Types of Alpha Synuclein Fibrillar Constructs
Please see the updated version of this article for additional information.
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the misfolding and accumulation of alpha-synuclein. Aggregated alpha synuclein is a key protein in PD pathogenesis and different forms of the protein can be used to develop disease models that reproduce the pathological features of this disorder. Alpha synuclein can aggregate generating soluble oligomers and insoluble fibrils. Misfolded α-synuclein aggregates are toxic and lead to neurodegeneration.
StressMarq Biosciences offers a wide variety of monomeric, oligomeric and fibrillar alpha synuclein constructs for PD research. These preparations have different characteristics and properties.
Which alpha synuclein constructs should I use?
Alpha Synuclein Monomers
What is a Monomer?
In chemistry, a monomer refers to a single molecule that can combine to form polymers. In the context of alpha synuclein, a monomer refers to a single alpha synuclein protein (~14 kDa). Studies have shown that alpha synuclein exists predominantly as a disordered monomer in the cytosol. Non-toxic alpha synuclein monomers rapidly aggregate into toxic oligomers, protofibrils, and ultimately large fibrils that can seed further aggregation. During this process, alpha synuclein adopts multiple conformations and there is a dynamic equilibrium between monomeric, oligomeric and fibrillar forms.
- Type 1 human, rat, and mouse: These monomers aggregate to form Type 1 preformed fibrils.
- A53T mutant human monomer
- N-terminal acetylated human monomer
- Type 2 human monomers aggregate to form Type 2 and Type 3 pre-formed fibrils.
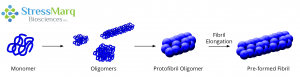
Monomers aggregate to form oligomers, protofibril oligomers, and ultimately lengthen into fibrils.
Alpha Synuclein Oligomers
An oligomer is composed of repeating monomer units and has quaternary structure. When monomers aggregate, they can form a variety of different sizes and types of oligomers. Oligomeric species usually have a roughly spherical structure (~25nm diameter). In Parkinson’s disease, alpha synuclein oligomers seem to induce significantly higher neuronal toxicity compared to fibrils but do not generate pSer129 pathology.

- Dopamine-stabilized alpha synuclein oligomers: The neurotransmitter dopamine can inhibit the aggregation of alpha synuclein into fibrils and stabilize oligomers. Dopamine-stabilized oligomers show toxicity in primary mouse neurons. They may inhibit monomer fibrillization.
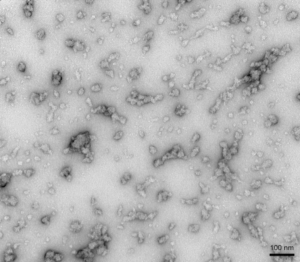
TEM of Human Recombinant Alpha Synuclein Oligomers (Dopamine HCL Stabilized) (catalog# SPR-466)
- EGCG- stabilized alpha synuclein oligomers: The flavonoid epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) has been shown to stabilize alpha synuclein in its oligomeric form. EGCG alpha synuclein oligomers are thought to be non-toxic and do not seed monomer aggregation in Thioflavin T assays.
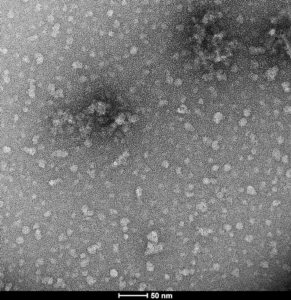
TEM of Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)-stabilized alpha synuclein oligomers (catalog# SPR-469)
Alpha Synuclein Filaments
Oligomers further aggregate into soluble protofibrils or filaments. Filaments can undergo a structural change from an alpha-helix to a beta-sheet and form insoluble fibrils. Under the electron microscope (EM), filaments look similar to mature fibrils but they have different properties.
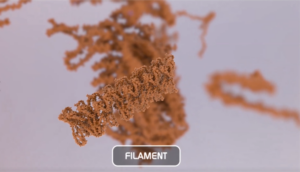
Alpha synuclein filaments do not generate pSer129 pathology or toxicity and do not show seeding capability in SH-SY5Y cells.
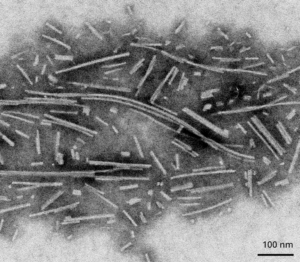
TEM of Active Human Recombinant Alpha Synuclein Protein Filaments (catalog# SPR-450)
Alpha Synuclein Pre-formed Fibrils (PFFs)
Alpha synuclein fibrils are formed through the polymerization of monomeric peptides into long fibers. These fibrils are insoluble aggregates characterized by an extended beta-sheet secondary structure.

Alpha synuclein fibrils can be isolated from PD patient brains and used to seed Lewy body pathology in models. These fibrils can also be manufactured recombinantly. Fibrils can be injected into cell cultures or directly into rodents and are transported within the cells. Active alpha synuclein fibrils are able to seed their monomeric alpha synuclein, which aggregates into more complex structures. Pathology develops much faster than in transgenic models. Certain mutants such as A53T promote aggressive aggregation.
StressMarq offers different types of fibrils that look similar under the electron microscope (EM), but they are different in terms of seeding and toxicity.
- Type 1 Human, Rat, and Mouse: These fibrils are 30-70 nm in length and have shown to induce pSer129 pathology in primary rat neurons within 14 days. Mouse PFFs seem to be more aggressive in producing pSer129 pathology compared to human PFFs. Type 1 fibrils also produce higher ThT values compared to Type 2 which means more effective seeding of alpha synuclein monomers into fibrils.
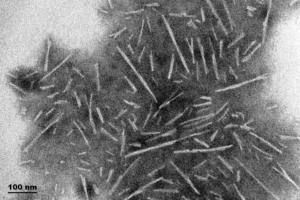
TEM of Type 1 Human Alpha Synuclein PFFs (catalog# SPR-322)
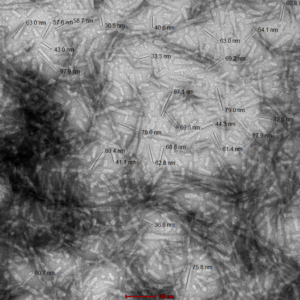
TEM of Type 1 Mouse Alpha Synuclein PFFs (catalog# SPR-324). Image was taken at 100kx magnification.
- ATTO 594-Conjugated Type 1 PFFs: Alpha synuclein PFFs can also be conjugated to fluorescent dyes to allow for tracking in vitro.
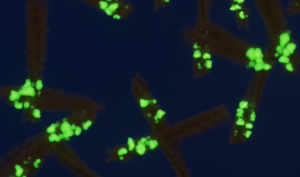
- Type 2: They do not induce Lewy body pathology in primary rat neurons. They appear more toxic than Type 1 fibrils but have lower seeding capability.
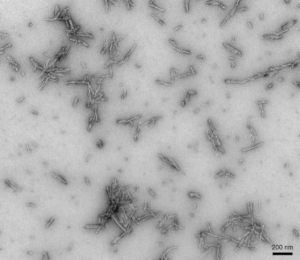
TEM of Type 2 Alpha Synuclein PFFs (catalog# SPR-317)
- A53T mutant: The A53T mutation has been linked to early-onset PD. These fibrils generate rapid aggregation and pSer129 pathology.
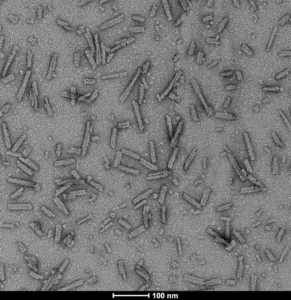
TEM of A53T alpha synuclein PFFs (catalog# SPR-326)
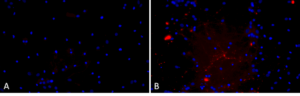
Primary rat hippocampal neurons show Lewy body inclusion formation when treated with A53T alpha synuclein PFFs (catalog# SPR-326) (B) but not when treated with a media control (A).
- N-Terminal Acetylated: These type 1 fibrils are modified by acetylation.
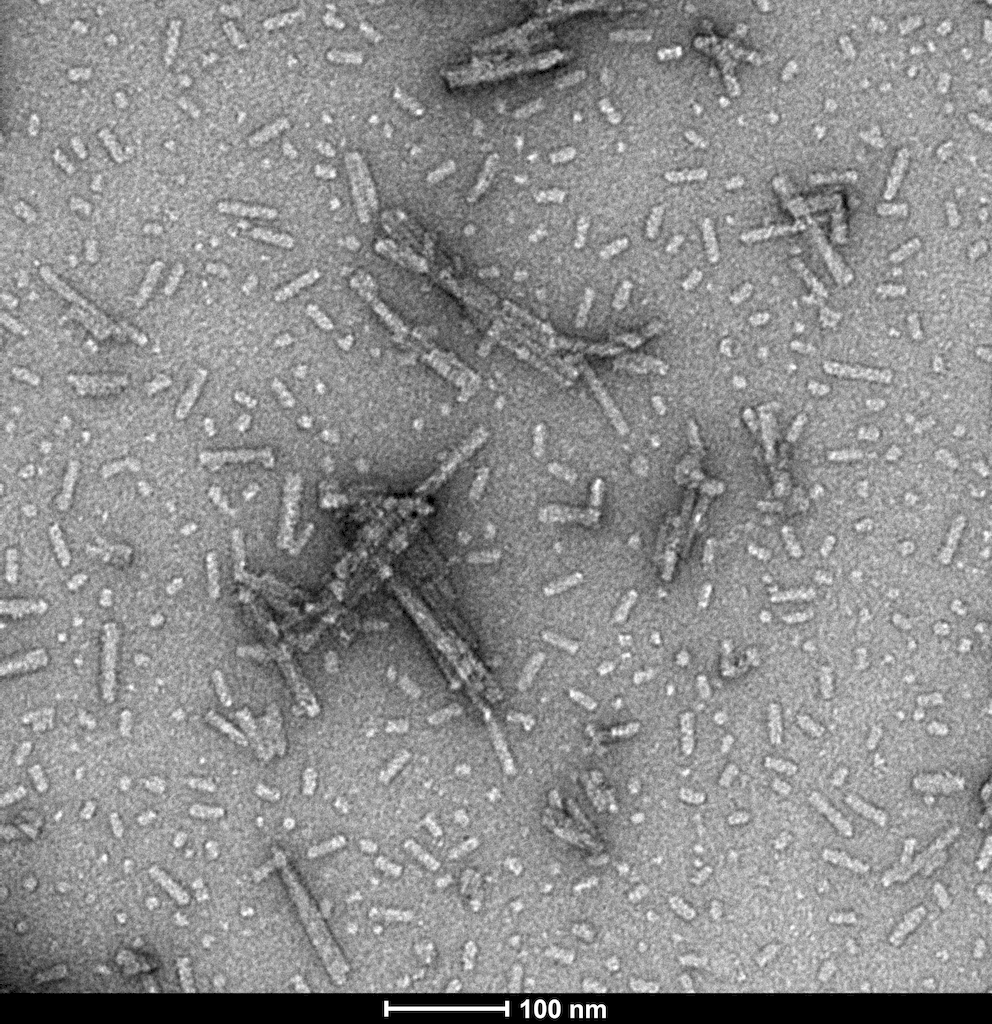
TEM of N-terminal acetylated alpha synuclein PFFs (catalog# SPR-332)

I have the same question as to the differences between type 1 and 2 fibrils
Hello Aditya,
Thank you for your inquiry. A member of our Technical Services team will contact you shortly to answer your questions.
Can you please describe to me the difference between type 1 and 2 fibrils, I see your description above but I was still unsure.
Hi Nicole, thank you for your comment. Someone from our Technical Services will contact you soon to answer your questions.