampus injected with Human Recombinant Tau (K18) P301L Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-330).
Human Tau (K18) Delta K280 Mutant: The K280 deletion mutation is linked with frontotemporal dementia and promotes fibrillization into paired helical filaments (PHFs) without using heparin or other inducers.
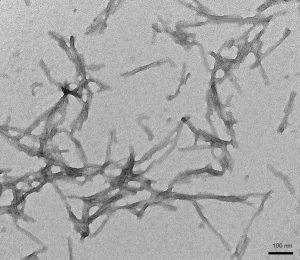
TEM of Human Recombinant Tau (K18) Delta K280 Mutant Pre-formed Fibrils (catalog# SPR-477).
Human Tau dGAE (AA297-391) AD-mimic: These AD-mimic PFFs are purified and fibrilized under these exact published conditions that replicate the disease-isolated AD-fold (Lovestam al. 2022. eLife).
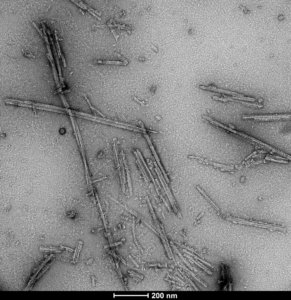
TEM of Human Recombinant Tau dGAE (AA297-331) AD-mimic PFFs (catalog# SPR-502).
Human Truncated Tau dGAE (AA297-391): Truncated tau (AA297-391) is the main component of paired helical filaments (PHFs) in neurofibrillary tangles isolated from AD brain tissue. This tau fragment has been shown to assemble into PHF-like fibrils in vitro in the absence of any inducer like heparin.
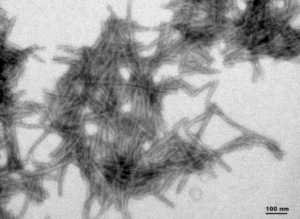
TEM of Human Recombinant Truncated Tau Fragment (AA297-391) (dGAE) PFFs (catalog# SPR-461)
Human Truncated Tau dGAE (AA297-391) C322A Mutant: The C322A mutation of the dGAE tau leads to enhanced self-assembly into long and ordered PHFs. This also does not require a scaffold and shows effective seeding in vitro.
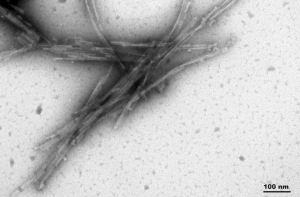
TEM of Human Recombinant Truncated Tau (AA297-391) (dGAE C322A) PFFs (catalog# SPR-462)
Human Tau-352 (fetal 0N3R) Wild-Type: The shortest isoform of tau, 0N3R, is expressed in the fetal human brain during neurogenesis and it has been shown to be more prone to form oligomers in vitro. The β-sheet core of Tau 0N3R fibrilized using heparin differs from all other tau fibril structures known to date.
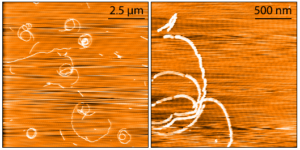
AFM images of Human Recombinant Tau-352 (fetal 0N3R) Wild-Type PFFs (catalog# SPR-491).
Human Wild-Type Tau-381 (1N3R), Tau-383 (0N4R) and Tau-412 (1N4R): Tau-381, Tau-383, and Tau-412 are 3 out of the 6 tau isoforms found in the adult human brain. These isoforms are generated through alternative splicing of the MAPT (microtubule-associated protein tau) gene. In neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, abnormal accumulation and aggregation of tau isoforms contribute to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles. NMR data indicates that both 3R and 4R tau are incorporated into AD-tau seeded fibrils. These tau constructs require heparin as a fibrillization scaffold.
Baculovirus/Sf9-expressed Tau Pre-formed Fibrils and Oligomers
StressMarq offers certain Tau PFFs and oligomers expressed in baculovirus. Baculovirus tau constructs are post-translationally modified and fibrillize without a scaffold. For more information on baculovirus expression, see our blog post Tau Post-Translational Modifications: An Overview of the Baculovirus Expression Vector System.
Human Tau-441 (2N4R) Wild-Type PFFs and Oligomers : These tau constructs are hyper-phosphorylated and are formed without the use of heparin or another anionic scaffold. Mass spectrometry analysis has revealed up to 20 phosphorylation sites. Tau 2N4R oligomers and fibrils show a dose-dependent toxicity to primary rat hippocampal neurons.
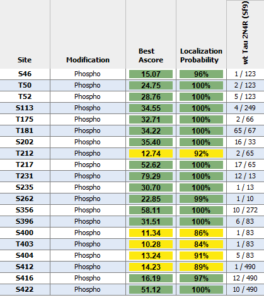
Mass spectrometry analysis of Human Recombinant Tau-441 (2N4R) Wild-Type PFFs (Baculovirus/Sf9) (catalog# SPR-498).
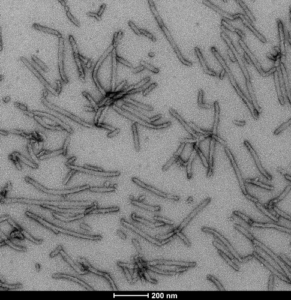
TEM image of Human Recombinant Tau-441 (2N4R) Wild-Type PFFs (Baculovirus/Sf9) (catalog# SPR-498).
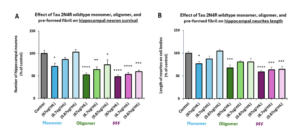
Tau 2N4R oligomers (catalog# SPR-497) and fibrils (catalog# SPR-498) show a dose-dependent toxicity to primary rat hippocampal neurons, but not monomers (catalog# SPR-496).
Human Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant PFFs: A hyper-phosphorylated tau P301S mutant with up to 38 phosphorylation sites according to mass spectrometry analysis. No scaffold is required for fibrillization.
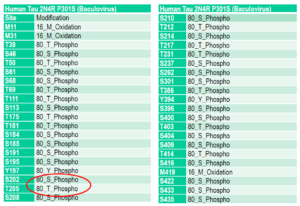
Mass spectrometry analysis of Human Recombinant Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant PFFs (Baculovirus/Sf9) (catalog# SPR-471).

TEM image of Human Recombinant Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant PFFs (Baculovirus/Sf9) (catalog# SPR-471).
Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells- expressed Tau PFFs
Human Tau- 441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant (N-glycosylated): CHO expression in mammalian cell line may lead to more “human” like phosphorylation/glycosylation patterns. N-glycosylated tau has been identified in human AD-diseased brains, but not healthy brains, and may precede tau hyperphosphorylation. Our CHO-expressed Tau 2N4R P301S will readily form fibrils in the absence of heparin and contains mammalian post-translational modifications that may better mimic tau in human AD-brains.
TEM of CHO-expressed Human Tau-441 (2N4R) P301S Mutant PFFs (catalog# SPR-516)
Alpha Synuclein and Tau Co-Polymer Fibrils (Mixed Fibrils/PFFs)
StressMarq’s co-polymer fibrils are developed by co-incubating monomers together to form fibrils that contain both tau and alpha synuclein proteins within a single fibril. Recombinant tau and alpha synuclein co-polymer fibrils have demonstrated a more widespread transmission of induced pathology in a rodent model of tauopathies compared to pure tau or alpha synuclein fibrils alone. These co-polymer fibrils have also shown enhanced alpha synuclein aggregation in vitro, and more severe alpha synuclein pathology and Parkinson’s disease-like symptoms in mice.
Human Tau-352 (fetal 0N3R) and Human Alpha Synuclein Co-Polymer Fibrils: Tau 0N3R, the shortest isoform of tau, is expressed in the fetal brain during neurogenesis and has been shown to be more prone to form oligomers in vitro. Tau-352 (fetal 0N3R) and alpha synuclein co-polymer fibrils seed fibril formation of both alpha synuclein monomers and of a mixture of alpha synuclein and fetal tau-352 monomers over 72 hours.
Human Tau-441 (2N4R) and Human Alpha Synuclein Co-Polymer Fibrils: The tau 2N4R isoform is expressed in the adult brain but is absent from the fetal brain. Tau-441 (2N4R) and alpha synuclein co-polymer fibrils seed fibril formation of both alpha synuclein monomers and of a mixture of alpha synuclein and tau-441 (2N4R) monomers over 72 hours.
Rigorous Quality Control
StressMarq’s quality control testing for neuroproteins includes:
- Sedimentation assays to ensure that most of the monomer was converted to fibril
- EM/AFM imaging to verify fibril formation
- Thioflavin T assay to assess seeding capability of the fibrils
- SDS-PAGE to ensure protein purity
- Sterility check
- Endotoxin testing
Product Citations
Many of StressMarq’s monomeric, fibrillar and conjugated tau preparations have been cited in research publications. Certain products have also been validated in both in vitro and in vivo studies by various StressMarq collaborators.

Leave a Reply