Types of Tau Fibrillar Constructs
Please see the updated version of this article for additional information.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a complex neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the extracellular deposition of amyloid plaques and the intracellular accumulation of insoluble tau neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in the brain. Tau protein is implicated in AD progress and its hyperphosphorylation and aggregation lead to the formation of NFTs and ultimately to neuronal dysfunction and death. Alzheimer’s currently has no cure and scientists generate new cellular and animal disease models that reproduce tau aggregation in order to develop new therapies.
StressMarq Biosciences is the only bioreagents company worldwide that manufactures tau monomers, oligomers, and pre-formed fibrils. These full-length and truncated fibrillar preparations can be used to induce tau pathology and develop disease models.
Which tau constructs should I use?
Tau Monomers
Tau protein is found in the axons of neurons and stabilizes microtubules. It has a natively unfolded structure and it is highly soluble. Monomeric tau is about 46kD and has a variety of isoforms which are generated by alternative splicing of tau gene. Tau monomers are soluble and can aggregate to form large insoluble fibrils.
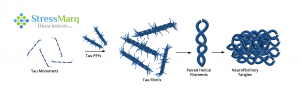
Tau PFFs can act as seeds, recruiting monomers into fibrils.
Types of Tau Monomers
- Tau-441 (2N4R, P301S) (human and mouse versions available): This is the full-length tau isoform (46kD) expressed in human brain. The P301S mutation impairs tau’s ability to assemble microtubules1. Tau-441 human and mouse monomers require heparin, as an induction scaffold, for seeding in Thioflavin T assays. There is also a tau monomer (SPR-473) that is post-translationally modified because it is expressed in a baculovirus expression system instead of E. Coli. Baculovirus-expressed tau monomers do not require a scaffold for fibrillization in Thioflavin T assays.
- Tau-441 (2N4R) Wild-Type: This is a full-length wild-type tau isoform (46kD) expressed in human brain.
- Tau K18 (4R, P301L): K18 is a truncated form of tau (15kD) also expressed in human brain. The P301L mutation, which has been linked to frontotemporal dementia, promotes beta-sheet and PHF formation2. Tau K18 requires heparin in Thioflavin T assays.
- dGAE (AA297-391): This is a truncated 95-amino acid tau fragment consisting of amino acids 297-391. It has been found in the core of PHFs from AD brains. dGAE fragment can assemble into PHF-like fibrils in the absence of additives or templates3.
- dGAE (AA297-391, C322A): This mutant monomer is the truncated 95-amino acid tau fragment of full- length tau which lacks cysteine residues. C322A mutation enhances tau’s ability to form long and ordered PHFs3. It does not require heparin for seeding in Thioflavin T assays.
- Tau K18 (K280 Deletion): This is the K18 truncated form of tau with the K280 deletion mutation, which is associated with frontotemporal dementia. These monomers can generate PHFs in the absence of heparin and other inducers4.
- Tau-352 (fetal 0N3R) Wild-Type: Brain-specific tau isoforms vary in the number of N-terminal inserts and C- terminal repeat domains due to alternative splicing of exons; only the shortest isoform of tau, 0N3R, is expressed in the fetal brain during neurogenesis.
Tau Filaments
Tau Paired Helical Filaments (PHFs) and Neurofibrillary Tangles (NFTs)
In Alzheimer’s disease tau hyperphosphorylation results in the transformation of normal tau into paired helical filaments and neurofibrillary tangles. PHFs are soluble with a twisted double-helical structure. Tau in the PHFs is more negatively charged than monomeric tau which disrupts its binding to microtubules and leads to neurodegeneration5.
NFTs, a major hallmark of AD, are composed of PHFs. These insoluble aggregates of tau have an increased beta sheet structure consisting of aggregated PHFs and may be toxic to cells6.
Tau-441 Filaments (2N4R, P301S): Soluble tau filaments are fibrilized using a natural linear anionic scaffold. This scaffold is then removed, and the filaments have a duplex twisted structure closely resemble brain-derived PHFs.
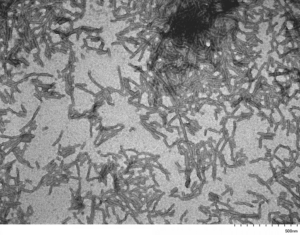
TEM of Human Recombinant Tau Filaments (catalog# SPR-463)
Tau Pre-formed Fibrils (PFFs)
Tau preformed fibrils are formed when soluble tau monomers polymerize into insoluble fibrils. Some tau PFFs induce endogenous tau phosphorylation and aggregation in vivo and can be used as tools to generate disease models that mimic Alzheimer’s pathophysiology. Injecting tau PFFs into animals generates tau pathology in a short period compared to transgenic models.
StressMarq offers several types of tau preformed fibrils that can be used in Alzheimer’s Disease research:
- Tau-441 (2N4R, P301S) (human and mouse versions available): This is a full-length isoform of tau protein with the P301S mutation. Heparin is used as an induction scaffold. Human and mouse PFFs are capable of seeding monomers and can induce tau aggregation. Baculovirus- expressed tau PFFs are post-translationally modified, fibrilize without a scaffold and are endotoxin free (Endotoxin <0.05 EU/mL, below the detectable range of the assay).
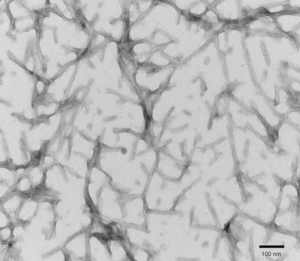
TEM of recombinant Tau441 (2N4R), P301S mutant PFFs at 150kx magnification. HV = 80kV. Fibrils were sonicated and stained with uranyl acetate. (catalog# SPR-329)
- Tau-441 (2N4R) Wild-Type: This full-length wild-type tau protein can seed aggregation of wild-type monomers
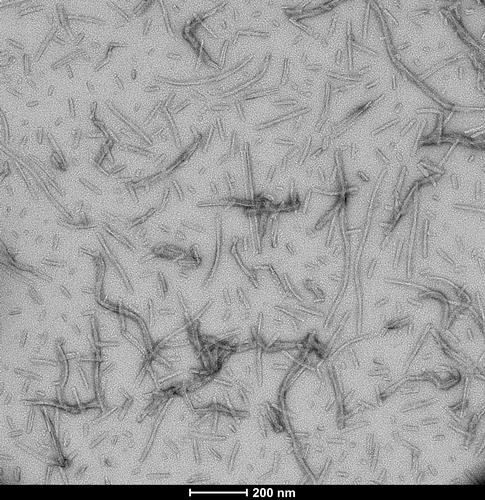

TEM of human recombinant Tau441 (2N4R) Wild-Type PFFs (catalog# SPR-480)
- ATTO 488- conjugated Tau 441 (2N4R, P301S): Tau441 PFFs can be conjugated to fluorescent dyes and tracked in vitro. ATTO-488 conjugated tau PFFs show enhanced seeding compared to unconjugated fibrils.
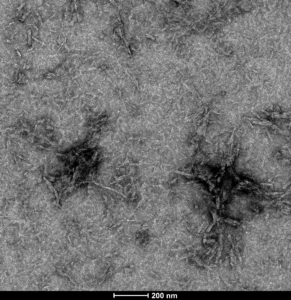
TEM of ATTO 488-conjugated tau PFFs (catalog# SPR-329-A488)
- Tau K18 (P301L): K18 tau PFFs have been injected in the hippocampus of tau transgenic mice (P301L), where they seed aggregation and induce tau pathology after 9 weeks.
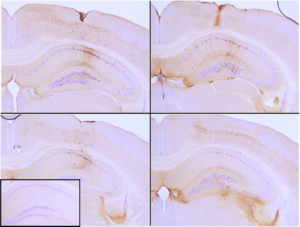
Immunohistochemistry analysis of P301L mouse hippocampus injected with K18 P301L tau PFFs (catalog# SPR-330) shows seeding of tau pathology at injection site nine weeks post-injection. AT8 (pSer202/pThr205) tau antibody shows tangle-like inclusions. Inset: negative control. Experiments performed at reMYND N.V.
- dGAE (AA297-391) : The dGAE wild-type PFFs can seed dGAE monomer aggregation.
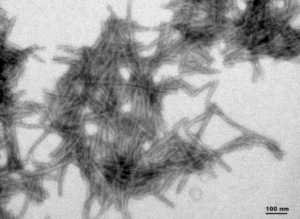
TEM of Active Human Recombinant Truncated Tau Fragment (AA297-391) (dGAE) PFFs (catalog# SPR-461)
- dGAE (AA297-391, C322A):The C322A mutant dGAE fibrils can also seed monomer aggregation.
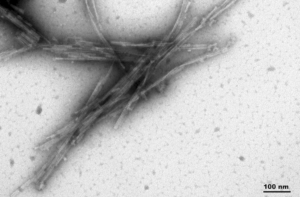
TEM of Human Recombinant Truncated Tau (AA297-391) (dGAE C322A) PFFs (catalog# SPR-462)
- Tau K18 (K280 Deletion): K18 (ΔK280) PFFs are capable of seeding K18 ΔK280 monomers.
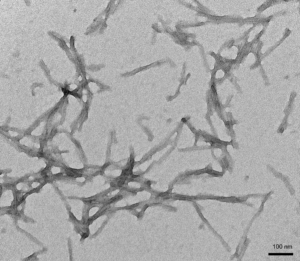
TEM of Human K18 K280 Deletion Tau PFFs (catalog# SPR-477)
- Tau-352 (fetal 0N3R): Brain-specific tau isoforms vary in the number of N-terminal inserts and C- terminal repeat domains due to alternative splicing of exons; only the shortest isoform of tau, 0N3R, is expressed in the fetal brain during neurogenesis
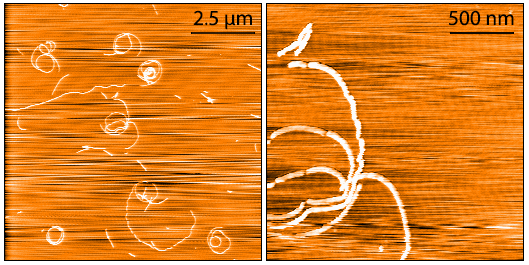
AFM of Fetal Tau 0N3R PFFs (catalog# SPR-491).
Tau pre-formed fibrils seed the formation of new tau fibrils when combined with tau monomers. Some of our tau proteins (catalog#’s SPR-327, SPR-328, SPR-329, SPR-329-A488, SPR-330, SPR-474, and SPR-475) require heparin for seeding in Thioflavin T assays (protocol available).
REFERENCES
- Bugiani, O. et al. (1999). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 58(6):667-77.
- Alberici, A. et al. (2004). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 75:1607-1610.
- Al-Hilaly, Y.K. et al. (2017) Alzheimer’s Disease-like Paired Helical Filament Assembly from Truncated Tau Protein Is Independent of Disulfide Crosslinking. J. Mol. Biol. 429(23):3650-3665.
- Von Bergen, M. et al. (2001). J Biol Chem. 276(51):48165-48174.
- Ksiezak-Reding, H., & Yen, S. (1991). Neuron, 6(5), 717-728.
- Barghorn, S. et al. (2004). Biochem, 43(6), 1694-1703.

The pdf Which-Tau-Construct-Should-I-Use-1.pdf is not accessible. Can you please update the link or send the pdf to us? It is very useful.
Dear Aditya,
Thank you for your comment. The link has been amended. For your convenient reference, a copy of the document has been emailed to you.
An updated version of this blog post is available here.
Have a wonderful day!
Best regards,
StressMarq Team